NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Which of the following monomers can undergo c...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene?
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerizatio...
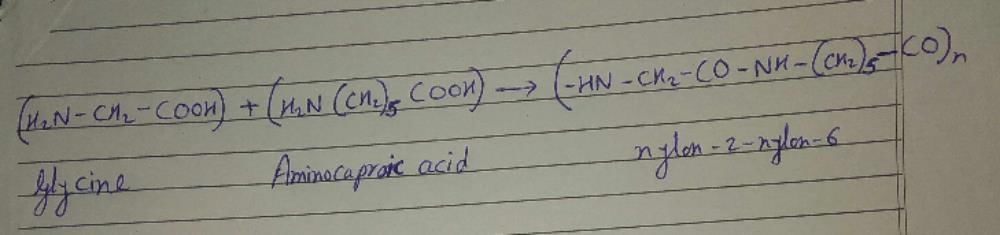
Community Answer
Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerizatio...
Monomers that can undergo condensation polymerization:
Condensation polymerization is a process in which monomers react together to form a polymer by the elimination of a small molecule, such as water or alcohol. This process involves the combination of two monomers, each with a reactive functional group, which leads to the formation of a covalent bond between the monomers and the release of a small molecule as a byproduct.
Out of the given options, the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization:
a) Styrene:
Styrene is a monomer commonly used in the production of polystyrene. It contains a vinyl group (C=C) that can react with another styrene monomer by the elimination of a hydrogen atom, resulting in the formation of a covalent bond and the release of a small molecule. This process repeats to form a long chain polymer.
b) Glycine:
Glycine is an amino acid that can undergo condensation polymerization to form polypeptides. It contains both an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) that can react with each other. The amino group of one glycine molecule can react with the carboxyl group of another glycine molecule, leading to the formation of a peptide bond and the release of a water molecule. This process repeats to form a chain of amino acids, which constitutes a polypeptide.
c) Isoprene:
Isoprene is a monomer that can undergo condensation polymerization to form natural rubber. It contains a double bond (C=C) that can react with another isoprene monomer by the elimination of a hydrogen atom. This reaction forms a covalent bond and releases a small molecule. The process continues, resulting in the formation of a long chain polymer of isoprene units.
d) Propene:
Propene, also known as propylene, is a monomer that undergoes addition polymerization rather than condensation polymerization. Addition polymerization occurs when monomers combine without the elimination of any small molecules. Propene has a double bond (C=C) that opens up and reacts with another propene monomer to form a covalent bond, resulting in the formation of a long chain polymer.
In summary, out of the given options, styrene, glycine, and isoprene can undergo condensation polymerization, while propene undergoes addition polymerization.
Condensation polymerization is a process in which monomers react together to form a polymer by the elimination of a small molecule, such as water or alcohol. This process involves the combination of two monomers, each with a reactive functional group, which leads to the formation of a covalent bond between the monomers and the release of a small molecule as a byproduct.
Out of the given options, the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization:
a) Styrene:
Styrene is a monomer commonly used in the production of polystyrene. It contains a vinyl group (C=C) that can react with another styrene monomer by the elimination of a hydrogen atom, resulting in the formation of a covalent bond and the release of a small molecule. This process repeats to form a long chain polymer.
b) Glycine:
Glycine is an amino acid that can undergo condensation polymerization to form polypeptides. It contains both an amino group (-NH2) and a carboxyl group (-COOH) that can react with each other. The amino group of one glycine molecule can react with the carboxyl group of another glycine molecule, leading to the formation of a peptide bond and the release of a water molecule. This process repeats to form a chain of amino acids, which constitutes a polypeptide.
c) Isoprene:
Isoprene is a monomer that can undergo condensation polymerization to form natural rubber. It contains a double bond (C=C) that can react with another isoprene monomer by the elimination of a hydrogen atom. This reaction forms a covalent bond and releases a small molecule. The process continues, resulting in the formation of a long chain polymer of isoprene units.
d) Propene:
Propene, also known as propylene, is a monomer that undergoes addition polymerization rather than condensation polymerization. Addition polymerization occurs when monomers combine without the elimination of any small molecules. Propene has a double bond (C=C) that opens up and reacts with another propene monomer to form a covalent bond, resulting in the formation of a long chain polymer.
In summary, out of the given options, styrene, glycine, and isoprene can undergo condensation polymerization, while propene undergoes addition polymerization.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene?
Question Description
Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene?.
Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene?.
Solutions for Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene?, a detailed solution for Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following monomers can undergo condensation polymerization ? a) styrene. b) Glycine. c) Isoprene. d) propene? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























