GATE Exam > GATE Questions > A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with th...
Start Learning for Free
A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?
(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)
- a)16.7 m/sec
- b)15.8 m/sec
- c)15.0 m/sec
- d)14.1 m/sec
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18...
For terminal velocity total weight of man and parachute will be balanced by drag force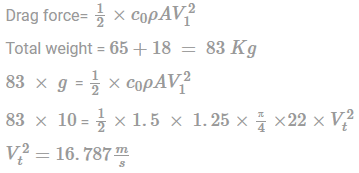
View all questions of this test
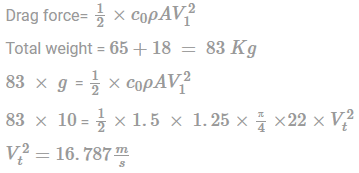
So, terminal velocity = 16.78 m/s
Most Upvoted Answer
A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18...
Understanding Terminal Velocity
Terminal velocity is the constant speed an object eventually reaches when falling through a fluid (in this case, air). At this speed, the gravitational force acting on the object is balanced by the drag force produced by the fluid.
Given Data
- Mass of the man, \( m = 65 \, \text{kg} \)
- Mass of the parachute, \( M = 18 \, \text{kg} \)
- Total mass, \( W = m + M = 83 \, \text{kg} \)
- Diameter of the parachute, \( D = 2 \, \text{m} \) (Radius \( r = 1 \, \text{m} \))
- Density of air, \( \rho = 0.00125 \, \text{g/cm}^3 = 1.25 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \)
- Drag coefficient, \( C_D = 1.5 \)
- Gravitational acceleration, \( g = 1000 \, \text{cm/sec}^2 = 10 \, \text{m/sec}^2 \)
Drag Force Calculation
The drag force \( F_d \) can be calculated using the formula:
\[
F_d = \frac{1}{2} C_D \rho A v^2
\]
Where:
- \( A \) is the cross-sectional area of the parachute.
The area \( A \) of a hemisphere is given by:
\[
A = \pi r^2 = \pi (1)^2 = \pi \, \text{m}^2
\]
Weight Calculation
The weight \( W \) acting downwards is:
\[
W = (m + M)g = 83 \times 10 = 830 \, \text{N}
\]
Setting Forces Equal at Terminal Velocity
At terminal velocity, the drag force equals the weight:
\[
\frac{1}{2} C_D \rho A v_t^2 = W
\]
Substituting the values:
\[
\frac{1}{2} \times 1.5 \times 1.25 \times \pi \times v_t^2 = 830
\]
Solving for \( v_t \):
1. Calculate the left side:
- \( \frac{1}{2} \times 1.5 \times 1.25 \approx 0.9375 \)
- Area \( A \approx 3.14 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Thus, \( 0.9375 \times 3.14 \approx 2.940625 \)
2. Set up the equation:
- \( 2.940625 \cdot v_t^2 = 830 \)
3. Solve for \( v_t \):
- \( v_t^2 \approx \frac{830}{2.940625} \approx 282.38 \)
- \( v_t \approx \sqrt{282.38} \approx 16.8 \, \text{m/sec} \)
Thus, the terminal velocity is approximately 16.7 m/sec, confirming option A is
Terminal velocity is the constant speed an object eventually reaches when falling through a fluid (in this case, air). At this speed, the gravitational force acting on the object is balanced by the drag force produced by the fluid.
Given Data
- Mass of the man, \( m = 65 \, \text{kg} \)
- Mass of the parachute, \( M = 18 \, \text{kg} \)
- Total mass, \( W = m + M = 83 \, \text{kg} \)
- Diameter of the parachute, \( D = 2 \, \text{m} \) (Radius \( r = 1 \, \text{m} \))
- Density of air, \( \rho = 0.00125 \, \text{g/cm}^3 = 1.25 \, \text{kg/m}^3 \)
- Drag coefficient, \( C_D = 1.5 \)
- Gravitational acceleration, \( g = 1000 \, \text{cm/sec}^2 = 10 \, \text{m/sec}^2 \)
Drag Force Calculation
The drag force \( F_d \) can be calculated using the formula:
\[
F_d = \frac{1}{2} C_D \rho A v^2
\]
Where:
- \( A \) is the cross-sectional area of the parachute.
The area \( A \) of a hemisphere is given by:
\[
A = \pi r^2 = \pi (1)^2 = \pi \, \text{m}^2
\]
Weight Calculation
The weight \( W \) acting downwards is:
\[
W = (m + M)g = 83 \times 10 = 830 \, \text{N}
\]
Setting Forces Equal at Terminal Velocity
At terminal velocity, the drag force equals the weight:
\[
\frac{1}{2} C_D \rho A v_t^2 = W
\]
Substituting the values:
\[
\frac{1}{2} \times 1.5 \times 1.25 \times \pi \times v_t^2 = 830
\]
Solving for \( v_t \):
1. Calculate the left side:
- \( \frac{1}{2} \times 1.5 \times 1.25 \approx 0.9375 \)
- Area \( A \approx 3.14 \, \text{m}^2 \)
- Thus, \( 0.9375 \times 3.14 \approx 2.940625 \)
2. Set up the equation:
- \( 2.940625 \cdot v_t^2 = 830 \)
3. Solve for \( v_t \):
- \( v_t^2 \approx \frac{830}{2.940625} \approx 282.38 \)
- \( v_t \approx \sqrt{282.38} \approx 16.8 \, \text{m/sec} \)
Thus, the terminal velocity is approximately 16.7 m/sec, confirming option A is

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)a)16.7 m/secb)15.8 m/secc)15.0 m/secd)14.1 m/secCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)a)16.7 m/secb)15.8 m/secc)15.0 m/secd)14.1 m/secCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)a)16.7 m/secb)15.8 m/secc)15.0 m/secd)14.1 m/secCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)a)16.7 m/secb)15.8 m/secc)15.0 m/secd)14.1 m/secCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)a)16.7 m/secb)15.8 m/secc)15.0 m/secd)14.1 m/secCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2024 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)a)16.7 m/secb)15.8 m/secc)15.0 m/secd)14.1 m/secCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)a)16.7 m/secb)15.8 m/secc)15.0 m/secd)14.1 m/secCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)a)16.7 m/secb)15.8 m/secc)15.0 m/secd)14.1 m/secCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for GATE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GATE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)a)16.7 m/secb)15.8 m/secc)15.0 m/secd)14.1 m/secCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)a)16.7 m/secb)15.8 m/secc)15.0 m/secd)14.1 m/secCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)a)16.7 m/secb)15.8 m/secc)15.0 m/secd)14.1 m/secCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)a)16.7 m/secb)15.8 m/secc)15.0 m/secd)14.1 m/secCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A man, 65 kg, descends to the ground with the help of a parachute, 18 kg. The parachute is hemispherical in shape, 2m diameter. Density of air can be taken as 0.00125 g/cm3 and its kinematic viscosity as 0.15 stoke. What is the terminal velocity of the parachute?(Take CD = 1.5 and g = 1000 cm/sec2)a)16.7 m/secb)15.8 m/secc)15.0 m/secd)14.1 m/secCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice GATE tests.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
















