SSC Exam > SSC Questions > A centrifugal pump will start delivering wat...
Start Learning for Free
A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than the
- a)Kinetic head
- b)Manometric head
- c)Static head
- d)Velocity head
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure...
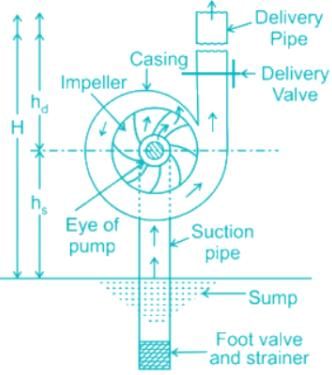
Main parts of a centrifugal pump
The static head is the actual difference in the elevations.
The kinetic and velocity heads are the same because of the pump’s kinetic energy in the pump because of the flow.
The total manometric head is the difference in pressure (in metres) between the pump’s inlet and outlet points. This value is always higher than the actual difference in elevation between these two points; when pumping is going on, the pump also needs to overcome friction losses occurring as the water flows through the intake and outlet pipes.
Thus, the pump will only deliver the water if the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or more than the manometric head.
Most Upvoted Answer
A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure...
Explanation:
A centrifugal pump works on the principle of converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. This is accomplished by accelerating the fluid in the impeller and converting the velocity energy into pressure energy as the fluid flows through the volute casing. The pressure rise in the impeller is caused by the centrifugal force generated by the high-speed rotation of the impeller.
The pressure rise in the impeller is measured in terms of head, which is the height of a column of water that would produce the same pressure. There are four types of heads associated with a centrifugal pump: kinetic head, manometric head, static head, and velocity head.
- Kinetic head: The kinetic head is the energy per unit weight of fluid due to its motion. It is given by the formula (V^2/2g), where V is the velocity of the fluid and g is the acceleration due to gravity. The kinetic head is not relevant for determining the starting of a centrifugal pump.
- Manometric head: The manometric head is the energy per unit weight of fluid due to its pressure. It is given by the formula (P/ρg), where P is the pressure of the fluid, ρ is the density of the fluid, and g is the acceleration due to gravity. The manometric head is the head that is required to overcome the losses due to friction and elevation in the system. A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than the manometric head.
- Static head: The static head is the energy per unit weight of fluid due to its elevation. It is given by the formula (h), where h is the height of the fluid above a reference point. The static head is the head that is required to lift the fluid from the source to the pump.
- Velocity head: The velocity head is the energy per unit weight of fluid due to its velocity. It is given by the formula (V^2/2g), where V is the velocity of the fluid and g is the acceleration due to gravity. The velocity head is the head that is required to overcome the kinetic energy of the fluid.
Conclusion:
Hence, we can conclude that the correct answer is option B, i.e., manometric head. A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than the manometric head.
A centrifugal pump works on the principle of converting mechanical energy into hydraulic energy. This is accomplished by accelerating the fluid in the impeller and converting the velocity energy into pressure energy as the fluid flows through the volute casing. The pressure rise in the impeller is caused by the centrifugal force generated by the high-speed rotation of the impeller.
The pressure rise in the impeller is measured in terms of head, which is the height of a column of water that would produce the same pressure. There are four types of heads associated with a centrifugal pump: kinetic head, manometric head, static head, and velocity head.
- Kinetic head: The kinetic head is the energy per unit weight of fluid due to its motion. It is given by the formula (V^2/2g), where V is the velocity of the fluid and g is the acceleration due to gravity. The kinetic head is not relevant for determining the starting of a centrifugal pump.
- Manometric head: The manometric head is the energy per unit weight of fluid due to its pressure. It is given by the formula (P/ρg), where P is the pressure of the fluid, ρ is the density of the fluid, and g is the acceleration due to gravity. The manometric head is the head that is required to overcome the losses due to friction and elevation in the system. A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than the manometric head.
- Static head: The static head is the energy per unit weight of fluid due to its elevation. It is given by the formula (h), where h is the height of the fluid above a reference point. The static head is the head that is required to lift the fluid from the source to the pump.
- Velocity head: The velocity head is the energy per unit weight of fluid due to its velocity. It is given by the formula (V^2/2g), where V is the velocity of the fluid and g is the acceleration due to gravity. The velocity head is the head that is required to overcome the kinetic energy of the fluid.
Conclusion:
Hence, we can conclude that the correct answer is option B, i.e., manometric head. A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than the manometric head.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than thea)Kinetic headb)Manometric headc)Static headd)Velocity headCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than thea)Kinetic headb)Manometric headc)Static headd)Velocity headCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than thea)Kinetic headb)Manometric headc)Static headd)Velocity headCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than thea)Kinetic headb)Manometric headc)Static headd)Velocity headCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than thea)Kinetic headb)Manometric headc)Static headd)Velocity headCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than thea)Kinetic headb)Manometric headc)Static headd)Velocity headCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than thea)Kinetic headb)Manometric headc)Static headd)Velocity headCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than thea)Kinetic headb)Manometric headc)Static headd)Velocity headCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than thea)Kinetic headb)Manometric headc)Static headd)Velocity headCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than thea)Kinetic headb)Manometric headc)Static headd)Velocity headCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than thea)Kinetic headb)Manometric headc)Static headd)Velocity headCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than thea)Kinetic headb)Manometric headc)Static headd)Velocity headCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A centrifugal pump will start delivering water only when the pressure rise in the impeller is equal to or greater than thea)Kinetic headb)Manometric headc)Static headd)Velocity headCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















