NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Human respiratory system structure.?
Start Learning for Free
Human respiratory system structure.?
Community Answer
Human respiratory system structure.?
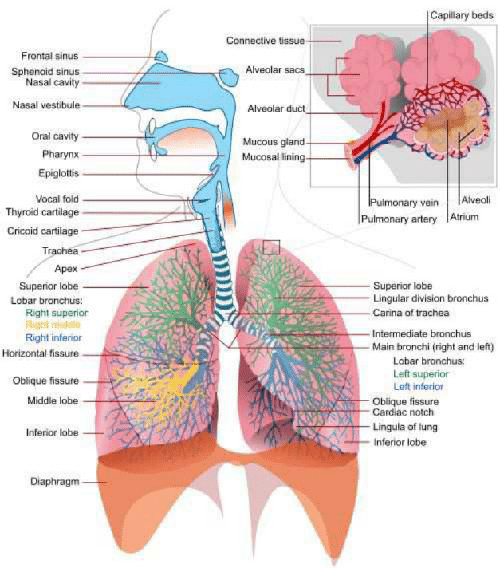
The human respiratory system is a complex network of organs and tissues that work together to take in oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. This system is essential for life and is responsible for the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. The respiratory system is composed of several structures that work together to facilitate respiration.
Structure of the human respiratory system:
Nasal Cavity:
The nasal cavity is the first structure of the respiratory system. It is a large, hollow space located behind the nose and is lined with mucous membranes. The nasal cavity has tiny hairs called cilia that filter out dust and other particles. It also has blood vessels that help to warm and moisten the air as it enters the body.
Pharynx:
The pharynx, or throat, is a muscular tube that connects the nasal cavity to the larynx. It has three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. The pharynx is responsible for allowing air to pass from the nasal cavity to the larynx and also plays a role in swallowing.
Larynx:
The larynx, or voice box, is located at the top of the trachea. It contains the vocal cords, which vibrate to produce sound when air passes over them. The larynx also prevents food and liquid from entering the trachea during swallowing.
Trachea:
The trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi. It is made up of cartilage rings that prevent it from collapsing and blocking the airway. The trachea also has cilia that help to remove mucus and other particles from the air.
Bronchi:
The bronchi are two tubes that branch off from the trachea and lead to the lungs. They are lined with smooth muscle and have cartilage rings that help to keep them open. The bronchi further divide into smaller tubes called bronchioles.
Lungs:
The lungs are the largest organs in the respiratory system. They are located in the chest and are surrounded by a thin layer of tissue called the pleura. The lungs are composed of small air sacs called alveoli, which are responsible for the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. The lungs also have blood vessels that help to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body.
In conclusion, the human respiratory system is a complex network of structures that work together to facilitate respiration. Each structure plays an important role in ensuring that the body receives the oxygen it needs to function properly.
Structure of the human respiratory system:
- Nasal Cavity
- Pharynx
- Larynx
- Trachea
- Bronchi
- Lungs
Nasal Cavity:
The nasal cavity is the first structure of the respiratory system. It is a large, hollow space located behind the nose and is lined with mucous membranes. The nasal cavity has tiny hairs called cilia that filter out dust and other particles. It also has blood vessels that help to warm and moisten the air as it enters the body.
Pharynx:
The pharynx, or throat, is a muscular tube that connects the nasal cavity to the larynx. It has three sections: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. The pharynx is responsible for allowing air to pass from the nasal cavity to the larynx and also plays a role in swallowing.
Larynx:
The larynx, or voice box, is located at the top of the trachea. It contains the vocal cords, which vibrate to produce sound when air passes over them. The larynx also prevents food and liquid from entering the trachea during swallowing.
Trachea:
The trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi. It is made up of cartilage rings that prevent it from collapsing and blocking the airway. The trachea also has cilia that help to remove mucus and other particles from the air.
Bronchi:
The bronchi are two tubes that branch off from the trachea and lead to the lungs. They are lined with smooth muscle and have cartilage rings that help to keep them open. The bronchi further divide into smaller tubes called bronchioles.
Lungs:
The lungs are the largest organs in the respiratory system. They are located in the chest and are surrounded by a thin layer of tissue called the pleura. The lungs are composed of small air sacs called alveoli, which are responsible for the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. The lungs also have blood vessels that help to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body.
In conclusion, the human respiratory system is a complex network of structures that work together to facilitate respiration. Each structure plays an important role in ensuring that the body receives the oxygen it needs to function properly.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Human respiratory system structure.?
Question Description
Human respiratory system structure.? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Human respiratory system structure.? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Human respiratory system structure.?.
Human respiratory system structure.? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Human respiratory system structure.? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Human respiratory system structure.?.
Solutions for Human respiratory system structure.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Human respiratory system structure.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Human respiratory system structure.?, a detailed solution for Human respiratory system structure.? has been provided alongside types of Human respiratory system structure.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Human respiratory system structure.? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.