NEET Exam > NEET Questions > what is Lambert's cosine law
Start Learning for Free
what is Lambert's cosine law
Verified Answer
what is Lambert's cosine law
It states that the intensity of illumination or illuminance E at a point on a surface is proportional to the cosine of the angle of incidence of the light at that point. It is used to find the illumination of a surface, when it falls on the surface along any slanting direction.
Let us consider S is a point source of light falling on a surface area A as shown in figure. The normal to the surface makes an angle θ with the direction. Then, component of A normal to the direction of light ray is A cos θ.
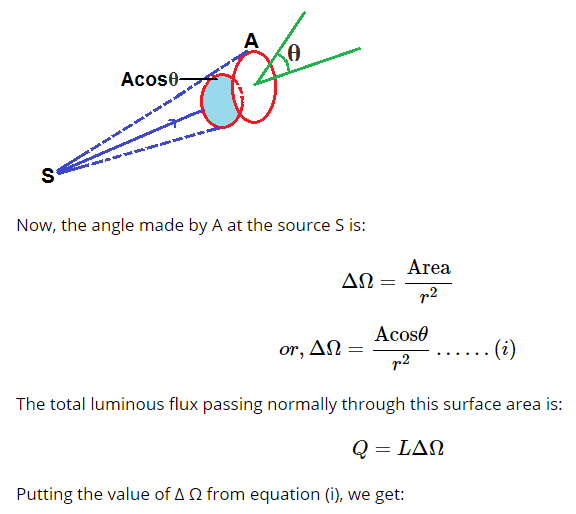
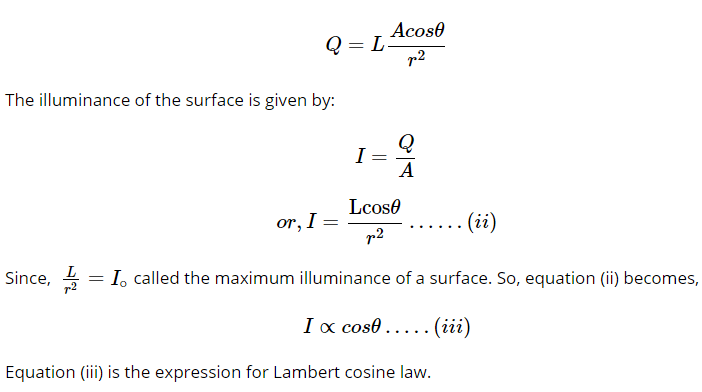
Equation (iii) is the expression for Lambert cosine law.
From Lambert cosine law, we concluded that the illumination at a point due to source is:
Directly proportional to the luminous intensity of the source.
Inversely proportional to the square of distance of the point from the source.
Directly proportional to the cosine of angle of incidence of luminous flux.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
Most Upvoted Answer
what is Lambert's cosine law
Lambert's Cosine Law
Lambert's cosine law, also known as the Lambertian reflectance, is a fundamental concept in physics and optics that describes how light is reflected off a surface. It states that the intensity of light reflected from a surface is directly proportional to the cosine of the angle between the incident light and the normal to the surface. Lambert's cosine law is applicable to ideal diffuse or matte surfaces that scatter light uniformly in all directions.
Explanation:
Lambert's cosine law can be understood by breaking down the concept into the following key points:
1. Incident Light:
When light falls on a surface, it is referred to as incident light. Incident light can be thought of as a ray of light coming from a source and striking the surface.
2. Surface Normal:
The surface normal is a line perpendicular to the surface at a given point. It represents the direction in which the surface is facing. The angle between the incident light and the surface normal is denoted as θ (theta).
3. Reflected Light:
When light strikes a surface, it can be either absorbed, transmitted, or reflected. Lambert's cosine law specifically focuses on the reflected light. The reflected light is the light that bounces off the surface and travels in a different direction.
4. Intensity of Reflected Light:
According to Lambert's cosine law, the intensity of the reflected light is directly proportional to the cosine of the angle between the incident light and the surface normal. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
Intensity of Reflected Light ∝ cos(θ)
5. Diffuse or Matte Surfaces:
Lambert's cosine law applies to surfaces that are diffuse or matte. These surfaces scatter light uniformly in all directions, resulting in a consistent reflection.
6. Application:
Lambert's cosine law has numerous applications in various fields. It is commonly used in computer graphics to model the behavior of light on different surfaces. It helps create realistic lighting effects and shading in 3D computer-generated images. Lambert's cosine law is also employed in remote sensing, photography, and radiometry to analyze and interpret the behavior of light.
In conclusion, Lambert's cosine law provides a fundamental understanding of how light behaves when it interacts with a surface. It states that the intensity of reflected light is directly proportional to the cosine of the angle between the incident light and the surface normal. This concept is widely used in various scientific and technological applications to study and manipulate light.
Lambert's cosine law, also known as the Lambertian reflectance, is a fundamental concept in physics and optics that describes how light is reflected off a surface. It states that the intensity of light reflected from a surface is directly proportional to the cosine of the angle between the incident light and the normal to the surface. Lambert's cosine law is applicable to ideal diffuse or matte surfaces that scatter light uniformly in all directions.
Explanation:
Lambert's cosine law can be understood by breaking down the concept into the following key points:
1. Incident Light:
When light falls on a surface, it is referred to as incident light. Incident light can be thought of as a ray of light coming from a source and striking the surface.
2. Surface Normal:
The surface normal is a line perpendicular to the surface at a given point. It represents the direction in which the surface is facing. The angle between the incident light and the surface normal is denoted as θ (theta).
3. Reflected Light:
When light strikes a surface, it can be either absorbed, transmitted, or reflected. Lambert's cosine law specifically focuses on the reflected light. The reflected light is the light that bounces off the surface and travels in a different direction.
4. Intensity of Reflected Light:
According to Lambert's cosine law, the intensity of the reflected light is directly proportional to the cosine of the angle between the incident light and the surface normal. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
Intensity of Reflected Light ∝ cos(θ)
5. Diffuse or Matte Surfaces:
Lambert's cosine law applies to surfaces that are diffuse or matte. These surfaces scatter light uniformly in all directions, resulting in a consistent reflection.
6. Application:
Lambert's cosine law has numerous applications in various fields. It is commonly used in computer graphics to model the behavior of light on different surfaces. It helps create realistic lighting effects and shading in 3D computer-generated images. Lambert's cosine law is also employed in remote sensing, photography, and radiometry to analyze and interpret the behavior of light.
In conclusion, Lambert's cosine law provides a fundamental understanding of how light behaves when it interacts with a surface. It states that the intensity of reflected light is directly proportional to the cosine of the angle between the incident light and the surface normal. This concept is widely used in various scientific and technological applications to study and manipulate light.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
what is Lambert's cosine law
Question Description
what is Lambert's cosine law for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about what is Lambert's cosine law covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is Lambert's cosine law.
what is Lambert's cosine law for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about what is Lambert's cosine law covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is Lambert's cosine law.
Solutions for what is Lambert's cosine law in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of what is Lambert's cosine law defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
what is Lambert's cosine law, a detailed solution for what is Lambert's cosine law has been provided alongside types of what is Lambert's cosine law theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice what is Lambert's cosine law tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























