NEET Exam > NEET Questions > The epithelial cells found in taste buds are...
Start Learning for Free
The epithelial cells found in taste buds are called
- a)glandular epithelium cells
- b)pigmented epithelial cells
- c)neuroepithelial cells
- d)absorptive epithelial cells
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithe...
The correct answer is option 'C': neuroepithelial cells.
Explanation:
1. Introduction to taste buds:
Taste buds are specialized sensory organs located on the tongue and other parts of the oral cavity that help in the perception of taste. They play a crucial role in detecting different flavors such as sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami.
2. Structure of taste buds:
Taste buds are composed of several types of cells, including supporting cells, basal cells, and the main sensory cells called neuroepithelial cells or taste receptor cells. These cells are arranged in clusters and are embedded within papillae, which are small bumps on the tongue and other areas of the oral cavity.
3. Neuroepithelial cells:
Neuroepithelial cells are the primary cells found in taste buds. They are specialized epithelial cells that have the ability to transmit nerve signals to the brain, allowing us to perceive different tastes. These cells have long microvilli called taste hairs or taste receptors that project into the taste pore, which is a small opening on the surface of the taste bud.
4. Function of neuroepithelial cells:
Neuroepithelial cells are responsible for detecting taste molecules present in food or beverages. When these molecules come into contact with the taste hairs, they bind to specific receptors on the surface of the neuroepithelial cells, triggering a series of biochemical reactions. These reactions generate electrical signals that are transmitted to the brain through sensory nerves, ultimately resulting in the perception of taste.
5. Other cells in taste buds:
- Supporting cells: These cells surround and provide structural support to the neuroepithelial cells. They also help in the maintenance and regeneration of taste buds.
- Basal cells: Basal cells are undifferentiated cells located at the base of taste buds. They can divide and differentiate into new neuroepithelial cells, ensuring the continuous turnover and replacement of taste bud cells.
Conclusion:
The epithelial cells found in taste buds are called neuroepithelial cells. These specialized cells are responsible for detecting taste molecules and transmitting signals to the brain, allowing us to perceive different tastes. Supporting cells and basal cells are also present within taste buds and play important roles in their structure and function.
Explanation:
1. Introduction to taste buds:
Taste buds are specialized sensory organs located on the tongue and other parts of the oral cavity that help in the perception of taste. They play a crucial role in detecting different flavors such as sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami.
2. Structure of taste buds:
Taste buds are composed of several types of cells, including supporting cells, basal cells, and the main sensory cells called neuroepithelial cells or taste receptor cells. These cells are arranged in clusters and are embedded within papillae, which are small bumps on the tongue and other areas of the oral cavity.
3. Neuroepithelial cells:
Neuroepithelial cells are the primary cells found in taste buds. They are specialized epithelial cells that have the ability to transmit nerve signals to the brain, allowing us to perceive different tastes. These cells have long microvilli called taste hairs or taste receptors that project into the taste pore, which is a small opening on the surface of the taste bud.
4. Function of neuroepithelial cells:
Neuroepithelial cells are responsible for detecting taste molecules present in food or beverages. When these molecules come into contact with the taste hairs, they bind to specific receptors on the surface of the neuroepithelial cells, triggering a series of biochemical reactions. These reactions generate electrical signals that are transmitted to the brain through sensory nerves, ultimately resulting in the perception of taste.
5. Other cells in taste buds:
- Supporting cells: These cells surround and provide structural support to the neuroepithelial cells. They also help in the maintenance and regeneration of taste buds.
- Basal cells: Basal cells are undifferentiated cells located at the base of taste buds. They can divide and differentiate into new neuroepithelial cells, ensuring the continuous turnover and replacement of taste bud cells.
Conclusion:
The epithelial cells found in taste buds are called neuroepithelial cells. These specialized cells are responsible for detecting taste molecules and transmitting signals to the brain, allowing us to perceive different tastes. Supporting cells and basal cells are also present within taste buds and play important roles in their structure and function.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithe...
Neuroepithelial cells are stem cells that differentiate into neurons and glia, essential components of the human central nervous system, following the process of neurogenesis. These cells are also found in taste buds. They form the receptor cells of taste buds.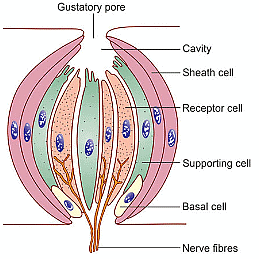

Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithelium cellsb)pigmented epithelial cellsc)neuroepithelial cellsd)absorptive epithelial cellsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithelium cellsb)pigmented epithelial cellsc)neuroepithelial cellsd)absorptive epithelial cellsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithelium cellsb)pigmented epithelial cellsc)neuroepithelial cellsd)absorptive epithelial cellsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithelium cellsb)pigmented epithelial cellsc)neuroepithelial cellsd)absorptive epithelial cellsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithelium cellsb)pigmented epithelial cellsc)neuroepithelial cellsd)absorptive epithelial cellsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithelium cellsb)pigmented epithelial cellsc)neuroepithelial cellsd)absorptive epithelial cellsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithelium cellsb)pigmented epithelial cellsc)neuroepithelial cellsd)absorptive epithelial cellsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithelium cellsb)pigmented epithelial cellsc)neuroepithelial cellsd)absorptive epithelial cellsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithelium cellsb)pigmented epithelial cellsc)neuroepithelial cellsd)absorptive epithelial cellsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithelium cellsb)pigmented epithelial cellsc)neuroepithelial cellsd)absorptive epithelial cellsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithelium cellsb)pigmented epithelial cellsc)neuroepithelial cellsd)absorptive epithelial cellsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithelium cellsb)pigmented epithelial cellsc)neuroepithelial cellsd)absorptive epithelial cellsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The epithelial cells found in taste buds are calleda)glandular epithelium cellsb)pigmented epithelial cellsc)neuroepithelial cellsd)absorptive epithelial cellsCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























