SSC Exam > SSC Questions > The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for ...
Start Learning for Free
The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -
- a)Liquidity index
- b)Shrinkage ratio
- c)Consistency index
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)...
Liquidity index 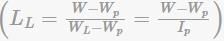
View all questions of this test
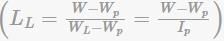
Shrinkage ratio- It is defined as the ratio of a given volume change in a soil expressed as a percentage of dry volume to the corresponding change in water content above the shrinkage limit. 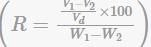
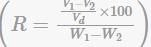
Consistency index 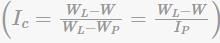
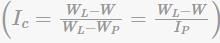
Most Upvoted Answer
The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)...
Explanation:
The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called the liquidity index. The liquidity index is an important parameter that is used to classify soils based on their consistency and behavior.
Liquidity Index:
The liquidity index (LI) is defined as the ratio of the difference between the liquid limit (LL) and the plastic limit (PL) to the plasticity index (PI) of the soil mass.
Liquidity Index (LI) = (LL - PL) / PI
Significance of Liquidity Index:
The liquidity index provides valuable information about the behavior and consistency of the soil. It helps in determining the state of the soil, whether it is in a liquid, plastic, or solid state.
The liquidity index can be used to classify soils into different categories based on their consistency and behavior. These categories include:
- Very stiff soil (LI > 1)
- Stiff soil (0.7 < li="" ≤="" />
- Plastic soil (0.3 < li="" ≤="" />
- Semi-plastic soil (0.1 < li="" ≤="" />
- Slightly plastic soil (0 < li="" ≤="" />
- Non-plastic soil (LI = 0)
Other Options:
Option 'A': Liquidity index is the correct answer and not the ratio of liquid to plasticity index.
Option 'B': Shrinkage ratio is the ratio of the change in volume of the soil mass to the initial volume of the soil mass. It is not related to the ratio of liquid to plasticity index.
Option 'C': Consistency index is a measure of the stiffness or hardness of a soil. It is not related to the ratio of liquid to plasticity index.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D': None of the above.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Similar SSC Doubts
The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)Liquidity indexb)Shrinkage ratioc)Consistency indexd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)Liquidity indexb)Shrinkage ratioc)Consistency indexd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)Liquidity indexb)Shrinkage ratioc)Consistency indexd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)Liquidity indexb)Shrinkage ratioc)Consistency indexd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)Liquidity indexb)Shrinkage ratioc)Consistency indexd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for SSC 2024 is part of SSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the SSC exam syllabus. Information about The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)Liquidity indexb)Shrinkage ratioc)Consistency indexd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for SSC 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)Liquidity indexb)Shrinkage ratioc)Consistency indexd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)Liquidity indexb)Shrinkage ratioc)Consistency indexd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for SSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for SSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)Liquidity indexb)Shrinkage ratioc)Consistency indexd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)Liquidity indexb)Shrinkage ratioc)Consistency indexd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)Liquidity indexb)Shrinkage ratioc)Consistency indexd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)Liquidity indexb)Shrinkage ratioc)Consistency indexd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The ratio of liquid to plasticity index for a soil mass is called -a)Liquidity indexb)Shrinkage ratioc)Consistency indexd)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice SSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for SSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















