Chemical Engineering Exam > Chemical Engineering Questions > A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick la...
Start Learning for Free
A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.
- a)364.19 & 73.76
- b)364.19 & 364.19
- c)73.76 & 364.19
- d)73.76 & 73.76
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/...
Let ti be the temperature at the interface.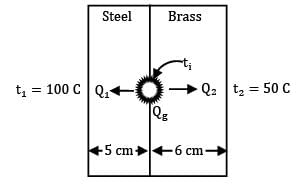
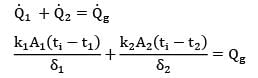
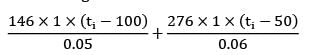
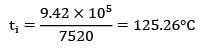
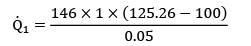

View all questions of this test
Under stipulation for heat dissipation from
both sides,

ti >t1>t2
Accordingly we may write
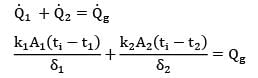
Considering unit surface area
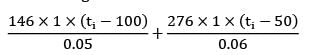
= 4.2 X 105
Or 2920 (ti - 100) + 4600 (ti - 50)
= 4.2 X 105
or 7520 ti = 4.2 X 105+ 2.92 X 105 + 2.3 X 105
= 9.42 X 105
∴ Temperature at the interface,
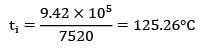
Heat transfer through the steel layer,
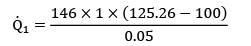
= 73759 kJ/m2-hr
Heat transfer through the brass layer,

Most Upvoted Answer
A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/...
To calculate the heat flow rate through the steel slab, we can use Fourier's law of heat conduction:
q = (k * A * (T2 - T1)) / d
Where:
q = heat flow rate (in kJ/m2-hr)
k = thermal conductivity (in kJ/m-hr-°C)
A = surface area (in m2)
T2 = temperature on the right side (in °C)
T1 = temperature on the left side (in °C)
d = thickness of the slab (in m)
For the steel slab:
k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C
A = 1 m2 (assuming a unit area)
T2 = 50°C
T1 = 100°C
d = 5 cm = 0.05 m
Plugging in these values, we have:
q_steel = (146 * 1 * (50 - 100)) / 0.05 = -146000 kJ/m2-hr
Since heat always flows from higher temperature to lower temperature, the negative sign indicates that heat is flowing in the opposite direction (from brass to steel). Therefore, the heat flow rate through the steel slab is 146000 kJ/m2-hr.
For the brass slab:
k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C
A = 1 m2 (assuming a unit area)
T2 = 50°C
T1 = 100°C
d = 6 cm = 0.06 m
Plugging in these values, we have:
q_brass = (276 * 1 * (100 - 50)) / 0.06 = 460000 kJ/m2-hr
Therefore, the heat flow rate through the brass slab is 460000 kJ/m2-hr.
In MJ/m2-hr, the heat flow rates through the steel and brass slabs are:
q_steel = 146000 / 1000 = 146 MJ/m2-hr
q_brass = 460000 / 1000 = 460 MJ/m2-hr
So, the heat flow rate through the steel slab is 146 MJ/m2-hr and the heat flow rate through the brass slab is 460 MJ/m2-hr.
q = (k * A * (T2 - T1)) / d
Where:
q = heat flow rate (in kJ/m2-hr)
k = thermal conductivity (in kJ/m-hr-°C)
A = surface area (in m2)
T2 = temperature on the right side (in °C)
T1 = temperature on the left side (in °C)
d = thickness of the slab (in m)
For the steel slab:
k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C
A = 1 m2 (assuming a unit area)
T2 = 50°C
T1 = 100°C
d = 5 cm = 0.05 m
Plugging in these values, we have:
q_steel = (146 * 1 * (50 - 100)) / 0.05 = -146000 kJ/m2-hr
Since heat always flows from higher temperature to lower temperature, the negative sign indicates that heat is flowing in the opposite direction (from brass to steel). Therefore, the heat flow rate through the steel slab is 146000 kJ/m2-hr.
For the brass slab:
k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C
A = 1 m2 (assuming a unit area)
T2 = 50°C
T1 = 100°C
d = 6 cm = 0.06 m
Plugging in these values, we have:
q_brass = (276 * 1 * (100 - 50)) / 0.06 = 460000 kJ/m2-hr
Therefore, the heat flow rate through the brass slab is 460000 kJ/m2-hr.
In MJ/m2-hr, the heat flow rates through the steel and brass slabs are:
q_steel = 146000 / 1000 = 146 MJ/m2-hr
q_brass = 460000 / 1000 = 460 MJ/m2-hr
So, the heat flow rate through the steel slab is 146 MJ/m2-hr and the heat flow rate through the brass slab is 460 MJ/m2-hr.

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Chemical Engineering Doubts
A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.a) 364.19 & 73.76b) 364.19 & 364.19c) 73.76 & 364.19d) 73.76 & 73.76Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.a) 364.19 & 73.76b) 364.19 & 364.19c) 73.76 & 364.19d) 73.76 & 73.76Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2024 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.a) 364.19 & 73.76b) 364.19 & 364.19c) 73.76 & 364.19d) 73.76 & 73.76Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.a) 364.19 & 73.76b) 364.19 & 364.19c) 73.76 & 364.19d) 73.76 & 73.76Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.a) 364.19 & 73.76b) 364.19 & 364.19c) 73.76 & 364.19d) 73.76 & 73.76Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2024 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.a) 364.19 & 73.76b) 364.19 & 364.19c) 73.76 & 364.19d) 73.76 & 73.76Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.a) 364.19 & 73.76b) 364.19 & 364.19c) 73.76 & 364.19d) 73.76 & 73.76Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.a) 364.19 & 73.76b) 364.19 & 364.19c) 73.76 & 364.19d) 73.76 & 73.76Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.a) 364.19 & 73.76b) 364.19 & 364.19c) 73.76 & 364.19d) 73.76 & 73.76Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.a) 364.19 & 73.76b) 364.19 & 364.19c) 73.76 & 364.19d) 73.76 & 73.76Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.a) 364.19 & 73.76b) 364.19 & 364.19c) 73.76 & 364.19d) 73.76 & 73.76Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.a) 364.19 & 73.76b) 364.19 & 364.19c) 73.76 & 364.19d) 73.76 & 73.76Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A composite slab consists of a 5 cm thick layer of steel (k = 146 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the left side and a 6 cm thick layer of brass (k = 276 kJ/m-hr-°C) on the right hand side. The outer surfaces of the steel and brass layer are maintained at 100°C and 50°C respectively. The contact between the two slabs is perfect and heat is generated at the rate of 4.2 X 105kJ/m2-hr at the plane of contact. The heat thus generated is dissipated from both sides of composite slab for steady state conditions to calculate heat flow rate through steel and brass slab respectively in MJ/m2-hr.a) 364.19 & 73.76b) 364.19 & 364.19c) 73.76 & 364.19d) 73.76 & 73.76Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















