NEET Exam > NEET Questions > A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic c...
Start Learning for Free
A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:
- a)Sodium hydroxide
- b)Sodium sulphate
- c)Calcium chloride
- d)Sodium bicarbonate
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separatio...
Separation of Phenol (A) and Aromatic Carboxylic Acid (B) using Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
Phenol (A) and aromatic carboxylic acid (B) can be separated easily by using a solution of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3). This method is based on the difference in their acid-base properties.
1. Acid-Base Properties of Phenol and Aromatic Carboxylic Acid
- Phenol (A): Phenol is a weak acid and does not readily dissociate in water. It does not react with sodium bicarbonate.
- Aromatic Carboxylic Acid (B): Aromatic carboxylic acids are stronger acids than phenol. They readily dissociate in water to form carboxylate ions, which can react with sodium bicarbonate.
2. Reaction between Aromatic Carboxylic Acid and Sodium Bicarbonate
When an aromatic carboxylic acid (B) is treated with a solution of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), the following reaction occurs:
RCOOH + NaHCO3 → RCOONa + H2O + CO2
The carboxylic acid (B) reacts with sodium bicarbonate to form a carboxylate salt (RCOONa), water (H2O), and carbon dioxide gas (CO2). This reaction is known as an acid-base reaction.
3. Separation Procedure
The separation of phenol (A) and aromatic carboxylic acid (B) using sodium bicarbonate can be carried out as follows:
Step 1: Prepare a solution of sodium bicarbonate by dissolving it in water.
Step 2: Add the mixture of phenol (A) and aromatic carboxylic acid (B) to the sodium bicarbonate solution.
Step 3: Stir the mixture gently.
Step 4: Observe the formation of effervescence (bubbling) due to the evolution of carbon dioxide gas. This effervescence indicates the presence of aromatic carboxylic acid (B).
Step 5: Separate the two layers formed. The top layer will contain phenol (A), and the bottom layer will contain the sodium carboxylate salt (RCOONa) of the aromatic carboxylic acid (B).
Step 6: Acidify the bottom layer by adding dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) to regenerate the aromatic carboxylic acid (B). The carboxylic acid will separate as an oily layer.
Step 7: Finally, the phenol (A) can be recovered from the top layer by extraction with an organic solvent.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the separation of a mixture containing a lighter phenol (A) and an aromatic carboxylic acid (B) can be achieved by using a solution of sodium bicarbonate. The difference in their acid-base properties allows the aromatic carboxylic acid to react with sodium bicarbonate, forming a carboxylate salt and liberating carbon dioxide gas. This reaction facilitates the separation of the two components.
Phenol (A) and aromatic carboxylic acid (B) can be separated easily by using a solution of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3). This method is based on the difference in their acid-base properties.
1. Acid-Base Properties of Phenol and Aromatic Carboxylic Acid
- Phenol (A): Phenol is a weak acid and does not readily dissociate in water. It does not react with sodium bicarbonate.
- Aromatic Carboxylic Acid (B): Aromatic carboxylic acids are stronger acids than phenol. They readily dissociate in water to form carboxylate ions, which can react with sodium bicarbonate.
2. Reaction between Aromatic Carboxylic Acid and Sodium Bicarbonate
When an aromatic carboxylic acid (B) is treated with a solution of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3), the following reaction occurs:
RCOOH + NaHCO3 → RCOONa + H2O + CO2
The carboxylic acid (B) reacts with sodium bicarbonate to form a carboxylate salt (RCOONa), water (H2O), and carbon dioxide gas (CO2). This reaction is known as an acid-base reaction.
3. Separation Procedure
The separation of phenol (A) and aromatic carboxylic acid (B) using sodium bicarbonate can be carried out as follows:
Step 1: Prepare a solution of sodium bicarbonate by dissolving it in water.
Step 2: Add the mixture of phenol (A) and aromatic carboxylic acid (B) to the sodium bicarbonate solution.
Step 3: Stir the mixture gently.
Step 4: Observe the formation of effervescence (bubbling) due to the evolution of carbon dioxide gas. This effervescence indicates the presence of aromatic carboxylic acid (B).
Step 5: Separate the two layers formed. The top layer will contain phenol (A), and the bottom layer will contain the sodium carboxylate salt (RCOONa) of the aromatic carboxylic acid (B).
Step 6: Acidify the bottom layer by adding dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) to regenerate the aromatic carboxylic acid (B). The carboxylic acid will separate as an oily layer.
Step 7: Finally, the phenol (A) can be recovered from the top layer by extraction with an organic solvent.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the separation of a mixture containing a lighter phenol (A) and an aromatic carboxylic acid (B) can be achieved by using a solution of sodium bicarbonate. The difference in their acid-base properties allows the aromatic carboxylic acid to react with sodium bicarbonate, forming a carboxylate salt and liberating carbon dioxide gas. This reaction facilitates the separation of the two components.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separatio...
Carboxylic acids dissolve in NaHCO 3 but phenols do not.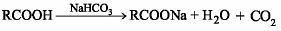
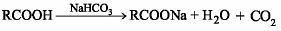
by evolving CO2 gas.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:a)Sodium hydroxideb)Sodium sulphatec)Calcium chlorided)Sodium bicarbonateCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:a)Sodium hydroxideb)Sodium sulphatec)Calcium chlorided)Sodium bicarbonateCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:a)Sodium hydroxideb)Sodium sulphatec)Calcium chlorided)Sodium bicarbonateCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:a)Sodium hydroxideb)Sodium sulphatec)Calcium chlorided)Sodium bicarbonateCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:a)Sodium hydroxideb)Sodium sulphatec)Calcium chlorided)Sodium bicarbonateCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:a)Sodium hydroxideb)Sodium sulphatec)Calcium chlorided)Sodium bicarbonateCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:a)Sodium hydroxideb)Sodium sulphatec)Calcium chlorided)Sodium bicarbonateCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:a)Sodium hydroxideb)Sodium sulphatec)Calcium chlorided)Sodium bicarbonateCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:a)Sodium hydroxideb)Sodium sulphatec)Calcium chlorided)Sodium bicarbonateCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:a)Sodium hydroxideb)Sodium sulphatec)Calcium chlorided)Sodium bicarbonateCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:a)Sodium hydroxideb)Sodium sulphatec)Calcium chlorided)Sodium bicarbonateCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:a)Sodium hydroxideb)Sodium sulphatec)Calcium chlorided)Sodium bicarbonateCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A is a lighter phenol and B is an aromatic carboxylic acid. Separation of a mixture of A and B can be carried out easily by using a solution of:a)Sodium hydroxideb)Sodium sulphatec)Calcium chlorided)Sodium bicarbonateCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























