UPSC Exam > UPSC Questions > The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputra...
Start Learning for Free
The capital of Kashi was ______.
- a)Pataliputra
- b)Varanasi
- c)Taxila
- d)Kaushambi
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)Kaush...
Introduction:
Kashi, also known as Varanasi, is a city located in the northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It holds great historical and cultural significance and is considered one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. Kashi has been the capital of several ancient kingdoms throughout history.
The Capital of Kashi:
The capital of Kashi was Varanasi.
Explanation:
- Kashi, also known as Varanasi, has a rich history that dates back thousands of years.
- It has been an important center of trade, spirituality, and education since ancient times.
- Kashi has witnessed the rise and fall of various kingdoms and dynasties throughout its history.
- However, it is important to note that Kashi itself was never the capital of a major kingdom or empire.
- The city of Varanasi, also known as Kashi, served as a cultural and religious center rather than a political capital.
- The ancient city of Pataliputra, located in present-day Patna, Bihar, was the capital of several important empires, including the Maurya and Gupta empires.
- Taxila, located in present-day Pakistan, was a renowned center of learning and a capital during the time of the Gandhara kingdom.
- Kaushambi, located near present-day Allahabad, served as the capital of the Vatsa kingdom during ancient times.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Kashi, also known as Varanasi, was never the capital of a major kingdom or empire. It held great cultural and religious significance and served as a center of trade, spirituality, and education. Other cities such as Pataliputra, Taxila, and Kaushambi served as capitals during different periods in ancient Indian history.
Kashi, also known as Varanasi, is a city located in the northern Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It holds great historical and cultural significance and is considered one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. Kashi has been the capital of several ancient kingdoms throughout history.
The Capital of Kashi:
The capital of Kashi was Varanasi.
Explanation:
- Kashi, also known as Varanasi, has a rich history that dates back thousands of years.
- It has been an important center of trade, spirituality, and education since ancient times.
- Kashi has witnessed the rise and fall of various kingdoms and dynasties throughout its history.
- However, it is important to note that Kashi itself was never the capital of a major kingdom or empire.
- The city of Varanasi, also known as Kashi, served as a cultural and religious center rather than a political capital.
- The ancient city of Pataliputra, located in present-day Patna, Bihar, was the capital of several important empires, including the Maurya and Gupta empires.
- Taxila, located in present-day Pakistan, was a renowned center of learning and a capital during the time of the Gandhara kingdom.
- Kaushambi, located near present-day Allahabad, served as the capital of the Vatsa kingdom during ancient times.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Kashi, also known as Varanasi, was never the capital of a major kingdom or empire. It held great cultural and religious significance and served as a center of trade, spirituality, and education. Other cities such as Pataliputra, Taxila, and Kaushambi served as capitals during different periods in ancient Indian history.
Community Answer
The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)Kaush...
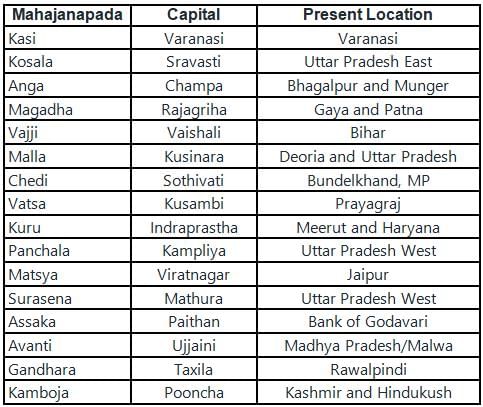
- The capital of Kashi (Mahajanapada) was Varanasi.
- This city got its name from rivers Varuna and Asi as cited in the Matsya Purana.
- Kingdoms that rose to fame from the 6th Century BC onward were called Mahajanapdas.
- The Mahajanapadas signify the tribes that came together to form different groups and later gave rise to a permanent area of settlements called ‘states’ or ‘Janapadas.’
Important Points


|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Similar UPSC Doubts
The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)KaushambiCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)KaushambiCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for UPSC 2025 is part of UPSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UPSC exam syllabus. Information about The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)KaushambiCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UPSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)KaushambiCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)KaushambiCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for UPSC 2025 is part of UPSC preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UPSC exam syllabus. Information about The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)KaushambiCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UPSC 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)KaushambiCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)KaushambiCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for UPSC.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UPSC Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)KaushambiCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)KaushambiCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)KaushambiCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)KaushambiCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The capital of Kashi was ______.a)Pataliputrab)Varanasic)Taxilad)KaushambiCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice UPSC tests.

|
Explore Courses for UPSC exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























