NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Hey.here is all main examples of morphology i...
Start Learning for Free
Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it h...
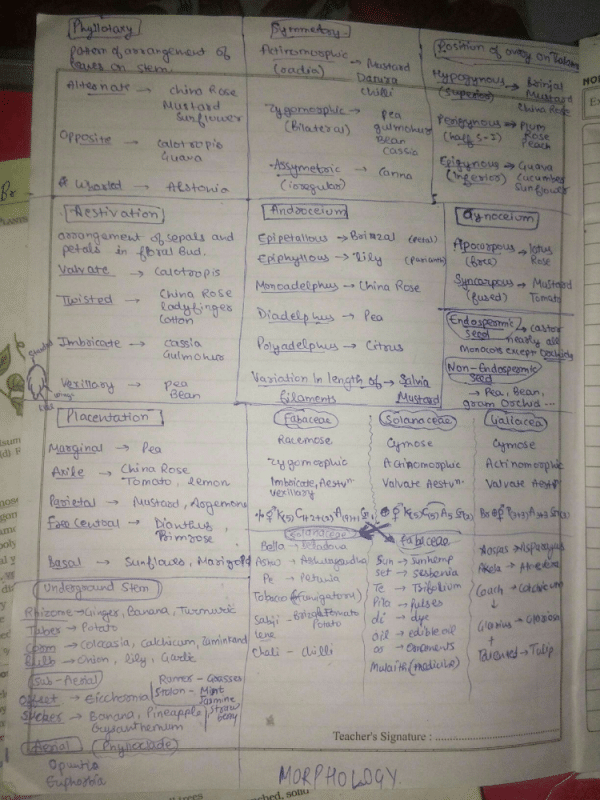
Community Answer
Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it h...
Morphology
Morphology is a branch of linguistics that focuses on the study of the internal structure and formation of words. It examines how words are formed and how they are related to other words in a language. Morphology is concerned with the rules and patterns that govern word formation, including the addition of prefixes and suffixes, the alteration of word stems, and the creation of new words.
Types of Morphemes
Morphemes are the smallest meaningful units in a language. They can be classified into two main types:
1. Free Morphemes: These are morphemes that can stand alone as separate words and have meaning by themselves. For example:
- Dog
- Book
- Run
2. Bound Morphemes: These are morphemes that cannot stand alone and must be attached to other morphemes to convey meaning. They include prefixes, suffixes, and infixes. For example:
- Un- (prefix meaning "not")
- -ed (suffix indicating past tense)
- -s (suffix indicating plural)
Word Formation Processes
There are several processes by which new words can be formed in a language. These processes include:
1. Affixation: This involves the addition of prefixes, suffixes, or infixes to a root or base word. For example:
- Unhappiness (un- + happy + -ness)
- Beautifully (beauty + -ful + -ly)
2. Compounding: This involves combining two or more words to create a new word. For example:
- Blackboard (black + board)
- Firefly (fire + fly)
3. Conversion: This involves changing the grammatical category of a word without changing its form. For example:
- Verb to noun: The swim (swim as a noun)
- Noun to verb: He will table the motion (table as a verb)
4. Reduplication: This involves repeating part or all of a word to create a new word. For example:
- Bye-bye
- Tick-tock
Inflection vs. Derivation
Morphological processes can be further divided into inflection and derivation:
1. Inflection: This involves adding affixes to a word to indicate grammatical relationships and features such as tense, number, and case. Inflection does not change the word's basic meaning or category. For example:
- Walks (walk + -s indicating third person singular)
2. Derivation: This involves adding affixes to a word to create a new word with a different meaning or category. Derivation can change the word's basic meaning and category. For example:
- Happiness (happy + -ness)
- Beautiful (beauty + -ful)
Conclusion
Morphology plays a crucial role in understanding how words are formed and structured in a language. By studying the rules and patterns of word formation, linguists can gain insights into the underlying principles of a language and how it functions. Understanding morphology is essential for language learners and researchers alike, as it provides a foundation for studying and analyzing the structure of words.
Morphology is a branch of linguistics that focuses on the study of the internal structure and formation of words. It examines how words are formed and how they are related to other words in a language. Morphology is concerned with the rules and patterns that govern word formation, including the addition of prefixes and suffixes, the alteration of word stems, and the creation of new words.
Types of Morphemes
Morphemes are the smallest meaningful units in a language. They can be classified into two main types:
1. Free Morphemes: These are morphemes that can stand alone as separate words and have meaning by themselves. For example:
- Dog
- Book
- Run
2. Bound Morphemes: These are morphemes that cannot stand alone and must be attached to other morphemes to convey meaning. They include prefixes, suffixes, and infixes. For example:
- Un- (prefix meaning "not")
- -ed (suffix indicating past tense)
- -s (suffix indicating plural)
Word Formation Processes
There are several processes by which new words can be formed in a language. These processes include:
1. Affixation: This involves the addition of prefixes, suffixes, or infixes to a root or base word. For example:
- Unhappiness (un- + happy + -ness)
- Beautifully (beauty + -ful + -ly)
2. Compounding: This involves combining two or more words to create a new word. For example:
- Blackboard (black + board)
- Firefly (fire + fly)
3. Conversion: This involves changing the grammatical category of a word without changing its form. For example:
- Verb to noun: The swim (swim as a noun)
- Noun to verb: He will table the motion (table as a verb)
4. Reduplication: This involves repeating part or all of a word to create a new word. For example:
- Bye-bye
- Tick-tock
Inflection vs. Derivation
Morphological processes can be further divided into inflection and derivation:
1. Inflection: This involves adding affixes to a word to indicate grammatical relationships and features such as tense, number, and case. Inflection does not change the word's basic meaning or category. For example:
- Walks (walk + -s indicating third person singular)
2. Derivation: This involves adding affixes to a word to create a new word with a different meaning or category. Derivation can change the word's basic meaning and category. For example:
- Happiness (happy + -ness)
- Beautiful (beauty + -ful)
Conclusion
Morphology plays a crucial role in understanding how words are formed and structured in a language. By studying the rules and patterns of word formation, linguists can gain insights into the underlying principles of a language and how it functions. Understanding morphology is essential for language learners and researchers alike, as it provides a foundation for studying and analyzing the structure of words.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer?
Question Description
Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer?.
Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer?.
Solutions for Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer?, a detailed solution for Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer? has been provided alongside types of Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Hey.here is all main examples of morphology in a short note .hope it help. notes is given in answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























