GATE Exam > GATE Questions > An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltag...
Start Learning for Free
An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)
- a)- 1V
- b)- 0.2 V
- c)1 V
- d)5 V
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and fr...
At both sides of origin, voltages at the displacement of 1 mm would be the same.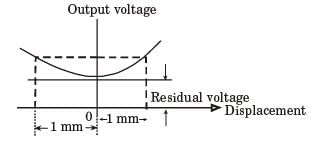
View all questions of this test

Most Upvoted Answer
An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and fr...
LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer)
Given Data:
- Amplitude of sinusoidal voltage: 5 V
- Frequency of sinusoidal voltage: 1 kHz
- Reading of voltmeter for 1 mm displacement from null position: 1 V
To Determine:
- Reading of voltmeter for 1 mm displacement in the opposite direction from null position
Explanation:
Working Principle of LVDT:
- LVDT is a type of electromechanical transducer that converts linear displacement into an electrical signal.
- It consists of a primary coil, two secondary coils, and a movable core.
- The primary coil is connected to a sinusoidal voltage source, and the two secondary coils are connected in series opposition.
- When there is no displacement, the magnetic flux is equal in both secondary coils, resulting in zero output voltage.
- When the core is displaced in one direction, the magnetic flux in one secondary coil increases while the flux in the other coil decreases, resulting in a differential output voltage.
- The magnitude of the output voltage depends on the amplitude and frequency of the input voltage as well as the displacement.
Relationship between Output Voltage and Displacement:
- The output voltage of an LVDT is given by the equation Vout = K * V * d, where Vout is the output voltage, V is the voltage amplitude, K is the sensitivity constant, and d is the displacement.
- The sensitivity constant (K) represents the change in output voltage per unit displacement.
- In this case, the sensitivity constant is given as 1 V/mm.
Calculation:
- Given that the reading of the voltmeter for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position is 1 V.
- Using the equation Vout = K * V * d, we can calculate the sensitivity constant:
- 1 V = K * 5 V * 1 mm
- K = 1/5 V/mm = 0.2 V/mm
Reading of Voltmeter for 1 mm Displacement in the Opposite Direction:
- When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the output voltage can be calculated using the equation Vout = K * V * d:
- Vout = 0.2 V/mm * 5 V * (-1 mm) = -1 V
Conclusion:
- The reading of the voltmeter for a displacement of 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position is -1 V.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option C) 1 V.
Given Data:
- Amplitude of sinusoidal voltage: 5 V
- Frequency of sinusoidal voltage: 1 kHz
- Reading of voltmeter for 1 mm displacement from null position: 1 V
To Determine:
- Reading of voltmeter for 1 mm displacement in the opposite direction from null position
Explanation:
Working Principle of LVDT:
- LVDT is a type of electromechanical transducer that converts linear displacement into an electrical signal.
- It consists of a primary coil, two secondary coils, and a movable core.
- The primary coil is connected to a sinusoidal voltage source, and the two secondary coils are connected in series opposition.
- When there is no displacement, the magnetic flux is equal in both secondary coils, resulting in zero output voltage.
- When the core is displaced in one direction, the magnetic flux in one secondary coil increases while the flux in the other coil decreases, resulting in a differential output voltage.
- The magnitude of the output voltage depends on the amplitude and frequency of the input voltage as well as the displacement.
Relationship between Output Voltage and Displacement:
- The output voltage of an LVDT is given by the equation Vout = K * V * d, where Vout is the output voltage, V is the voltage amplitude, K is the sensitivity constant, and d is the displacement.
- The sensitivity constant (K) represents the change in output voltage per unit displacement.
- In this case, the sensitivity constant is given as 1 V/mm.
Calculation:
- Given that the reading of the voltmeter for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position is 1 V.
- Using the equation Vout = K * V * d, we can calculate the sensitivity constant:
- 1 V = K * 5 V * 1 mm
- K = 1/5 V/mm = 0.2 V/mm
Reading of Voltmeter for 1 mm Displacement in the Opposite Direction:
- When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the output voltage can be calculated using the equation Vout = K * V * d:
- Vout = 0.2 V/mm * 5 V * (-1 mm) = -1 V
Conclusion:
- The reading of the voltmeter for a displacement of 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position is -1 V.
- Therefore, the correct answer is option C) 1 V.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Similar GATE Doubts
An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)a)- 1Vb)- 0.2 Vc)1 Vd)5 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)a)- 1Vb)- 0.2 Vc)1 Vd)5 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)a)- 1Vb)- 0.2 Vc)1 Vd)5 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)a)- 1Vb)- 0.2 Vc)1 Vd)5 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)a)- 1Vb)- 0.2 Vc)1 Vd)5 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)a)- 1Vb)- 0.2 Vc)1 Vd)5 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)a)- 1Vb)- 0.2 Vc)1 Vd)5 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)a)- 1Vb)- 0.2 Vc)1 Vd)5 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for GATE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GATE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)a)- 1Vb)- 0.2 Vc)1 Vd)5 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)a)- 1Vb)- 0.2 Vc)1 Vd)5 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)a)- 1Vb)- 0.2 Vc)1 Vd)5 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)a)- 1Vb)- 0.2 Vc)1 Vd)5 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An LVDT is supplied with a sinusoidal voltage of amplitude 5 V and frequency 1 kHz. The output is connected to an ac voltmeter. The reading of the voltmeter is 1 V for a displacement of 1 mm from the null position. When the displacement is 1 mm in the opposite direction from the null position, the reading of the voltmeter is (2009)a)- 1Vb)- 0.2 Vc)1 Vd)5 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice GATE tests.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















