SSC Exam > SSC Questions > The shear stress- shear strain rate graph fo...
Start Learning for Free
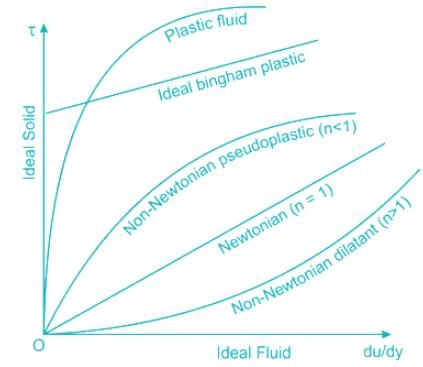
The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is a
- a)Straight line
- b)Parabolic Curve
- c)Hyperbolic Curve
- d)Elliptical
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa...
Newtonian fluids are defined as fluids for which the shear stress is linearly proportional to the shear strain rate. Newtonian fluids are analogous to elastic solids (Hooke’s law: stress proportional to strain). Any common fluids, such as air and other gases, water, kerosene, gasoline, and other oil-based liquids, are Newtonian fluids.
Fluids for which the shear stress is not linearly related to the shear strain rate are called non- Newtonian fluids. Examples include slurries and colloidal suspensions, polymer solutions, blood, paste, and cake batter.
Most Upvoted Answer
The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa...
Explanation:
Newtonian Fluid Behavior:
- Newtonian fluids exhibit linear behavior in the shear stress-shear strain rate graph.
- The shear stress is directly proportional to the shear strain rate, resulting in a straight line relationship.
Reason for Straight Line Graph:
- In Newtonian fluids, the viscosity remains constant regardless of the shear rate.
- This leads to a constant slope in the shear stress-shear strain rate graph, resulting in a straight line.
Characteristics of Newtonian Fluids:
- Examples of Newtonian fluids include water, glycerin, and mineral oil.
- They have a constant viscosity and exhibit linear flow behavior.
Practical Implications:
- The linear relationship in the shear stress-shear strain rate graph simplifies the analysis of flow properties in Newtonian fluids.
- This behavior is useful in various industrial applications where precise control of viscosity is required.
Conclusion:
- The shear stress-shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is a straight line due to the constant viscosity of these fluids. This linear behavior simplifies the analysis and application of Newtonian fluids in various industries.
Newtonian Fluid Behavior:
- Newtonian fluids exhibit linear behavior in the shear stress-shear strain rate graph.
- The shear stress is directly proportional to the shear strain rate, resulting in a straight line relationship.
Reason for Straight Line Graph:
- In Newtonian fluids, the viscosity remains constant regardless of the shear rate.
- This leads to a constant slope in the shear stress-shear strain rate graph, resulting in a straight line.
Characteristics of Newtonian Fluids:
- Examples of Newtonian fluids include water, glycerin, and mineral oil.
- They have a constant viscosity and exhibit linear flow behavior.
Practical Implications:
- The linear relationship in the shear stress-shear strain rate graph simplifies the analysis of flow properties in Newtonian fluids.
- This behavior is useful in various industrial applications where precise control of viscosity is required.
Conclusion:
- The shear stress-shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is a straight line due to the constant viscosity of these fluids. This linear behavior simplifies the analysis and application of Newtonian fluids in various industries.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa)Straight lineb)Parabolic Curvec)Hyperbolic Curved)EllipticalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa)Straight lineb)Parabolic Curvec)Hyperbolic Curved)EllipticalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa)Straight lineb)Parabolic Curvec)Hyperbolic Curved)EllipticalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa)Straight lineb)Parabolic Curvec)Hyperbolic Curved)EllipticalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa)Straight lineb)Parabolic Curvec)Hyperbolic Curved)EllipticalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa)Straight lineb)Parabolic Curvec)Hyperbolic Curved)EllipticalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa)Straight lineb)Parabolic Curvec)Hyperbolic Curved)EllipticalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa)Straight lineb)Parabolic Curvec)Hyperbolic Curved)EllipticalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa)Straight lineb)Parabolic Curvec)Hyperbolic Curved)EllipticalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa)Straight lineb)Parabolic Curvec)Hyperbolic Curved)EllipticalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa)Straight lineb)Parabolic Curvec)Hyperbolic Curved)EllipticalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa)Straight lineb)Parabolic Curvec)Hyperbolic Curved)EllipticalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The shear stress- shear strain rate graph for a Newtonian fluid is aa)Straight lineb)Parabolic Curvec)Hyperbolic Curved)EllipticalCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















