NEET Exam > NEET Questions > In situ and ex situ conservation?
Start Learning for Free
In situ and ex situ conservation?
Most Upvoted Answer
In situ and ex situ conservation?
In Situ and Ex Situ Conservation
In conservation biology, there are two main approaches to protect endangered species: in situ conservation and ex situ conservation.
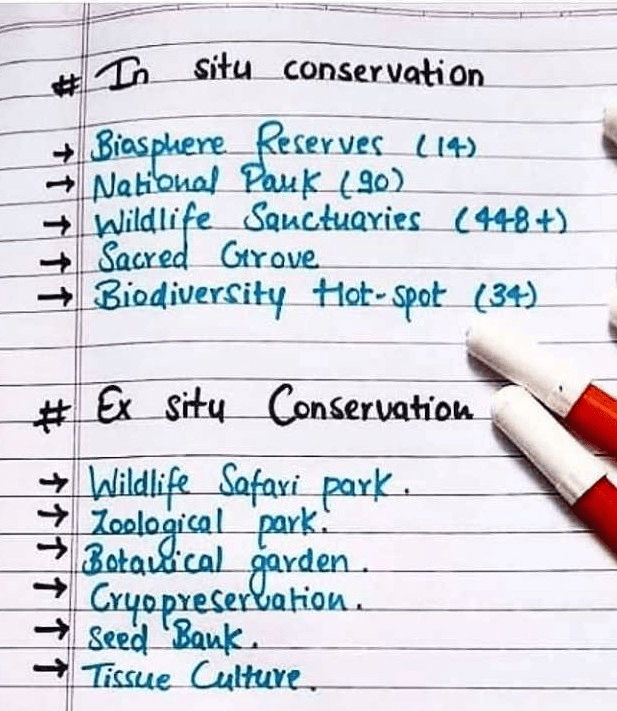
In Situ Conservation
In situ conservation refers to the protection of endangered species within their natural habitats. It involves maintaining the natural ecosystem and the species that live within it. Some methods of in situ conservation include:
- Protected areas: Setting up protected areas such as national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves to safeguard the natural habitats and the species that live within them.
- Habitat restoration: Restoring degraded habitats to their natural state to provide better living conditions for the endangered species.
- Sustainable use: Promoting the sustainable use of natural resources in a way that does not harm the environment and the species that depend on it.
- Community participation: Encouraging local communities to participate in conservation efforts and providing them with incentives to protect the environment.
In situ conservation is considered the best method for preserving biodiversity because it allows species to evolve and adapt to changing environmental conditions. It also helps to maintain the ecological balance of the natural ecosystem.
Ex Situ Conservation
Ex situ conservation refers to the protection of endangered species outside of their natural habitats. It involves removing the species from their natural environment and placing them in a controlled environment such as a zoo, botanical garden, or wildlife sanctuary. Some methods of ex situ conservation include:
- Captive breeding: Breeding endangered species in captivity to increase their population and prevent their extinction.
- Seed banks: Collecting and storing seeds of endangered plant species in seed banks to preserve their genetic diversity.
- Cryopreservation: Freezing sperm, embryos or tissue samples of endangered species for future use.
- Reintroduction: Reintroducing endangered species back into their natural habitats after they have been bred or conserved in other ways.
Ex situ conservation is useful for species that are critically endangered and cannot survive in their natural habitats due to habitat destruction, fragmentation or other factors. However, it is not a long-term solution as it does not address the root causes of the species' decline.
Conclusion
In situ and ex situ conservation are both important methods of preserving biodiversity. Ideally, both methods should be used together to ensure the long-term survival of endangered species.
In conservation biology, there are two main approaches to protect endangered species: in situ conservation and ex situ conservation.
In Situ Conservation
In situ conservation refers to the protection of endangered species within their natural habitats. It involves maintaining the natural ecosystem and the species that live within it. Some methods of in situ conservation include:
- Protected areas: Setting up protected areas such as national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and biosphere reserves to safeguard the natural habitats and the species that live within them.
- Habitat restoration: Restoring degraded habitats to their natural state to provide better living conditions for the endangered species.
- Sustainable use: Promoting the sustainable use of natural resources in a way that does not harm the environment and the species that depend on it.
- Community participation: Encouraging local communities to participate in conservation efforts and providing them with incentives to protect the environment.
In situ conservation is considered the best method for preserving biodiversity because it allows species to evolve and adapt to changing environmental conditions. It also helps to maintain the ecological balance of the natural ecosystem.
Ex Situ Conservation
Ex situ conservation refers to the protection of endangered species outside of their natural habitats. It involves removing the species from their natural environment and placing them in a controlled environment such as a zoo, botanical garden, or wildlife sanctuary. Some methods of ex situ conservation include:
- Captive breeding: Breeding endangered species in captivity to increase their population and prevent their extinction.
- Seed banks: Collecting and storing seeds of endangered plant species in seed banks to preserve their genetic diversity.
- Cryopreservation: Freezing sperm, embryos or tissue samples of endangered species for future use.
- Reintroduction: Reintroducing endangered species back into their natural habitats after they have been bred or conserved in other ways.
Ex situ conservation is useful for species that are critically endangered and cannot survive in their natural habitats due to habitat destruction, fragmentation or other factors. However, it is not a long-term solution as it does not address the root causes of the species' decline.
Conclusion
In situ and ex situ conservation are both important methods of preserving biodiversity. Ideally, both methods should be used together to ensure the long-term survival of endangered species.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
In situ and ex situ conservation?
Question Description
In situ and ex situ conservation? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about In situ and ex situ conservation? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In situ and ex situ conservation?.
In situ and ex situ conservation? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about In situ and ex situ conservation? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In situ and ex situ conservation?.
Solutions for In situ and ex situ conservation? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In situ and ex situ conservation? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In situ and ex situ conservation?, a detailed solution for In situ and ex situ conservation? has been provided alongside types of In situ and ex situ conservation? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In situ and ex situ conservation? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.