SSC Exam > SSC Questions > If air is heated without changing its moistu...
Start Learning for Free
If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.
- a)Increase
- b)Decrease
- c)Remain the same
- d)Unpredictable
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point...
Concept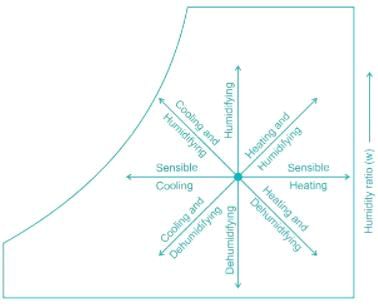
View all questions of this test
Dry Bulb Temperature: Actual temperature of gas or mixture of gases.
Wet-bulb temperature: Temperature obtained by an accurate thermometer having a wick moistened with distilled water.
Dew point temperature: Temperature at which the liquid droplets just appear when the moist air is cooled continuously.
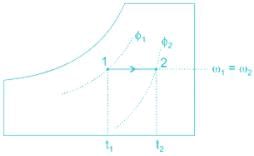
Sensible heating: Moisture content of air remains constant, so specific humidity is constant, temperature increases as it flows over a heating coil.
Sensible cooling: The moisture content of air remains constant, so specific humidity is constant, but its temperature decreases as it flows over a cooling coil.

According to the question:
If air is heated without changing its moisture content, ⇒ Sensible heating.
Sensible heating: It is the process of increasing the Dry bulb temperature at a constant specific humidity.

Effects of sensible heating:
- Dry bulb temperature increases
- Sp. Humidity or humidity ratio remains constant
- Dew point temperature is constant
- Relative humidity decreases
- Enthalpy increases
- Specific Volume Increases
- Wet-bulb temperature increases
Most Upvoted Answer
If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point...
Explanation:
When air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point remains the same. This is because the dew point is the temperature at which the air becomes saturated with water vapor, causing condensation to occur. The moisture content of the air is determined by the amount of water vapor present, and heating the air does not change the amount of water vapor in it.
Factors Affecting Dew Point:
To understand why the dew point remains the same when air is heated without changing its moisture content, it is important to consider the factors that affect the dew point:
1. Temperature: The dew point is directly related to the temperature of the air. As the temperature decreases, the air can hold less water vapor, leading to condensation and a lower dew point.
2. Humidity: The amount of water vapor present in the air affects the dew point. Higher humidity means more moisture in the air, resulting in a higher dew point.
3. Moisture Content: The moisture content of the air, which is determined by the amount of water vapor present, is a key factor in determining the dew point.
Impact of Heating on Dew Point:
When air is heated without changing its moisture content, the temperature increases but the amount of water vapor remains the same. This means that the relative humidity decreases because the air can now hold more moisture at the higher temperature. However, since the moisture content does not change, the dew point remains the same.
Example:
For example, let's consider a sample of air with a temperature of 20°C and a dew point of 10°C. If we heat this air to 30°C without adding or removing any moisture, the relative humidity will decrease because the air can now hold more water vapor at the higher temperature. However, the dew point remains the same at 10°C because the moisture content has not changed.
Therefore, when air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point remains the same.
When air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point remains the same. This is because the dew point is the temperature at which the air becomes saturated with water vapor, causing condensation to occur. The moisture content of the air is determined by the amount of water vapor present, and heating the air does not change the amount of water vapor in it.
Factors Affecting Dew Point:
To understand why the dew point remains the same when air is heated without changing its moisture content, it is important to consider the factors that affect the dew point:
1. Temperature: The dew point is directly related to the temperature of the air. As the temperature decreases, the air can hold less water vapor, leading to condensation and a lower dew point.
2. Humidity: The amount of water vapor present in the air affects the dew point. Higher humidity means more moisture in the air, resulting in a higher dew point.
3. Moisture Content: The moisture content of the air, which is determined by the amount of water vapor present, is a key factor in determining the dew point.
Impact of Heating on Dew Point:
When air is heated without changing its moisture content, the temperature increases but the amount of water vapor remains the same. This means that the relative humidity decreases because the air can now hold more moisture at the higher temperature. However, since the moisture content does not change, the dew point remains the same.
Example:
For example, let's consider a sample of air with a temperature of 20°C and a dew point of 10°C. If we heat this air to 30°C without adding or removing any moisture, the relative humidity will decrease because the air can now hold more water vapor at the higher temperature. However, the dew point remains the same at 10°C because the moisture content has not changed.
Therefore, when air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point remains the same.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.a)Increaseb)Decreasec)Remain the samed)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.a)Increaseb)Decreasec)Remain the samed)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.a)Increaseb)Decreasec)Remain the samed)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.a)Increaseb)Decreasec)Remain the samed)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.a)Increaseb)Decreasec)Remain the samed)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.a)Increaseb)Decreasec)Remain the samed)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.a)Increaseb)Decreasec)Remain the samed)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.a)Increaseb)Decreasec)Remain the samed)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.a)Increaseb)Decreasec)Remain the samed)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.a)Increaseb)Decreasec)Remain the samed)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.a)Increaseb)Decreasec)Remain the samed)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.a)Increaseb)Decreasec)Remain the samed)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice If air is heated without changing its moisture content, the dew point will _____.a)Increaseb)Decreasec)Remain the samed)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















