SSC Exam > SSC Questions > In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)...
Start Learning for Free
In arc welding, penetration is minimum for
- a)DC – Electrode Positive
- b)DC – Electrode Negative
- c)AC
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)...
In arc welding, penetration is minimum for DC – Electrode Positive.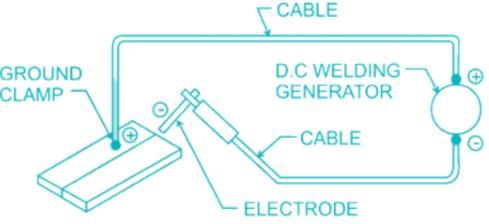
View all questions of this test
Types and importance of polarity in arc welding
Polarity indicates the direction of current flow in the welding circuit.
Kinds of polarity
- Straight polarity or electrode negative (DCEN)
- Reverse polarity or electrode positive (DCEP)
Straight polarity: In straight polarity, the electrode is connected to the negative and the work to the positive terminal of the power source.

Electrode Negative Or straight polarity (DCEN)
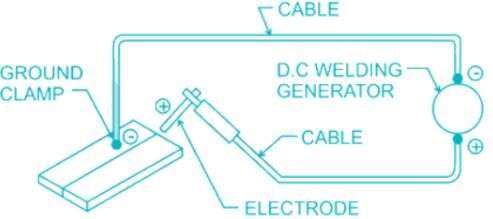
Reverse Polarity: In reverse polarity, the electrode is connected to the positive and the work to the negative terminal of the power source.

Electrode Positive Or Reverse Polarity (DCEN)

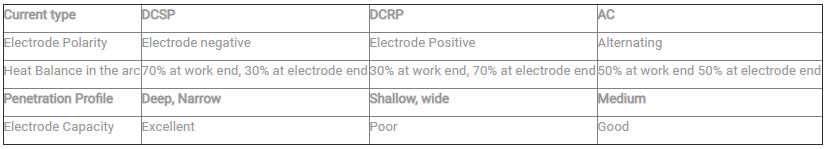
DCSP (Electrode Negative)—Maximum penetration.
AC—Moderate penetration.
DCRP (Electrode Positive)—Minimum penetration
Most Upvoted Answer
In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)...
Explanation:
Arc welding is a process in which two metal pieces are joined together using an electric arc. The electric arc is created by an electric current passing through an electrode and the workpiece. One of the important factors in arc welding is penetration, which refers to the depth of fusion between the two metal pieces being welded.
DC – Electrode Positive:
- In DC – Electrode Positive polarity, the electrode is connected to the positive terminal of the power supply, and the workpiece is connected to the negative terminal.
- In this polarity, the electrons flow from the workpiece to the electrode, resulting in a concentrated heat at the tip of the electrode.
- The intense heat generated at the electrode tip allows for better penetration as compared to other polarities.
- The high temperature created by the concentrated heat facilitates the melting of both the electrode and the workpiece, leading to a deeper fusion between the two metal pieces being welded.
DC – Electrode Negative:
- In DC – Electrode Negative polarity, the electrode is connected to the negative terminal of the power supply, and the workpiece is connected to the positive terminal.
- In this polarity, the electrons flow from the electrode to the workpiece, causing the heat to be concentrated at the workpiece.
- The heat generated at the workpiece is comparatively lower than in DC – Electrode Positive polarity, resulting in reduced penetration.
- However, this polarity is often used for welding thin materials, as the lower heat concentration helps prevent burn-through.
AC:
- In AC (alternating current), the polarity of the electrode continuously switches between positive and negative.
- As a result, the heat distribution is not as concentrated as in DC – Electrode Positive polarity, leading to reduced penetration.
- AC is commonly used for welding aluminum and magnesium alloys, as it helps prevent arc blow and improves the stability of the arc.
Conclusion:
In arc welding, penetration is minimum for DC – Electrode Negative polarity. DC – Electrode Positive polarity provides better penetration due to the concentrated heat generated at the electrode tip. AC polarity offers intermediate penetration levels, making it suitable for specific applications.
Arc welding is a process in which two metal pieces are joined together using an electric arc. The electric arc is created by an electric current passing through an electrode and the workpiece. One of the important factors in arc welding is penetration, which refers to the depth of fusion between the two metal pieces being welded.
DC – Electrode Positive:
- In DC – Electrode Positive polarity, the electrode is connected to the positive terminal of the power supply, and the workpiece is connected to the negative terminal.
- In this polarity, the electrons flow from the workpiece to the electrode, resulting in a concentrated heat at the tip of the electrode.
- The intense heat generated at the electrode tip allows for better penetration as compared to other polarities.
- The high temperature created by the concentrated heat facilitates the melting of both the electrode and the workpiece, leading to a deeper fusion between the two metal pieces being welded.
DC – Electrode Negative:
- In DC – Electrode Negative polarity, the electrode is connected to the negative terminal of the power supply, and the workpiece is connected to the positive terminal.
- In this polarity, the electrons flow from the electrode to the workpiece, causing the heat to be concentrated at the workpiece.
- The heat generated at the workpiece is comparatively lower than in DC – Electrode Positive polarity, resulting in reduced penetration.
- However, this polarity is often used for welding thin materials, as the lower heat concentration helps prevent burn-through.
AC:
- In AC (alternating current), the polarity of the electrode continuously switches between positive and negative.
- As a result, the heat distribution is not as concentrated as in DC – Electrode Positive polarity, leading to reduced penetration.
- AC is commonly used for welding aluminum and magnesium alloys, as it helps prevent arc blow and improves the stability of the arc.
Conclusion:
In arc welding, penetration is minimum for DC – Electrode Negative polarity. DC – Electrode Positive polarity provides better penetration due to the concentrated heat generated at the electrode tip. AC polarity offers intermediate penetration levels, making it suitable for specific applications.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)DC – Electrode Negativec)ACd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)DC – Electrode Negativec)ACd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)DC – Electrode Negativec)ACd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)DC – Electrode Negativec)ACd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)DC – Electrode Negativec)ACd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)DC – Electrode Negativec)ACd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)DC – Electrode Negativec)ACd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)DC – Electrode Negativec)ACd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)DC – Electrode Negativec)ACd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)DC – Electrode Negativec)ACd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)DC – Electrode Negativec)ACd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)DC – Electrode Negativec)ACd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In arc welding, penetration is minimum fora)DC – Electrode Positiveb)DC – Electrode Negativec)ACd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















