NEET Exam > NEET Questions > What is magneson reagent ?
Start Learning for Free
What is magneson reagent ?
Most Upvoted Answer
What is magneson reagent ?
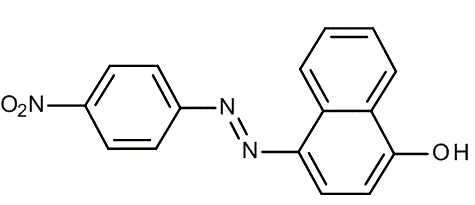
4-(4-Nitrophenylazo) resorcinol, also known as azo violet or magneson I, is a red colored powder. It functions as a spot test reagent and forms blue lake on reaction with Mg(OH)2 in alkaline solution. It is mainly used for determining the presence of magnesium in the solution.
Community Answer
What is magneson reagent ?
Magneson Reagent: An Overview
Magneson reagent is a chemical compound widely used in analytical chemistry for the detection and determination of various elements, particularly metals. It is named after its discoverer, Austrian chemist Karl A. Magneson. This reagent consists of a complex formed between a heterocyclic compound called 2,4-pentanedione (also known as acetylacetone) and a metal ion, usually a transition metal.
Composition and Structure
Magneson reagent is typically prepared by dissolving 2,4-pentanedione in a suitable organic solvent, such as ethanol or acetone, and then adding a metal salt to the solution. The metal ion forms a chelate complex with the 2,4-pentanedione, resulting in the formation of the Magneson reagent.
The molecular structure of the Magneson reagent consists of the 2,4-pentanedione molecule, which acts as a ligand, and the metal ion, which serves as the central atom. The metal ion is coordinated to the oxygen atoms of the 2,4-pentanedione molecule, forming a stable complex.
Applications
Magneson reagent finds extensive applications in analytical chemistry due to its ability to form colored complexes with various metal ions. The color of the complex formed depends on the nature of the metal ion present, allowing for easy identification and quantification. Some key applications of Magneson reagent include:
1. Metal Ion Detection: Magneson reagent is commonly used for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of metal ions in various samples. The formation of colored complexes enables the detection and identification of metal ions in solution.
2. Metal Ion Determination: The concentration of metal ions can be determined by measuring the intensity of the color generated by the Magneson reagent complex. This method is widely employed in environmental analysis, pharmaceutical analysis, and industrial quality control.
3. Complexometric Titrations: Magneson reagent is often utilized as a titrant in complexometric titrations to determine the concentration of metal ions in a sample. The Magneson reagent reacts with the metal ions to form a colored complex, and the endpoint of the titration is determined visually or with the aid of a spectrophotometer.
Conclusion
In summary, Magneson reagent is a powerful tool in analytical chemistry for the detection and determination of metal ions. Its ability to form colored complexes with various metals makes it a valuable reagent in qualitative and quantitative analysis. Through its applications, Magneson reagent contributes to scientific research, environmental monitoring, and quality control in various industries.
Magneson reagent is a chemical compound widely used in analytical chemistry for the detection and determination of various elements, particularly metals. It is named after its discoverer, Austrian chemist Karl A. Magneson. This reagent consists of a complex formed between a heterocyclic compound called 2,4-pentanedione (also known as acetylacetone) and a metal ion, usually a transition metal.
Composition and Structure
Magneson reagent is typically prepared by dissolving 2,4-pentanedione in a suitable organic solvent, such as ethanol or acetone, and then adding a metal salt to the solution. The metal ion forms a chelate complex with the 2,4-pentanedione, resulting in the formation of the Magneson reagent.
The molecular structure of the Magneson reagent consists of the 2,4-pentanedione molecule, which acts as a ligand, and the metal ion, which serves as the central atom. The metal ion is coordinated to the oxygen atoms of the 2,4-pentanedione molecule, forming a stable complex.
Applications
Magneson reagent finds extensive applications in analytical chemistry due to its ability to form colored complexes with various metal ions. The color of the complex formed depends on the nature of the metal ion present, allowing for easy identification and quantification. Some key applications of Magneson reagent include:
1. Metal Ion Detection: Magneson reagent is commonly used for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of metal ions in various samples. The formation of colored complexes enables the detection and identification of metal ions in solution.
2. Metal Ion Determination: The concentration of metal ions can be determined by measuring the intensity of the color generated by the Magneson reagent complex. This method is widely employed in environmental analysis, pharmaceutical analysis, and industrial quality control.
3. Complexometric Titrations: Magneson reagent is often utilized as a titrant in complexometric titrations to determine the concentration of metal ions in a sample. The Magneson reagent reacts with the metal ions to form a colored complex, and the endpoint of the titration is determined visually or with the aid of a spectrophotometer.
Conclusion
In summary, Magneson reagent is a powerful tool in analytical chemistry for the detection and determination of metal ions. Its ability to form colored complexes with various metals makes it a valuable reagent in qualitative and quantitative analysis. Through its applications, Magneson reagent contributes to scientific research, environmental monitoring, and quality control in various industries.
Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
What is magneson reagent ?
Question Description
What is magneson reagent ? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about What is magneson reagent ? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is magneson reagent ?.
What is magneson reagent ? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about What is magneson reagent ? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is magneson reagent ?.
Solutions for What is magneson reagent ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is magneson reagent ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is magneson reagent ?, a detailed solution for What is magneson reagent ? has been provided alongside types of What is magneson reagent ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is magneson reagent ? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























