NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Functional group in organic chemistry /\?
Start Learning for Free
Functional group in organic chemistry /\?
Most Upvoted Answer
Functional group in organic chemistry /\?
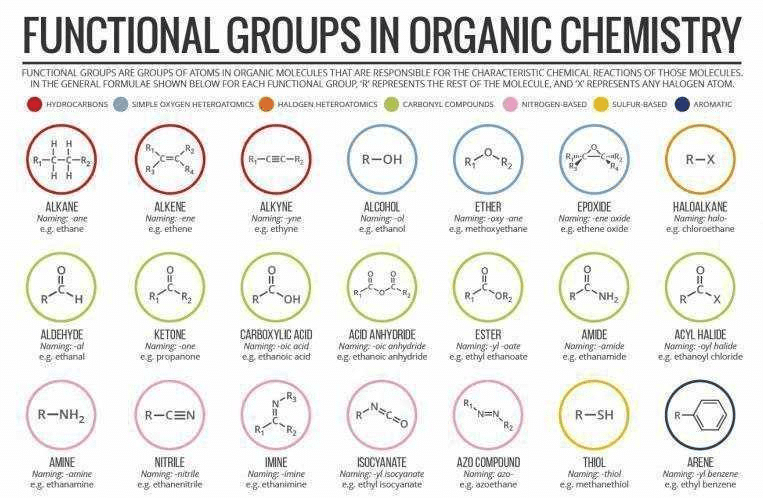
Functional Group in Organic Chemistry
Definition:
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a specific group of atoms within a molecule that determines its chemical properties and reactivity. It is responsible for the characteristic reactions and physical properties of organic compounds. Functional groups are the reactive centers in organic molecules, and they play a crucial role in the formation of new chemical bonds and the transformation of organic compounds.
Importance:
Functional groups provide a way to classify and categorize organic compounds based on their chemical behavior and properties. They allow chemists to predict the reactivity and behavior of organic molecules, which is essential for designing and synthesizing new compounds for various applications, such as pharmaceuticals, materials, and agrochemicals.
Common Functional Groups:
There are numerous functional groups in organic chemistry, each with its specific set of properties and reactions. Some common functional groups include:
1. Alcohols (-OH): Alcohols are characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom. They are polar compounds and can participate in hydrogen bonding, making them soluble in water. Alcohols undergo various reactions, such as oxidation, dehydration, and esterification.
2. Aldehydes (-CHO): Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a carbon atom and a hydrogen atom. They are highly reactive and easily undergo oxidation and nucleophilic addition reactions.
3. Ketones (R-C=O-R'): Ketones have a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two carbon atoms. They are important intermediates in organic synthesis and exhibit unique reactivity due to the presence of the carbonyl group.
4. Carboxylic acids (-COOH): Carboxylic acids consist of a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the same carbon atom. They are acidic in nature and can undergo various reactions, including esterification and decarboxylation.
5. Amines (-NH2): Amines contain a nitrogen atom bonded to one or more carbon atoms. They can be primary, secondary, or tertiary, depending on the number of carbon groups attached to the nitrogen atom. Amines participate in reactions such as nucleophilic substitution and can act as bases.
6. Ethers (R-O-R'): Ethers consist of an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms. They have low reactivity and are commonly used as solvents and as protecting groups in organic synthesis.
Conclusion:
Functional groups play a fundamental role in organic chemistry by determining the reactivity and properties of organic compounds. They provide a way to classify and predict the behavior of organic molecules, making them essential for understanding and designing new chemical reactions and compounds.
Definition:
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a specific group of atoms within a molecule that determines its chemical properties and reactivity. It is responsible for the characteristic reactions and physical properties of organic compounds. Functional groups are the reactive centers in organic molecules, and they play a crucial role in the formation of new chemical bonds and the transformation of organic compounds.
Importance:
Functional groups provide a way to classify and categorize organic compounds based on their chemical behavior and properties. They allow chemists to predict the reactivity and behavior of organic molecules, which is essential for designing and synthesizing new compounds for various applications, such as pharmaceuticals, materials, and agrochemicals.
Common Functional Groups:
There are numerous functional groups in organic chemistry, each with its specific set of properties and reactions. Some common functional groups include:
1. Alcohols (-OH): Alcohols are characterized by the presence of a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom. They are polar compounds and can participate in hydrogen bonding, making them soluble in water. Alcohols undergo various reactions, such as oxidation, dehydration, and esterification.
2. Aldehydes (-CHO): Aldehydes contain a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a carbon atom and a hydrogen atom. They are highly reactive and easily undergo oxidation and nucleophilic addition reactions.
3. Ketones (R-C=O-R'): Ketones have a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to two carbon atoms. They are important intermediates in organic synthesis and exhibit unique reactivity due to the presence of the carbonyl group.
4. Carboxylic acids (-COOH): Carboxylic acids consist of a carbonyl group (C=O) and a hydroxyl group (-OH) bonded to the same carbon atom. They are acidic in nature and can undergo various reactions, including esterification and decarboxylation.
5. Amines (-NH2): Amines contain a nitrogen atom bonded to one or more carbon atoms. They can be primary, secondary, or tertiary, depending on the number of carbon groups attached to the nitrogen atom. Amines participate in reactions such as nucleophilic substitution and can act as bases.
6. Ethers (R-O-R'): Ethers consist of an oxygen atom bonded to two carbon atoms. They have low reactivity and are commonly used as solvents and as protecting groups in organic synthesis.
Conclusion:
Functional groups play a fundamental role in organic chemistry by determining the reactivity and properties of organic compounds. They provide a way to classify and predict the behavior of organic molecules, making them essential for understanding and designing new chemical reactions and compounds.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Functional group in organic chemistry /\?
Question Description
Functional group in organic chemistry /\? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Functional group in organic chemistry /\? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Functional group in organic chemistry /\?.
Functional group in organic chemistry /\? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Functional group in organic chemistry /\? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Functional group in organic chemistry /\?.
Solutions for Functional group in organic chemistry /\? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Functional group in organic chemistry /\? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Functional group in organic chemistry /\?, a detailed solution for Functional group in organic chemistry /\? has been provided alongside types of Functional group in organic chemistry /\? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Functional group in organic chemistry /\? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.