SSC Exam > SSC Questions > In triaxial test -a)stress in all three dire...
Start Learning for Free
In triaxial test -
- a)stress in all three directions is the same
- b)stress in all three directions is different
- c)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directions
- d)none of the above
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stres...
In the triaxial test stress in the vertical direction is different from stress in the other two directions.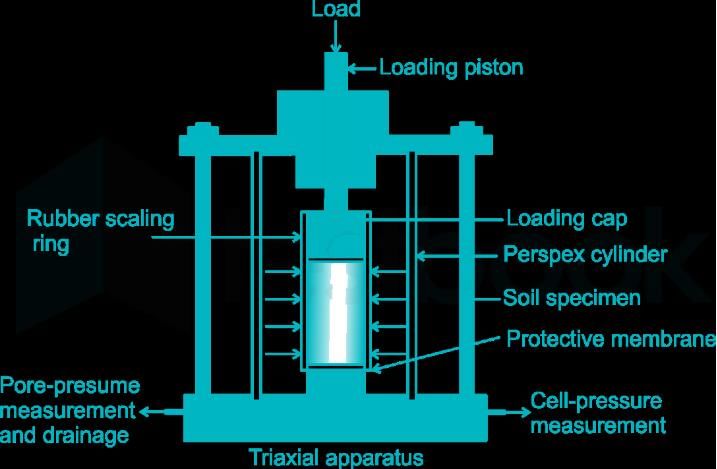
View all questions of this test

Most Upvoted Answer
In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stres...
Triaxial Test
In a triaxial test, stress is applied in three different directions to a soil sample to analyze its behavior under different stress conditions. The correct answer to the question is option 'C', which states that the stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directions.
Stress Distribution in Triaxial Test
- In a triaxial test, the stress is typically applied in the vertical direction, which is known as the axial stress, and also in two horizontal directions called the confining stresses.
- The vertical stress applied to the soil sample creates a major principal stress along the vertical axis.
- The confining stresses are applied in the horizontal directions to simulate the lateral confinement experienced by soil in the ground.
Role of Different Stresses
- The vertical stress applied during the triaxial test is different from the confining stresses as it represents the stress experienced by soil due to the overlying weight of soil layers.
- The confining stresses, on the other hand, represent the lateral pressure exerted on the soil sample due to surrounding soil or rock layers.
- The difference in stress distribution helps in understanding how soil behaves under different stress conditions and provides valuable data for engineering purposes.
Importance of Different Stress Directions
- By applying different stresses in the triaxial test, engineers can determine the strength and deformation characteristics of soil under various stress scenarios.
- The data obtained from the triaxial test helps in designing foundations, retaining walls, and other structures that interact with soil in the ground.
- Understanding the response of soil to different stress directions is crucial for ensuring the stability and safety of civil engineering projects.
In a triaxial test, stress is applied in three different directions to a soil sample to analyze its behavior under different stress conditions. The correct answer to the question is option 'C', which states that the stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directions.
Stress Distribution in Triaxial Test
- In a triaxial test, the stress is typically applied in the vertical direction, which is known as the axial stress, and also in two horizontal directions called the confining stresses.
- The vertical stress applied to the soil sample creates a major principal stress along the vertical axis.
- The confining stresses are applied in the horizontal directions to simulate the lateral confinement experienced by soil in the ground.
Role of Different Stresses
- The vertical stress applied during the triaxial test is different from the confining stresses as it represents the stress experienced by soil due to the overlying weight of soil layers.
- The confining stresses, on the other hand, represent the lateral pressure exerted on the soil sample due to surrounding soil or rock layers.
- The difference in stress distribution helps in understanding how soil behaves under different stress conditions and provides valuable data for engineering purposes.
Importance of Different Stress Directions
- By applying different stresses in the triaxial test, engineers can determine the strength and deformation characteristics of soil under various stress scenarios.
- The data obtained from the triaxial test helps in designing foundations, retaining walls, and other structures that interact with soil in the ground.
- Understanding the response of soil to different stress directions is crucial for ensuring the stability and safety of civil engineering projects.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stress in all three directions is differentc)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directionsd)none of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stress in all three directions is differentc)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directionsd)none of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stress in all three directions is differentc)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directionsd)none of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stress in all three directions is differentc)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directionsd)none of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stress in all three directions is differentc)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directionsd)none of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stress in all three directions is differentc)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directionsd)none of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stress in all three directions is differentc)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directionsd)none of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stress in all three directions is differentc)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directionsd)none of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stress in all three directions is differentc)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directionsd)none of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stress in all three directions is differentc)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directionsd)none of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stress in all three directions is differentc)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directionsd)none of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stress in all three directions is differentc)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directionsd)none of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In triaxial test -a)stress in all three directions is the sameb)stress in all three directions is differentc)stress in the vertical direction is different from the stress in the other two directionsd)none of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















