SSC Exam > SSC Questions > Pick up the correct statement from the follow...
Start Learning for Free
Pick up the correct statement from the following.
- a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cement
- b)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.
- c)The concrete does not set at freezing point
- d)All options are correct
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains ...
The concrete gains strength due to the hydration of cement.
The concrete does not set at freezing point.
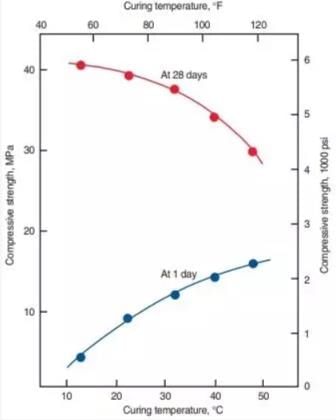
Excessive rates of heating and cooling should be avoided to prevent damaging volume changes. Temperatures in the enclosure surrounding the concrete should not be increased or decreased more than 22°C to 33°C (40°F to 60°F) per hour depending on the size and shape of the concrete element. For example, there is reduced drying shrinkage and creep as compared to concrete cured at 23°C (73°F) for 28 days.
One-day strength increases with increasing curing temperature, but 28-day strength decreases with
increasing curing temperature.
The concrete does not set at freezing point.
Excessive rates of heating and cooling should be avoided to prevent damaging volume changes. Temperatures in the enclosure surrounding the concrete should not be increased or decreased more than 22°C to 33°C (40°F to 60°F) per hour depending on the size and shape of the concrete element. For example, there is reduced drying shrinkage and creep as compared to concrete cured at 23°C (73°F) for 28 days.
One-day strength increases with increasing curing temperature, but 28-day strength decreases with
increasing curing temperature.

Most Upvoted Answer
Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains ...
Concrete Strength and Curing Temperature
- The strength of concrete is a function of the hydration of cement particles. As water is added to the mix, the cement particles react with it to form a crystalline structure that binds the aggregates together. This process is called hydration, and it continues for a long time after the concrete has set.
- The strength of concrete increases with time as more and more cement particles hydrate. In general, the longer the concrete is allowed to cure, the stronger it becomes. The strength of concrete is usually measured after 28 days of curing, although it continues to increase for many years after that.
- The curing temperature of concrete can have a significant effect on its strength. In general, higher curing temperatures lead to faster hydration and stronger concrete. However, if the temperature is too high, the concrete can crack or shrink as it dries out too quickly.
- The optimal curing temperature for concrete depends on several factors, including the type of cement used, the water-cement ratio, and the ambient temperature and humidity. In general, a curing temperature between 50 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit is recommended for most types of concrete.
- It is important to note that the strength of concrete can decrease if it is subjected to very high temperatures during the curing process. This is because the heat can cause the water in the mix to evaporate too quickly, which can lead to cracking and shrinkage. Therefore, it is important to carefully control the curing temperature to ensure that the concrete reaches its optimal strength.
Concrete Setting at Freezing Point
- Concrete can set and harden at temperatures below freezing (32 degrees Fahrenheit). However, the process is slower and requires special precautions to prevent damage to the concrete.
- If the concrete mix freezes before it has a chance to set, the water in the mix can expand and cause the concrete to crack and weaken. Therefore, it is important to protect the concrete from freezing during the curing process.
- One way to prevent the concrete from freezing is to use heated enclosures or blankets to maintain the temperature above freezing. Another option is to use special additives in the mix that can help prevent freezing and improve the strength and durability of the concrete.
Conclusion
- All of the statements in the options are correct. The strength of concrete increases due to hydration of cement, the 28-day strength generally increases with increasing curing temperature (up to a point), and concrete can set at temperatures below freezing with proper precautions.
- The strength of concrete is a function of the hydration of cement particles. As water is added to the mix, the cement particles react with it to form a crystalline structure that binds the aggregates together. This process is called hydration, and it continues for a long time after the concrete has set.
- The strength of concrete increases with time as more and more cement particles hydrate. In general, the longer the concrete is allowed to cure, the stronger it becomes. The strength of concrete is usually measured after 28 days of curing, although it continues to increase for many years after that.
- The curing temperature of concrete can have a significant effect on its strength. In general, higher curing temperatures lead to faster hydration and stronger concrete. However, if the temperature is too high, the concrete can crack or shrink as it dries out too quickly.
- The optimal curing temperature for concrete depends on several factors, including the type of cement used, the water-cement ratio, and the ambient temperature and humidity. In general, a curing temperature between 50 and 70 degrees Fahrenheit is recommended for most types of concrete.
- It is important to note that the strength of concrete can decrease if it is subjected to very high temperatures during the curing process. This is because the heat can cause the water in the mix to evaporate too quickly, which can lead to cracking and shrinkage. Therefore, it is important to carefully control the curing temperature to ensure that the concrete reaches its optimal strength.
Concrete Setting at Freezing Point
- Concrete can set and harden at temperatures below freezing (32 degrees Fahrenheit). However, the process is slower and requires special precautions to prevent damage to the concrete.
- If the concrete mix freezes before it has a chance to set, the water in the mix can expand and cause the concrete to crack and weaken. Therefore, it is important to protect the concrete from freezing during the curing process.
- One way to prevent the concrete from freezing is to use heated enclosures or blankets to maintain the temperature above freezing. Another option is to use special additives in the mix that can help prevent freezing and improve the strength and durability of the concrete.
Conclusion
- All of the statements in the options are correct. The strength of concrete increases due to hydration of cement, the 28-day strength generally increases with increasing curing temperature (up to a point), and concrete can set at temperatures below freezing with proper precautions.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cementb)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.c)The concrete does not set at freezing pointd)All options are correctCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cementb)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.c)The concrete does not set at freezing pointd)All options are correctCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cementb)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.c)The concrete does not set at freezing pointd)All options are correctCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cementb)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.c)The concrete does not set at freezing pointd)All options are correctCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cementb)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.c)The concrete does not set at freezing pointd)All options are correctCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cementb)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.c)The concrete does not set at freezing pointd)All options are correctCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cementb)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.c)The concrete does not set at freezing pointd)All options are correctCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cementb)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.c)The concrete does not set at freezing pointd)All options are correctCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cementb)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.c)The concrete does not set at freezing pointd)All options are correctCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cementb)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.c)The concrete does not set at freezing pointd)All options are correctCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cementb)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.c)The concrete does not set at freezing pointd)All options are correctCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cementb)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.c)The concrete does not set at freezing pointd)All options are correctCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Pick up the correct statement from the following.a)The concrete gains strength due to hydration of cementb)28-day strength decreases with increasing curing temperature.c)The concrete does not set at freezing pointd)All options are correctCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















