UPSC Exam > UPSC Questions > Which of the following is NOT correctly matc...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?
- a)The Panchayats - Part - IX
- b)The Municipalities - Part - IX A
- c)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societies
- d)Tribunals - Part - X
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constituti...
Important Point
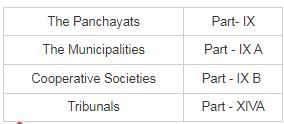
Mistake Point
- The Scheduled and Tribal Areas- Part- X
Additional Information
- Original Indian Constitution had 22 parts and 395 articles. Later 3 parts were added to it as amendments making the tally 25.
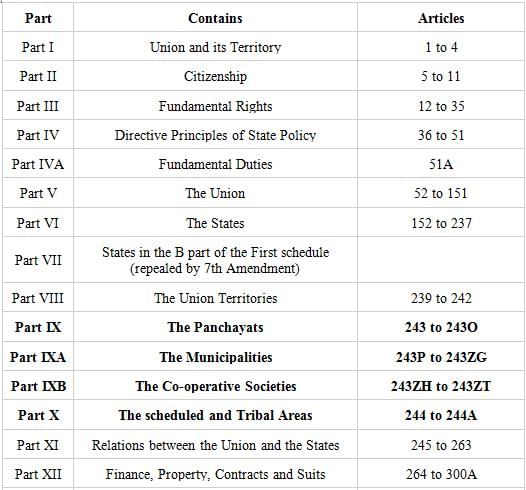
- Parts of Indian Constitution
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constituti...
The Constitution of India
The Constitution of India is the supreme law of the country that lays down the framework that defines the political principles, establishes the structure, procedures, powers, and duties of the government institutions, and sets out the fundamental rights, directive principles, and responsibilities of citizens. It is a comprehensive document that covers various aspects of governance and administration.
Panchayats - Part - IX
Part IX of the Constitution of India deals with the Panchayats, which are the local self-government institutions at the village, intermediate, and district levels. This part provides for the establishment, composition, powers, and functions of the Panchayats. It ensures that democratic principles are followed at the grassroots level and empowers the local communities to participate in decision-making processes.
Municipalities - Part - IX A
Part IX A of the Constitution of India deals with the Municipalities, which are the local self-government institutions in urban areas. This part provides for the establishment, composition, powers, and functions of the Municipalities. It aims to ensure effective urban governance and empower the residents of cities and towns to participate in the development and management of their localities.
Cooperative Societies - Part - IX B
Part IX B of the Constitution of India deals with the Cooperative Societies. It provides for the promotion, development, and regulation of cooperative societies, which are voluntary associations formed for the economic and social betterment of their members. This part ensures that cooperative societies operate in a democratic and transparent manner and contribute to the overall development of the society.
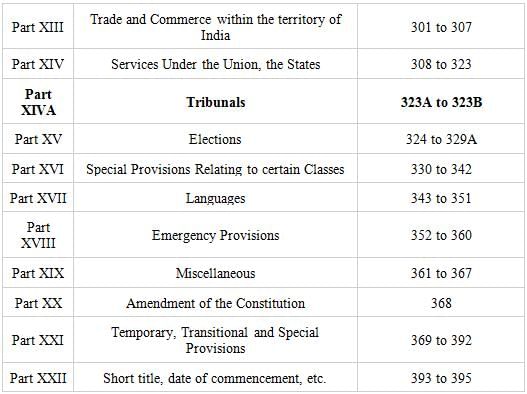
Tribunals - Part - X
Part X of the Constitution of India deals with the Tribunals. It provides for the establishment of administrative and other tribunals for the speedy and efficient resolution of disputes and grievances. These tribunals are meant to reduce the burden on the regular courts and provide specialized expertise in specific areas of law. They function independently and have the power to make binding decisions.
Conclusion
From the given options, it is clear that the establishment of Tribunals is correctly matched as per the Constitution of India. Therefore, the correct answer is option D, which states that Tribunals are not correctly matched.
The Constitution of India is the supreme law of the country that lays down the framework that defines the political principles, establishes the structure, procedures, powers, and duties of the government institutions, and sets out the fundamental rights, directive principles, and responsibilities of citizens. It is a comprehensive document that covers various aspects of governance and administration.
Panchayats - Part - IX
Part IX of the Constitution of India deals with the Panchayats, which are the local self-government institutions at the village, intermediate, and district levels. This part provides for the establishment, composition, powers, and functions of the Panchayats. It ensures that democratic principles are followed at the grassroots level and empowers the local communities to participate in decision-making processes.
Municipalities - Part - IX A
Part IX A of the Constitution of India deals with the Municipalities, which are the local self-government institutions in urban areas. This part provides for the establishment, composition, powers, and functions of the Municipalities. It aims to ensure effective urban governance and empower the residents of cities and towns to participate in the development and management of their localities.
Cooperative Societies - Part - IX B
Part IX B of the Constitution of India deals with the Cooperative Societies. It provides for the promotion, development, and regulation of cooperative societies, which are voluntary associations formed for the economic and social betterment of their members. This part ensures that cooperative societies operate in a democratic and transparent manner and contribute to the overall development of the society.
Tribunals - Part - X
Part X of the Constitution of India deals with the Tribunals. It provides for the establishment of administrative and other tribunals for the speedy and efficient resolution of disputes and grievances. These tribunals are meant to reduce the burden on the regular courts and provide specialized expertise in specific areas of law. They function independently and have the power to make binding decisions.
Conclusion
From the given options, it is clear that the establishment of Tribunals is correctly matched as per the Constitution of India. Therefore, the correct answer is option D, which states that Tribunals are not correctly matched.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Similar UPSC Doubts
Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?a)The Panchayats - Part - IXb)The Municipalities - Part - IX Ac)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societiesd)Tribunals - Part - XCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?a)The Panchayats - Part - IXb)The Municipalities - Part - IX Ac)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societiesd)Tribunals - Part - XCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for UPSC 2025 is part of UPSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UPSC exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?a)The Panchayats - Part - IXb)The Municipalities - Part - IX Ac)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societiesd)Tribunals - Part - XCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UPSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?a)The Panchayats - Part - IXb)The Municipalities - Part - IX Ac)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societiesd)Tribunals - Part - XCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?a)The Panchayats - Part - IXb)The Municipalities - Part - IX Ac)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societiesd)Tribunals - Part - XCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for UPSC 2025 is part of UPSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UPSC exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?a)The Panchayats - Part - IXb)The Municipalities - Part - IX Ac)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societiesd)Tribunals - Part - XCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UPSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?a)The Panchayats - Part - IXb)The Municipalities - Part - IX Ac)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societiesd)Tribunals - Part - XCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?a)The Panchayats - Part - IXb)The Municipalities - Part - IX Ac)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societiesd)Tribunals - Part - XCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for UPSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?a)The Panchayats - Part - IXb)The Municipalities - Part - IX Ac)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societiesd)Tribunals - Part - XCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?a)The Panchayats - Part - IXb)The Municipalities - Part - IX Ac)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societiesd)Tribunals - Part - XCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?a)The Panchayats - Part - IXb)The Municipalities - Part - IX Ac)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societiesd)Tribunals - Part - XCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?a)The Panchayats - Part - IXb)The Municipalities - Part - IX Ac)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societiesd)Tribunals - Part - XCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following is NOT correctly matched as per the Constitution of India?a)The Panchayats - Part - IXb)The Municipalities - Part - IX Ac)The Cooperative - Part - IX B Societiesd)Tribunals - Part - XCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice UPSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























