SSC Exam > SSC Questions > Which gas among the following has the highes...
Start Learning for Free
Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?
- a)Helium
- b)Nitrogen
- c)Oxygen
- d)Methane
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic ...
The ratio of CP to CV (CP/CV) for gas is known as the specific heat ratio or adiabatic index and is usually denoted by the Greek letter gamma. 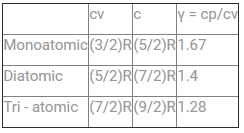
View all questions of this test
- For an ideal monatomic gas (e.g., Helium, Argon, etc.), the adiabatic index is 5/3 or 1.67
- For diatomic gases, the adiabatic index is 7/5 or 1.4
- For polyatomic gases, the adiabatic index is even lesser than the monoatomic and diatomic gases
- Out of the given options, Helium is monoatomic, so it have the highest adiabatic index

Most Upvoted Answer
Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic ...
Adiabatic Index and its Significance
The adiabatic index or the ratio of specific heats is a thermodynamic parameter that measures the ratio of the heat capacity at constant pressure to the heat capacity at constant volume of a gas. It is denoted by the symbol γ.
The adiabatic index plays a significant role in understanding the behavior of gases during adiabatic processes. Adiabatic processes are those where there is no exchange of heat between the system and the surrounding environment.
Higher value of Adiabatic Index
The higher the value of the adiabatic index, the stiffer the gas is. A stiff gas is one that is difficult to compress and has a higher speed of sound.
Helium has the highest adiabatic index among the given options, which makes it a stiff gas. This is because helium is a monoatomic gas with the simplest atomic structure, and hence it experiences the least amount of intermolecular interactions among its atoms.
The adiabatic index of helium is approximately 1.67, while that of nitrogen, oxygen, and methane are 1.40, 1.40, and 1.30 respectively. This means that helium has a higher heat capacity at constant pressure than the other gases, making it more resistant to compression and more efficient in transmitting sound waves.
Conclusion
In conclusion, helium has the highest value of the adiabatic index among the given options, making it a stiff gas. This property makes it an important gas in various applications such as gas chromatography, cooling systems, and as a lifting gas in balloons and airships.
The adiabatic index or the ratio of specific heats is a thermodynamic parameter that measures the ratio of the heat capacity at constant pressure to the heat capacity at constant volume of a gas. It is denoted by the symbol γ.
The adiabatic index plays a significant role in understanding the behavior of gases during adiabatic processes. Adiabatic processes are those where there is no exchange of heat between the system and the surrounding environment.
Higher value of Adiabatic Index
The higher the value of the adiabatic index, the stiffer the gas is. A stiff gas is one that is difficult to compress and has a higher speed of sound.
Helium has the highest adiabatic index among the given options, which makes it a stiff gas. This is because helium is a monoatomic gas with the simplest atomic structure, and hence it experiences the least amount of intermolecular interactions among its atoms.
The adiabatic index of helium is approximately 1.67, while that of nitrogen, oxygen, and methane are 1.40, 1.40, and 1.30 respectively. This means that helium has a higher heat capacity at constant pressure than the other gases, making it more resistant to compression and more efficient in transmitting sound waves.
Conclusion
In conclusion, helium has the highest value of the adiabatic index among the given options, making it a stiff gas. This property makes it an important gas in various applications such as gas chromatography, cooling systems, and as a lifting gas in balloons and airships.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?a)Heliumb)Nitrogenc)Oxygend)MethaneCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?a)Heliumb)Nitrogenc)Oxygend)MethaneCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?a)Heliumb)Nitrogenc)Oxygend)MethaneCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?a)Heliumb)Nitrogenc)Oxygend)MethaneCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?a)Heliumb)Nitrogenc)Oxygend)MethaneCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?a)Heliumb)Nitrogenc)Oxygend)MethaneCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?a)Heliumb)Nitrogenc)Oxygend)MethaneCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?a)Heliumb)Nitrogenc)Oxygend)MethaneCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?a)Heliumb)Nitrogenc)Oxygend)MethaneCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?a)Heliumb)Nitrogenc)Oxygend)MethaneCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?a)Heliumb)Nitrogenc)Oxygend)MethaneCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?a)Heliumb)Nitrogenc)Oxygend)MethaneCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which gas among the following has the highest value of the adiabatic index?a)Heliumb)Nitrogenc)Oxygend)MethaneCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















