SSC Exam > SSC Questions > If cohesion between molecules of fluid is gr...
Start Learning for Free
If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will be
- a)Higher than the surface of the liquid
- b)The same as the surface of the liquid
- c)Lower than the surface of the liquid
- d)Unpredictable
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion b...
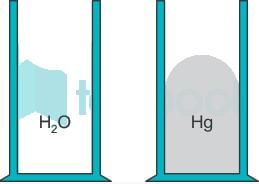
The meniscus in a graduated cylinder of water is due to the adhesion between water molecules and the sides of the tube. The adhesion is greater than the cohesion between the water molecules.
A concave meniscus occurs when the liquid particles are more strongly attracted to the container (adhesion) than to each other (cohesion), causing the liquid to climb the walls of the container. This occurs between water and glass.
The reverse is true about a column of mercury. In mercury, atoms are attracted to each other more strongly than they are attracted to the sides of the tube.
A convex meniscus occurs when the particles in the liquid have a stronger attraction to each other than to the material of the container. Convex meniscus occurs, for example, between mercury and glass.
Capillary Action in:
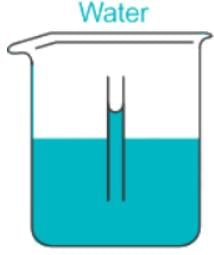
Adhesion is greater than Cohesion.
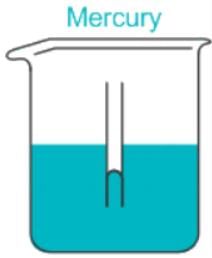
Adhesion is less than Cohesion.
When the cohesion between fluid molecules is greater than the adhesion between fluid and the glass, then the free level of fluid in the glass tube dipped in the glass vessel will be lower than the surface of the fluid.
Most Upvoted Answer
If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion b...
Cohesion and Adhesion in Fluids
Cohesion refers to the attraction between molecules of the same substance, while adhesion refers to the attraction between molecules of different substances. In the case of a fluid, such as water, the cohesion between water molecules is typically stronger than the adhesion between water and glass molecules.
Explanation:
1. Cohesion between molecules of fluid:
- Cohesion between molecules of a fluid, such as water, is the result of intermolecular forces, such as hydrogen bonding.
- These forces cause water molecules to stick together, creating a cohesive force that holds the fluid together.
- Due to the strong cohesive forces, the molecules in the fluid tend to attract each other and form a continuous liquid surface.
2. Adhesion between fluid and glass:
- Adhesion between fluid and glass occurs due to intermolecular forces between the fluid molecules and the glass molecules.
- However, in the case of water and glass, the adhesion between the two is generally weaker compared to the cohesion between water molecules.
3. Dipped glass tube and free level of fluid:
- When a glass tube is dipped into a fluid, such as water, the fluid will rise in the tube due to capillary action.
- Capillary action is the result of the combination of cohesion and adhesion forces.
- If the cohesion between the fluid molecules is greater than the adhesion between the fluid and glass molecules, the fluid will be pulled upward in the tube, creating a concave meniscus.
- The level of the fluid in the tube will be lower than the surface of the liquid outside the tube.
- This is because the cohesive forces between the fluid molecules cause the fluid in the tube to resist being pulled upward by the adhesive forces between the fluid and the glass.
Conclusion:
In summary, when the cohesion between molecules of a fluid is greater than the adhesion between the fluid and the glass, the free level of the fluid in a dipped glass tube will be lower than the surface of the liquid. This is due to the strong cohesive forces within the fluid, which cause the fluid to resist being pulled upward by the adhesive forces between the fluid and the glass.
Cohesion refers to the attraction between molecules of the same substance, while adhesion refers to the attraction between molecules of different substances. In the case of a fluid, such as water, the cohesion between water molecules is typically stronger than the adhesion between water and glass molecules.
Explanation:
1. Cohesion between molecules of fluid:
- Cohesion between molecules of a fluid, such as water, is the result of intermolecular forces, such as hydrogen bonding.
- These forces cause water molecules to stick together, creating a cohesive force that holds the fluid together.
- Due to the strong cohesive forces, the molecules in the fluid tend to attract each other and form a continuous liquid surface.
2. Adhesion between fluid and glass:
- Adhesion between fluid and glass occurs due to intermolecular forces between the fluid molecules and the glass molecules.
- However, in the case of water and glass, the adhesion between the two is generally weaker compared to the cohesion between water molecules.
3. Dipped glass tube and free level of fluid:
- When a glass tube is dipped into a fluid, such as water, the fluid will rise in the tube due to capillary action.
- Capillary action is the result of the combination of cohesion and adhesion forces.
- If the cohesion between the fluid molecules is greater than the adhesion between the fluid and glass molecules, the fluid will be pulled upward in the tube, creating a concave meniscus.
- The level of the fluid in the tube will be lower than the surface of the liquid outside the tube.
- This is because the cohesive forces between the fluid molecules cause the fluid in the tube to resist being pulled upward by the adhesive forces between the fluid and the glass.
Conclusion:
In summary, when the cohesion between molecules of a fluid is greater than the adhesion between the fluid and the glass, the free level of the fluid in a dipped glass tube will be lower than the surface of the liquid. This is due to the strong cohesive forces within the fluid, which cause the fluid to resist being pulled upward by the adhesive forces between the fluid and the glass.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will bea)Higher than the surface of the liquidb)The same as the surface of the liquidc)Lower than the surface of the liquidd)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will bea)Higher than the surface of the liquidb)The same as the surface of the liquidc)Lower than the surface of the liquidd)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will bea)Higher than the surface of the liquidb)The same as the surface of the liquidc)Lower than the surface of the liquidd)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will bea)Higher than the surface of the liquidb)The same as the surface of the liquidc)Lower than the surface of the liquidd)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will bea)Higher than the surface of the liquidb)The same as the surface of the liquidc)Lower than the surface of the liquidd)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will bea)Higher than the surface of the liquidb)The same as the surface of the liquidc)Lower than the surface of the liquidd)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will bea)Higher than the surface of the liquidb)The same as the surface of the liquidc)Lower than the surface of the liquidd)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will bea)Higher than the surface of the liquidb)The same as the surface of the liquidc)Lower than the surface of the liquidd)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will bea)Higher than the surface of the liquidb)The same as the surface of the liquidc)Lower than the surface of the liquidd)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will bea)Higher than the surface of the liquidb)The same as the surface of the liquidc)Lower than the surface of the liquidd)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will bea)Higher than the surface of the liquidb)The same as the surface of the liquidc)Lower than the surface of the liquidd)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will bea)Higher than the surface of the liquidb)The same as the surface of the liquidc)Lower than the surface of the liquidd)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice If cohesion between molecules of fluid is greater than the adhesion between fluid and glass, then the free level of flid in a dipped glass tube will bea)Higher than the surface of the liquidb)The same as the surface of the liquidc)Lower than the surface of the liquidd)UnpredictableCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















