SSC Exam > SSC Questions > Following types of transition curves are mos...
Start Learning for Free
Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?
- a)Spinal
- b)Parabola
- c)Cubic parabola
- d)lemniscate
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railwa...
Cubic parabola Indian Railways mostly uses the cubic parabola for transition curves. The equation of the cubic parabola is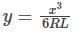
View all questions of this test
Most Upvoted Answer
Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railwa...
Cubic parabola is the type of transition curve that is mostly used in Indian Railways.
Explanation:
A transition curve is a curve that is introduced between a straight and a circular curve in railway tracks. It helps in the smooth transition from a straight track to a curved track, reducing the abrupt change in direction and providing a more comfortable ride for passengers.
Types of Transition Curves:
There are various types of transition curves used in railway engineering, such as:
1. Spinal Curve: This type of curve is rarely used in practice and is not commonly found in Indian Railways. It is a mathematical curve that is difficult to lay out and does not provide a smooth transition.
2. Parabolic Curve: This curve is defined by a parabolic equation and is commonly used in many countries. However, in Indian Railways, it is not widely used due to its limitations in terms of flexibility and ease of laying out.
3. Cubic Parabola: This is the most commonly used type of transition curve in Indian Railways. It is defined by a cubic equation and provides a smooth and easy transition from a straight track to a curved track. It has the advantage of being flexible and easy to lay out, making it suitable for the diverse terrains and varying radius of curves in the Indian railway network.
4. Lemniscate Curve: This curve is rarely used in practice and is not commonly found in Indian Railways. It is a closed loop curve with a shape resembling the numeral "8". It is difficult to lay out and does not provide a smooth transition.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the type of transition curve that is mostly used in Indian Railways is the cubic parabola. It provides a smooth and easy transition from a straight track to a curved track, making it suitable for the diverse terrains and varying radius of curves in the Indian railway network.
Explanation:
A transition curve is a curve that is introduced between a straight and a circular curve in railway tracks. It helps in the smooth transition from a straight track to a curved track, reducing the abrupt change in direction and providing a more comfortable ride for passengers.
Types of Transition Curves:
There are various types of transition curves used in railway engineering, such as:
1. Spinal Curve: This type of curve is rarely used in practice and is not commonly found in Indian Railways. It is a mathematical curve that is difficult to lay out and does not provide a smooth transition.
2. Parabolic Curve: This curve is defined by a parabolic equation and is commonly used in many countries. However, in Indian Railways, it is not widely used due to its limitations in terms of flexibility and ease of laying out.
3. Cubic Parabola: This is the most commonly used type of transition curve in Indian Railways. It is defined by a cubic equation and provides a smooth and easy transition from a straight track to a curved track. It has the advantage of being flexible and easy to lay out, making it suitable for the diverse terrains and varying radius of curves in the Indian railway network.
4. Lemniscate Curve: This curve is rarely used in practice and is not commonly found in Indian Railways. It is a closed loop curve with a shape resembling the numeral "8". It is difficult to lay out and does not provide a smooth transition.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the type of transition curve that is mostly used in Indian Railways is the cubic parabola. It provides a smooth and easy transition from a straight track to a curved track, making it suitable for the diverse terrains and varying radius of curves in the Indian railway network.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?a)Spinalb)Parabolac)Cubic parabolad)lemniscateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?a)Spinalb)Parabolac)Cubic parabolad)lemniscateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?a)Spinalb)Parabolac)Cubic parabolad)lemniscateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?a)Spinalb)Parabolac)Cubic parabolad)lemniscateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?a)Spinalb)Parabolac)Cubic parabolad)lemniscateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?a)Spinalb)Parabolac)Cubic parabolad)lemniscateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?a)Spinalb)Parabolac)Cubic parabolad)lemniscateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?a)Spinalb)Parabolac)Cubic parabolad)lemniscateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?a)Spinalb)Parabolac)Cubic parabolad)lemniscateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?a)Spinalb)Parabolac)Cubic parabolad)lemniscateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?a)Spinalb)Parabolac)Cubic parabolad)lemniscateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?a)Spinalb)Parabolac)Cubic parabolad)lemniscateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Following types of transition curves are mostly used in Indian Railway?a)Spinalb)Parabolac)Cubic parabolad)lemniscateCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
















