NEET Exam > NEET Questions > What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism?
Start Learning for Free
What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism?
Verified Answer
What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism?
Keto-enol tautomerism is tautomerism involving an aldehyde or a ketone and an enol.
eg. 1:
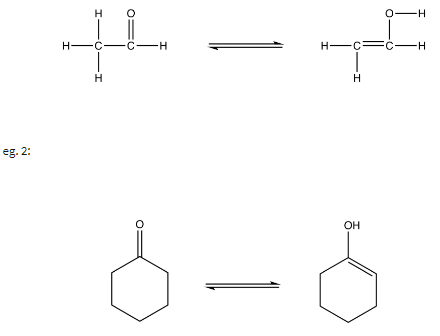
In keto-enol tautomerism, the aldehyde or the ketone is called the keto form and the enol is called the enol form. In most keto-enol tautomerisms, the equilibrium lies by far toward the keto form, indicating that the keto form is usually much more stable than the enol form, which can be attributed to the feet that a carbon-oxygen double bond is significantly stronger than a carbon-carbon double bond.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all NEET courses
Most Upvoted Answer
What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism?
Keto-Enol Tautomerism
Keto-enol tautomerism refers to the interconversion between keto and enol forms of a compound through the migration of a hydrogen atom and the rearrangement of double bonds. This phenomenon occurs in compounds containing a carbonyl group (C=O) and an α-hydrogen (hydrogen atom attached to the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group). The keto form has a carbonyl functional group, while the enol form has a hydroxyl group bonded to a carbon-carbon double bond.
Explanation:
Keto-enol tautomerism involves the following steps:
1. Keto form: The compound initially exists in the keto form, where the carbonyl carbon is bonded to an oxygen atom and is sp2 hybridized. The α-hydrogen is also attached to this carbon atom.
2. Proton transfer: In the presence of suitable conditions (such as acidic or basic conditions), the α-hydrogen migrates to the oxygen atom adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. This migration occurs through the breaking and formation of bonds.
3. Enol form: The result of the proton transfer is the formation of the enol form, where the carbonyl group is converted into a carbon-carbon double bond, and a hydroxyl group is formed on the adjacent carbon. The enol form is also referred to as the enolic form.
4. Equilibrium: The conversion between the keto and enol forms occurs rapidly and is reversible. The keto-enol equilibrium is influenced by factors such as temperature, solvent, and the presence of catalysts.
5. Stabilization: The equilibrium position is determined by the relative stability of the keto and enol forms. Generally, the keto form is more stable due to the presence of a strong C=O bond. However, resonance stabilization and hydrogen bonding in the enol form can also contribute to its stability.
Importance:
Keto-enol tautomerism is significant in organic chemistry due to its impact on the reactivity and properties of compounds. The enol form can participate in various reactions, such as nucleophilic additions, condensations, and keto-enol interconversions. These reactions can lead to the synthesis of complex organic molecules and play a crucial role in biological processes.
Examples:
- One classic example of keto-enol tautomerism is seen in the interconversion of ketones and enols. For instance, acetone can exist as both the keto form (propanone) and the enol form (prop-1-en-2-ol).
- Another example is the tautomeric forms of formaldehyde. It can exist as the keto form (H2C=O) and the enol form (HOCH=O).
Overall, keto-enol tautomerism is a fascinating phenomenon that showcases the dynamic nature of chemical compounds and their ability to exist in different forms.
Keto-enol tautomerism refers to the interconversion between keto and enol forms of a compound through the migration of a hydrogen atom and the rearrangement of double bonds. This phenomenon occurs in compounds containing a carbonyl group (C=O) and an α-hydrogen (hydrogen atom attached to the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group). The keto form has a carbonyl functional group, while the enol form has a hydroxyl group bonded to a carbon-carbon double bond.
Explanation:
Keto-enol tautomerism involves the following steps:
1. Keto form: The compound initially exists in the keto form, where the carbonyl carbon is bonded to an oxygen atom and is sp2 hybridized. The α-hydrogen is also attached to this carbon atom.
2. Proton transfer: In the presence of suitable conditions (such as acidic or basic conditions), the α-hydrogen migrates to the oxygen atom adjacent to the carbonyl carbon. This migration occurs through the breaking and formation of bonds.
3. Enol form: The result of the proton transfer is the formation of the enol form, where the carbonyl group is converted into a carbon-carbon double bond, and a hydroxyl group is formed on the adjacent carbon. The enol form is also referred to as the enolic form.
4. Equilibrium: The conversion between the keto and enol forms occurs rapidly and is reversible. The keto-enol equilibrium is influenced by factors such as temperature, solvent, and the presence of catalysts.
5. Stabilization: The equilibrium position is determined by the relative stability of the keto and enol forms. Generally, the keto form is more stable due to the presence of a strong C=O bond. However, resonance stabilization and hydrogen bonding in the enol form can also contribute to its stability.
Importance:
Keto-enol tautomerism is significant in organic chemistry due to its impact on the reactivity and properties of compounds. The enol form can participate in various reactions, such as nucleophilic additions, condensations, and keto-enol interconversions. These reactions can lead to the synthesis of complex organic molecules and play a crucial role in biological processes.
Examples:
- One classic example of keto-enol tautomerism is seen in the interconversion of ketones and enols. For instance, acetone can exist as both the keto form (propanone) and the enol form (prop-1-en-2-ol).
- Another example is the tautomeric forms of formaldehyde. It can exist as the keto form (H2C=O) and the enol form (HOCH=O).
Overall, keto-enol tautomerism is a fascinating phenomenon that showcases the dynamic nature of chemical compounds and their ability to exist in different forms.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism?
Question Description
What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism?.
What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism?.
Solutions for What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism?, a detailed solution for What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism? has been provided alongside types of What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is Keto-Enol Tautomerism? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























