Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Questions > What is Wheatstone bridge law ?
Start Learning for Free
What is Wheatstone bridge law ?
Verified Answer
What is Wheatstone bridge law ?
Wheatstone Bridge
Wheatstone bridge is used to measure the unknown resistance connected in a circuit. It consists of four resistors of which two resistors are known resistors, one variable resistor and one unknown resistor. It also consists of a galvanometer. It consists of two series-parallel arrangements of resistors.
Consider the diagram of Wheatstone bridge given below. It consists of four arms PQ, QR, RS and PS which has fixed and variable resistors. Resistors resists the flow of electric current. Its measure is called Resistance. Here R1 and R2 are the fixed resistors and R3 is the variable resistor and Rx is the unknown resistor. The resistor which restricts and also can control the flow of electric current is called Variable Resistor. It can either increase or decrease the resistance value and thus control the flow of current.
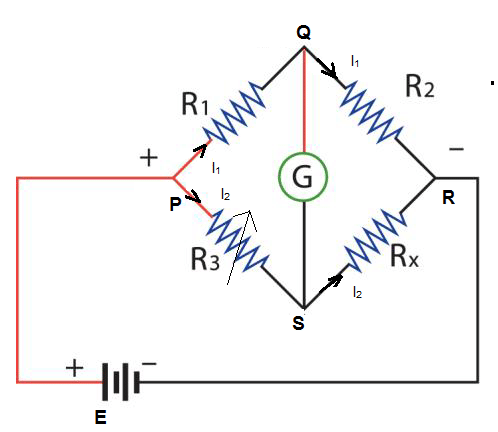
Wheatstone Bridge
The arms PQ and QR are known as Ratio Arms. We can see that a galvanometer is connected between the terminals Q and S. Q and S is called the galvanometer arm. Also the battery is connected to the other two terminals P and R. P and R is called the Battery Arm. By adjusting the value of variable resistor we need to make the deflection in galvanometer as null.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 10 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 10 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
What is Wheatstone bridge law ?
Wheatstone bridge law is an electrical circuit used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing the legs of a bridge circuit one leg of which includes the unknown component.Hope this help u........
Community Answer
What is Wheatstone bridge law ?
What is the Wheatstone Bridge Law?
The Wheatstone bridge law is a principle in electrical circuit theory that describes the relationship between the resistances in a Wheatstone bridge circuit. The Wheatstone bridge is a circuit configuration commonly used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing it with known resistances. The law, formulated by Samuel Hunter Christie and later popularized by Sir Charles Wheatstone, states that the ratio of the resistances in the bridge circuit is equal to the ratio of the voltages across them.
Wheatstone Bridge Circuit
The Wheatstone bridge circuit consists of four resistors connected in a diamond shape with a voltage source applied across two opposite corners. The two other corners are used for measurement purposes. One corner contains the unknown resistance, and the other corner has a known resistance. A galvanometer or a voltmeter is connected across the other two corners to measure the voltage difference. The goal is to adjust the known resistance until the bridge is balanced, meaning the voltage difference across the measurement corners is zero.
Wheatstone Bridge Law Equation
The Wheatstone bridge law can be mathematically represented as follows:
R₁/R₂ = V₁/V₂
Where:
- R₁ and R₂ are the known resistances
- V₁ and V₂ are the voltages across the known resistances
Applications of the Wheatstone Bridge Law
The Wheatstone bridge law finds numerous applications in various fields, including:
1. Strain gauges: Used to measure strain in materials by converting it into an electrical resistance change.
2. Temperature sensors: Temperature-dependent resistors can be used in a Wheatstone bridge configuration to measure temperature changes.
3. Pressure sensors: Wheatstone bridge circuits can be employed to measure changes in resistance due to pressure variations.
4. Electrical impedance measurements: The bridge can determine the impedance of unknown components, such as capacitors or inductors.
Advantages of Wheatstone Bridge
- High accuracy in measuring resistance values.
- Simple circuit design and implementation.
- Allows for precise measurements in a wide range of applications.
- Can be used with various types of resistive sensors.
Limitations of Wheatstone Bridge
- Requires a balanced bridge for accurate measurements.
- Sensitive to external factors like temperature changes and variations in the power supply.
- Not suitable for measuring very low or very high resistances without additional modifications.
The Wheatstone bridge law is a fundamental principle in electrical circuitry, providing a reliable method for measuring unknown resistances. Its wide range of applications and simplicity make it a valuable tool in various fields of science and engineering.
The Wheatstone bridge law is a principle in electrical circuit theory that describes the relationship between the resistances in a Wheatstone bridge circuit. The Wheatstone bridge is a circuit configuration commonly used to measure an unknown electrical resistance by balancing it with known resistances. The law, formulated by Samuel Hunter Christie and later popularized by Sir Charles Wheatstone, states that the ratio of the resistances in the bridge circuit is equal to the ratio of the voltages across them.
Wheatstone Bridge Circuit
The Wheatstone bridge circuit consists of four resistors connected in a diamond shape with a voltage source applied across two opposite corners. The two other corners are used for measurement purposes. One corner contains the unknown resistance, and the other corner has a known resistance. A galvanometer or a voltmeter is connected across the other two corners to measure the voltage difference. The goal is to adjust the known resistance until the bridge is balanced, meaning the voltage difference across the measurement corners is zero.
Wheatstone Bridge Law Equation
The Wheatstone bridge law can be mathematically represented as follows:
R₁/R₂ = V₁/V₂
Where:
- R₁ and R₂ are the known resistances
- V₁ and V₂ are the voltages across the known resistances
Applications of the Wheatstone Bridge Law
The Wheatstone bridge law finds numerous applications in various fields, including:
1. Strain gauges: Used to measure strain in materials by converting it into an electrical resistance change.
2. Temperature sensors: Temperature-dependent resistors can be used in a Wheatstone bridge configuration to measure temperature changes.
3. Pressure sensors: Wheatstone bridge circuits can be employed to measure changes in resistance due to pressure variations.
4. Electrical impedance measurements: The bridge can determine the impedance of unknown components, such as capacitors or inductors.
Advantages of Wheatstone Bridge
- High accuracy in measuring resistance values.
- Simple circuit design and implementation.
- Allows for precise measurements in a wide range of applications.
- Can be used with various types of resistive sensors.
Limitations of Wheatstone Bridge
- Requires a balanced bridge for accurate measurements.
- Sensitive to external factors like temperature changes and variations in the power supply.
- Not suitable for measuring very low or very high resistances without additional modifications.
The Wheatstone bridge law is a fundamental principle in electrical circuitry, providing a reliable method for measuring unknown resistances. Its wide range of applications and simplicity make it a valuable tool in various fields of science and engineering.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Similar Class 10 Doubts
What is Wheatstone bridge law ?
Question Description
What is Wheatstone bridge law ? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about What is Wheatstone bridge law ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is Wheatstone bridge law ?.
What is Wheatstone bridge law ? for Class 10 2025 is part of Class 10 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 10 exam syllabus. Information about What is Wheatstone bridge law ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 10 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is Wheatstone bridge law ?.
Solutions for What is Wheatstone bridge law ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 10.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 10 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is Wheatstone bridge law ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is Wheatstone bridge law ?, a detailed solution for What is Wheatstone bridge law ? has been provided alongside types of What is Wheatstone bridge law ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is Wheatstone bridge law ? tests, examples and also practice Class 10 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 10 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























