NEET Exam > NEET Questions > can anybody explain me about difference b/w t...
Start Learning for Free
can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation
Most Upvoted Answer
can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transform...
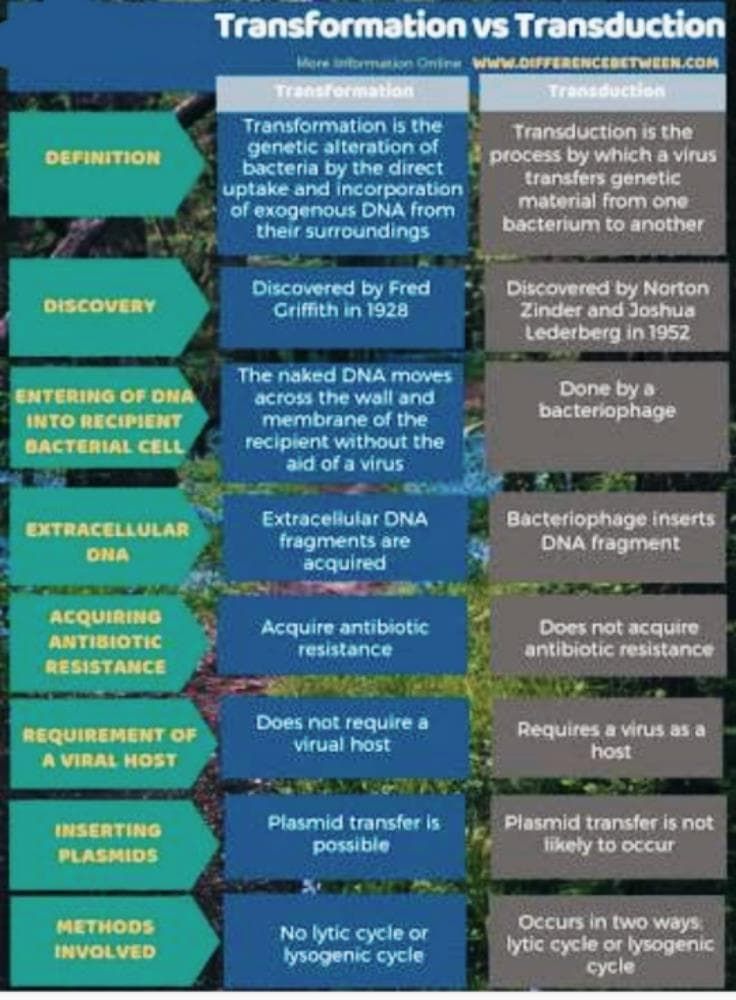
Community Answer
can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transform...
Transduction and Transformation
Transduction and transformation are two different mechanisms used by bacteria to acquire new genetic material from their environment. Here are the differences between the two processes.
Transduction
Transduction is a process in which bacterial DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a bacteriophage, a virus that infects bacteria. There are two types of transduction:
1. Generalized transduction: In generalized transduction, bacterial DNA is mistakenly packaged into the phage during the lytic cycle. When the phage infects a new bacterium, it injects the packaged DNA into the host cell. The transferred DNA can then integrate into the recipient cell's genome by recombination.
2. Specialized transduction: In specialized transduction, the phage integrates its DNA into the bacterial chromosome at a specific site. When the phage undergoes the lysogenic cycle, it carries with it a small piece of bacterial DNA adjacent to the integration site. When the phage excises itself from the bacterial chromosome, it may take some of the bacterial DNA with it. The phage then infects a new bacterium and transfers the bacterial DNA to the recipient cell.
Transformation
Transformation is a process in which bacteria take up DNA from their environment and incorporate it into their genome. This process occurs naturally in some bacterial species and can also be induced artificially in the laboratory. There are two types of transformation:
1. Natural transformation: In natural transformation, bacteria take up DNA from their environment, such as dead bacterial cells or free DNA released by other organisms. The DNA is then integrated into the recipient cell's genome by recombination.
2. Artificial transformation: In artificial transformation, bacteria are treated with a chemical or an electrical pulse that makes their cell membranes more permeable, allowing foreign DNA to enter the cell. The foreign DNA is then incorporated into the recipient cell's genome by recombination.
Conclusion
In summary, transduction is a process in which bacterial DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus, while transformation is a process in which bacteria take up DNA from their environment and incorporate it into their genome. Both processes can lead to the acquisition of new genetic material that can confer new traits, such as antibiotic resistance.
Transduction and transformation are two different mechanisms used by bacteria to acquire new genetic material from their environment. Here are the differences between the two processes.
Transduction
Transduction is a process in which bacterial DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a bacteriophage, a virus that infects bacteria. There are two types of transduction:
1. Generalized transduction: In generalized transduction, bacterial DNA is mistakenly packaged into the phage during the lytic cycle. When the phage infects a new bacterium, it injects the packaged DNA into the host cell. The transferred DNA can then integrate into the recipient cell's genome by recombination.
2. Specialized transduction: In specialized transduction, the phage integrates its DNA into the bacterial chromosome at a specific site. When the phage undergoes the lysogenic cycle, it carries with it a small piece of bacterial DNA adjacent to the integration site. When the phage excises itself from the bacterial chromosome, it may take some of the bacterial DNA with it. The phage then infects a new bacterium and transfers the bacterial DNA to the recipient cell.
Transformation
Transformation is a process in which bacteria take up DNA from their environment and incorporate it into their genome. This process occurs naturally in some bacterial species and can also be induced artificially in the laboratory. There are two types of transformation:
1. Natural transformation: In natural transformation, bacteria take up DNA from their environment, such as dead bacterial cells or free DNA released by other organisms. The DNA is then integrated into the recipient cell's genome by recombination.
2. Artificial transformation: In artificial transformation, bacteria are treated with a chemical or an electrical pulse that makes their cell membranes more permeable, allowing foreign DNA to enter the cell. The foreign DNA is then incorporated into the recipient cell's genome by recombination.
Conclusion
In summary, transduction is a process in which bacterial DNA is transferred from one bacterium to another by a virus, while transformation is a process in which bacteria take up DNA from their environment and incorporate it into their genome. Both processes can lead to the acquisition of new genetic material that can confer new traits, such as antibiotic resistance.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation
Question Description
can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation .
can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation .
Solutions for can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation , a detailed solution for can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation has been provided alongside types of can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice can anybody explain me about difference b/w transduction and transformation tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























