Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Len...
Start Learning for Free
The resistivity of a wire depends on its
- a)Length
- b)Cross-sectional area
- c)Dimensions
- d)Material
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional area...
Understanding Resistivity
Resistivity is a fundamental property of materials that quantifies how strongly they resist the flow of electric current. The resistivity of a wire is primarily determined by its material composition rather than its dimensions or shape.
Key Factors Influencing Resistivity
- Material Composition:
- The resistivity of a wire is intrinsically linked to the type of material it is made from. Different materials have unique atomic structures and electron mobility, which influence how easily electrons can flow through them.
- For example, metals like copper and aluminum have low resistivity, making them excellent conductors, while materials like rubber or glass have high resistivity, classifying them as insulators.
- Temperature Dependence:
- The resistivity of materials can also change with temperature. For most metals, resistivity increases with temperature due to increased atomic vibrations, which hinder the flow of electrons.
- Impurities and Alloying:
- The presence of impurities or the formation of alloys can also affect resistivity. Adding certain elements can either increase or decrease the resistivity of a metal, depending on the nature of the added material.
Dimensions and Resistivity
- Length and Cross-sectional Area:
- While the length and cross-sectional area of a wire affect its overall resistance (R = ρL/A), they do not influence its resistivity (ρ). The resistivity remains constant for a given material, regardless of the wire's size.
In summary, the resistivity of a wire is fundamentally determined by the material from which it is made, making option 'D' the correct choice. Understanding this concept is crucial for applications in electrical engineering and material science.
Resistivity is a fundamental property of materials that quantifies how strongly they resist the flow of electric current. The resistivity of a wire is primarily determined by its material composition rather than its dimensions or shape.
Key Factors Influencing Resistivity
- Material Composition:
- The resistivity of a wire is intrinsically linked to the type of material it is made from. Different materials have unique atomic structures and electron mobility, which influence how easily electrons can flow through them.
- For example, metals like copper and aluminum have low resistivity, making them excellent conductors, while materials like rubber or glass have high resistivity, classifying them as insulators.
- Temperature Dependence:
- The resistivity of materials can also change with temperature. For most metals, resistivity increases with temperature due to increased atomic vibrations, which hinder the flow of electrons.
- Impurities and Alloying:
- The presence of impurities or the formation of alloys can also affect resistivity. Adding certain elements can either increase or decrease the resistivity of a metal, depending on the nature of the added material.
Dimensions and Resistivity
- Length and Cross-sectional Area:
- While the length and cross-sectional area of a wire affect its overall resistance (R = ρL/A), they do not influence its resistivity (ρ). The resistivity remains constant for a given material, regardless of the wire's size.
In summary, the resistivity of a wire is fundamentally determined by the material from which it is made, making option 'D' the correct choice. Understanding this concept is crucial for applications in electrical engineering and material science.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional area...
From Resistance,
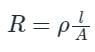
Where R = resistance, l = length, A = area of cross-section and ρ = resistivity
If l = 1 m and A = 1 m2, then
R = ρ i.e.
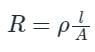
Where R = resistance, l = length, A = area of cross-section and ρ = resistivity
If l = 1 m and A = 1 m2, then
R = ρ i.e.
- Resistivity is numerically equal to the resistance of a substance having unit area of cross-section and unit length.
- Resistivity is the intrinsic property of the substance. It is independent of shape and size of the body i.e. on length and area. Hence, option 1 and 2 is incorrect.
- Formula of resistivity is
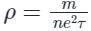
Where, m = mass of electron, n = Number of electron per unit volume of the conductor, τ = relaxation time. - Therefore, the resistivity of a wire depends on its material (n)
- For different substances their resistivity is also different as ‘n’ will be different.
- Resistivity depends on the temperature.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Question Description
The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional areac)Dimensionsd)MaterialCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional areac)Dimensionsd)MaterialCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional areac)Dimensionsd)MaterialCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional areac)Dimensionsd)MaterialCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional areac)Dimensionsd)MaterialCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional areac)Dimensionsd)MaterialCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional areac)Dimensionsd)MaterialCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional areac)Dimensionsd)MaterialCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional areac)Dimensionsd)MaterialCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional areac)Dimensionsd)MaterialCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional areac)Dimensionsd)MaterialCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The resistivity of a wire depends on itsa)Lengthb)Cross-sectional areac)Dimensionsd)MaterialCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























