NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ?
Start Learning for Free
Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ?
Most Upvoted Answer
Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ?
The Etard Reaction and its Catalyst
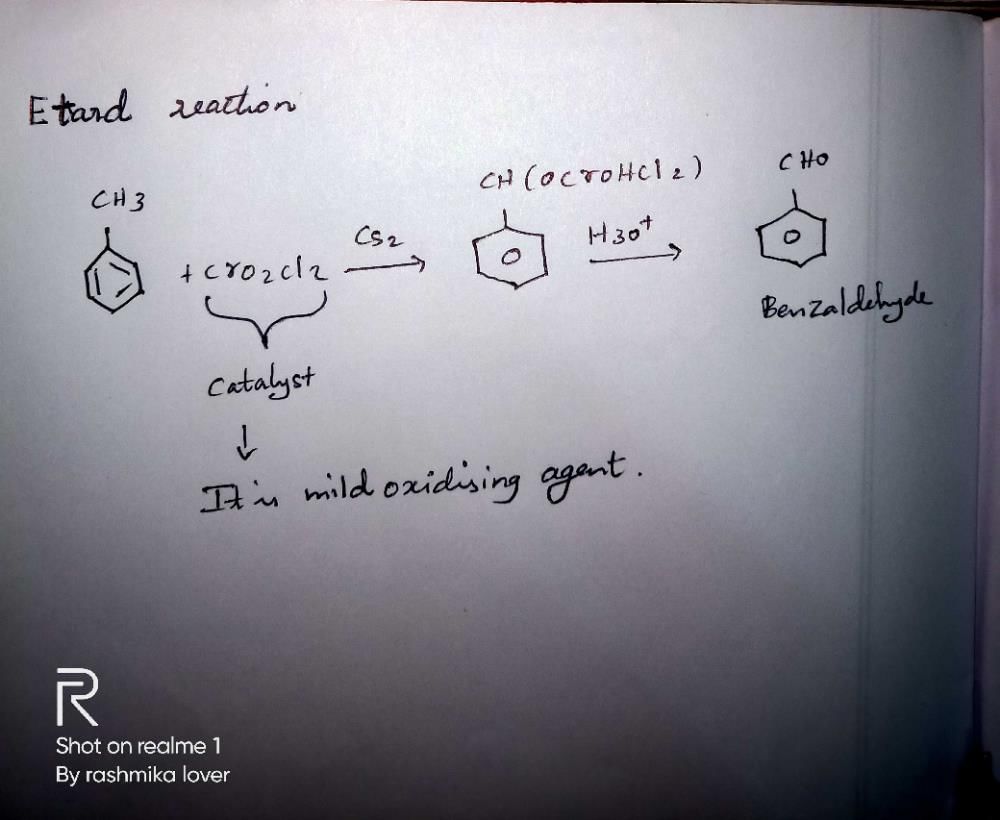
The Etard reaction is a type of oxidation reaction that is commonly used in organic chemistry to convert aromatic compounds into their corresponding ketones. This reaction is named after its discoverer, Francois Stanislas Etard. The reaction involves the use of a catalyst, which plays a crucial role in facilitating the oxidation process.
The Purpose of a Catalyst
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any permanent change itself. It works by providing an alternative pathway for the reaction with a lower activation energy, making it easier for the reaction to occur. In the case of the Etard reaction, the catalyst is responsible for the oxidation of the aromatic compound.
The Role of Chromium Trioxide (CrO₃) as a Catalyst in the Etard Reaction
The most commonly used catalyst in the Etard reaction is chromium trioxide (CrO₃). CrO₃ is a dark red solid that is highly soluble in water. It is a powerful oxidizing agent, meaning it has the ability to remove electrons from other substances and thereby facilitate oxidation reactions.
Mechanism of the Etard Reaction
The Etard reaction involves the oxidation of an aromatic compound, typically a substituted benzene ring, to form a ketone. The reaction proceeds through a series of steps, which can be summarized as follows:
1. Formation of the active catalyst: Chromium trioxide is dissolved in a suitable solvent, such as acetic acid, to form a solution of chromic acid (H₂CrO₄). This chromic acid acts as the active catalyst in the reaction.
2. Activation of the aromatic compound: The aromatic compound is added to the chromic acid solution, where it undergoes activation. The mechanism of this activation step is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve the formation of a complex between the aromatic compound and the chromic acid.
3. Oxidation of the aromatic compound: The activated aromatic compound reacts with the chromic acid, resulting in the transfer of oxygen atoms from the chromic acid to the aromatic compound. This oxidation process converts the aromatic compound into its corresponding ketone.
4. Regeneration of the catalyst: After the oxidation step, the chromic acid is reduced to chromium(III) species. These species can be reoxidized back to the active catalyst using an oxidizing agent, such as hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂).
Advantages of Chromium Trioxide as a Catalyst
- High selectivity: Chromium trioxide is a highly selective catalyst, meaning it primarily oxidizes the aromatic ring without affecting other functional groups present in the molecule.
- Easy availability: Chromium trioxide is commercially available and relatively inexpensive, making it a practical choice for large-scale reactions.
- Mild reaction conditions: The Etard reaction can be performed under mild reaction conditions, typically at room temperature or slightly elevated temperatures.
- Wide substrate scope: Chromium trioxide can be used to oxidize a wide range of aromatic compounds, including aromatic hydrocarbons, phenols, and anilines.
In conclusion, the Etard reaction is a useful oxidation reaction in organic chemistry, and chromium trioxide serves as an effective catalyst in facilitating the oxidation of aromatic compounds. Its high selectivity, easy availability, mild reaction conditions, and wide substrate scope make it a popular choice in this type of reaction.
The Etard reaction is a type of oxidation reaction that is commonly used in organic chemistry to convert aromatic compounds into their corresponding ketones. This reaction is named after its discoverer, Francois Stanislas Etard. The reaction involves the use of a catalyst, which plays a crucial role in facilitating the oxidation process.
The Purpose of a Catalyst
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction without undergoing any permanent change itself. It works by providing an alternative pathway for the reaction with a lower activation energy, making it easier for the reaction to occur. In the case of the Etard reaction, the catalyst is responsible for the oxidation of the aromatic compound.
The Role of Chromium Trioxide (CrO₃) as a Catalyst in the Etard Reaction
The most commonly used catalyst in the Etard reaction is chromium trioxide (CrO₃). CrO₃ is a dark red solid that is highly soluble in water. It is a powerful oxidizing agent, meaning it has the ability to remove electrons from other substances and thereby facilitate oxidation reactions.
Mechanism of the Etard Reaction
The Etard reaction involves the oxidation of an aromatic compound, typically a substituted benzene ring, to form a ketone. The reaction proceeds through a series of steps, which can be summarized as follows:
1. Formation of the active catalyst: Chromium trioxide is dissolved in a suitable solvent, such as acetic acid, to form a solution of chromic acid (H₂CrO₄). This chromic acid acts as the active catalyst in the reaction.
2. Activation of the aromatic compound: The aromatic compound is added to the chromic acid solution, where it undergoes activation. The mechanism of this activation step is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve the formation of a complex between the aromatic compound and the chromic acid.
3. Oxidation of the aromatic compound: The activated aromatic compound reacts with the chromic acid, resulting in the transfer of oxygen atoms from the chromic acid to the aromatic compound. This oxidation process converts the aromatic compound into its corresponding ketone.
4. Regeneration of the catalyst: After the oxidation step, the chromic acid is reduced to chromium(III) species. These species can be reoxidized back to the active catalyst using an oxidizing agent, such as hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂).
Advantages of Chromium Trioxide as a Catalyst
- High selectivity: Chromium trioxide is a highly selective catalyst, meaning it primarily oxidizes the aromatic ring without affecting other functional groups present in the molecule.
- Easy availability: Chromium trioxide is commercially available and relatively inexpensive, making it a practical choice for large-scale reactions.
- Mild reaction conditions: The Etard reaction can be performed under mild reaction conditions, typically at room temperature or slightly elevated temperatures.
- Wide substrate scope: Chromium trioxide can be used to oxidize a wide range of aromatic compounds, including aromatic hydrocarbons, phenols, and anilines.
In conclusion, the Etard reaction is a useful oxidation reaction in organic chemistry, and chromium trioxide serves as an effective catalyst in facilitating the oxidation of aromatic compounds. Its high selectivity, easy availability, mild reaction conditions, and wide substrate scope make it a popular choice in this type of reaction.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ?
Question Description
Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ?.
Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ?.
Solutions for Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ?, a detailed solution for Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ? has been provided alongside types of Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which catalyst is used in Etard reaction ? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.