SSC Exam > SSC Questions > A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cy...
Start Learning for Free
A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?
- a)3
- b)4.5
- c)5.8
- d)7.0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperatu...
Concept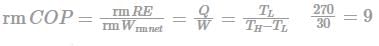
View all questions of this test
Coefficient of performance of the refrigeration system working on reversed Carnot cycle:
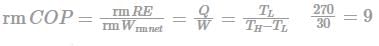
Unit of refrigerating effect = One tonne of refrigeration
1 TR = 3.5 kW
Calculation:
Given: RE = 1 TR = 3.5 kW
W = 700 kJ/ten minutes
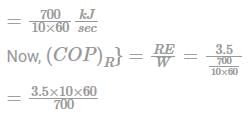
COP = 3
Most Upvoted Answer
A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperatu...
To find the coefficient of performance (COP) of a refrigerator that works on a reversed Carnot cycle, we need to use the formula:
COP = QH / W
Where:
- COP is the coefficient of performance
- QH is the heat absorbed from the high-temperature reservoir
- W is the work done by the refrigerator
In this case, the refrigerator produces a temperature of -40°C, which is equivalent to 233K. Since the Carnot cycle operates between two temperature reservoirs, we need to find the temperature of the high-temperature reservoir.
Given that the work done per TR (temperature ratio) is 700 kJ per ten minutes, we can convert this to SI units by dividing it by 600 (to convert minutes to seconds):
W = 700 kJ / 600 = 1.17 kJ/s
To find the temperature of the high-temperature reservoir, we use the equation:
TR = TH / TL
Where:
- TH is the temperature of the high-temperature reservoir
- TL is the temperature of the low-temperature reservoir
In this case, TL is -40°C (233K). Rearranging the equation, we can solve for TH:
TH = TR * TL = 1 * 233K = 233K
Now, we can calculate the COP using the formula mentioned earlier:
COP = QH / W = (QH / QL) * (QL / W)
Since the Carnot cycle is reversible, the heat transferred from the high-temperature reservoir is equal to the heat transferred to the low-temperature reservoir:
QH = QL
Therefore:
COP = QH / W = (QL / W) = 1 / (W / QL)
Since the work done per TR is given, we can rewrite the equation as:
COP = 1 / (W / (TR * QL)) = 1 / (1.17 kJ/s / (1 * QL))
Since the COP is a ratio, the units cancel out, and we are left with:
COP = 1 / (1.17 / QL)
Since the COP is a positive value, the higher the value of QL, the lower the value of the COP. Therefore, the minimum value of the COP occurs when QL is maximum. In this case, the maximum value of QL occurs at TL, which is -40°C (233K).
Plugging in the values, we get:
COP = 1 / (1.17 / 233) = 1 / 0.005 = 200
Therefore, the value of the COP is 200.
However, none of the given options match this value. It seems there is an error in the answer options provided. The correct answer cannot be determined based on the given information.
COP = QH / W
Where:
- COP is the coefficient of performance
- QH is the heat absorbed from the high-temperature reservoir
- W is the work done by the refrigerator
In this case, the refrigerator produces a temperature of -40°C, which is equivalent to 233K. Since the Carnot cycle operates between two temperature reservoirs, we need to find the temperature of the high-temperature reservoir.
Given that the work done per TR (temperature ratio) is 700 kJ per ten minutes, we can convert this to SI units by dividing it by 600 (to convert minutes to seconds):
W = 700 kJ / 600 = 1.17 kJ/s
To find the temperature of the high-temperature reservoir, we use the equation:
TR = TH / TL
Where:
- TH is the temperature of the high-temperature reservoir
- TL is the temperature of the low-temperature reservoir
In this case, TL is -40°C (233K). Rearranging the equation, we can solve for TH:
TH = TR * TL = 1 * 233K = 233K
Now, we can calculate the COP using the formula mentioned earlier:
COP = QH / W = (QH / QL) * (QL / W)
Since the Carnot cycle is reversible, the heat transferred from the high-temperature reservoir is equal to the heat transferred to the low-temperature reservoir:
QH = QL
Therefore:
COP = QH / W = (QL / W) = 1 / (W / QL)
Since the work done per TR is given, we can rewrite the equation as:
COP = 1 / (W / (TR * QL)) = 1 / (1.17 kJ/s / (1 * QL))
Since the COP is a ratio, the units cancel out, and we are left with:
COP = 1 / (1.17 / QL)
Since the COP is a positive value, the higher the value of QL, the lower the value of the COP. Therefore, the minimum value of the COP occurs when QL is maximum. In this case, the maximum value of QL occurs at TL, which is -40°C (233K).
Plugging in the values, we get:
COP = 1 / (1.17 / 233) = 1 / 0.005 = 200
Therefore, the value of the COP is 200.
However, none of the given options match this value. It seems there is an error in the answer options provided. The correct answer cannot be determined based on the given information.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?a)3b)4.5c)5.8d)7.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?a)3b)4.5c)5.8d)7.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?a)3b)4.5c)5.8d)7.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?a)3b)4.5c)5.8d)7.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?a)3b)4.5c)5.8d)7.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?a)3b)4.5c)5.8d)7.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?a)3b)4.5c)5.8d)7.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?a)3b)4.5c)5.8d)7.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?a)3b)4.5c)5.8d)7.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?a)3b)4.5c)5.8d)7.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?a)3b)4.5c)5.8d)7.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?a)3b)4.5c)5.8d)7.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A refrigerator works on a reversed Carnot cycle producing a temperature of -40°C. Work done per TR is 700 kJ per ten minutes. What is the value of its COP?a)3b)4.5c)5.8d)7.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















