NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2...
Start Learning for Free
Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ?
Most Upvoted Answer
Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241...
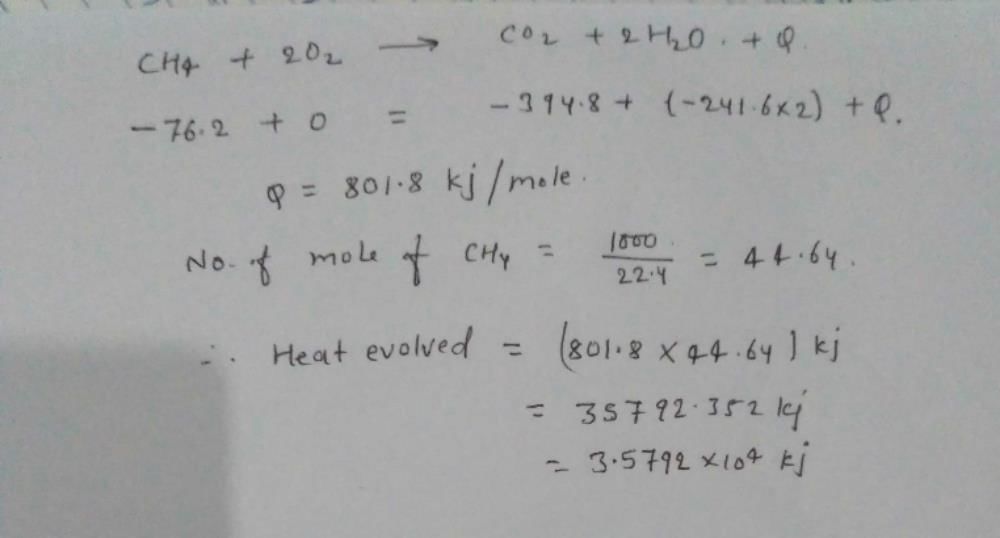
Community Answer
Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241...
Calculation of Heat Evolved by Burning CH4
To calculate the amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4, we need to use the heat of formation values of CH4, CO2 and H2O.
- The balanced equation for the combustion of CH4 is:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
- The heat of formation values of the compounds involved in the reaction are:
ΔHf(CH4) = -76.2 kJ/mol
ΔHf(CO2) = -394.8 kJ/mol
ΔHf(H2O) = -241.6 kJ/mol
- We can use the heat of formation values to calculate the heat of reaction, which is the amount of heat evolved or absorbed during a chemical reaction. The heat of reaction (ΔH) for the combustion of CH4 is:
ΔH = ΣnΔHf(products) - ΣnΔHf(reactants)
where n is the number of moles of each compound involved in the reaction.
- In this case, we are burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 at normal conditions, which is equivalent to 0.717 kg (or 0.0285 moles) of CH4. Therefore, the heat of reaction for the combustion of CH4 is:
ΔH = (1 mol CO2 × -394.8 kJ/mol) + (2 mol H2O × -241.6 kJ/mol) - (0.0285 mol CH4 × -76.2 kJ/mol)
ΔH = -802.3 kJ/mol
- The negative sign indicates that the reaction is exothermic, meaning that heat is evolved during the reaction.
- To calculate the amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4, we need to multiply the heat of reaction by the number of moles of CH4 burned:
Heat evolved = ΔH × n
Heat evolved = -802.3 kJ/mol × 0.0285 mol
Heat evolved = -22.9 kJ
- However, we want to express the heat evolved in kJ/m3, so we need to convert the mass of CH4 burned to volume using the ideal gas law:
PV = nRT
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature. At normal conditions (0°C and 1 atm), the ideal gas law becomes:
V = nRT/P
- Using the ideal gas law, we can calculate the volume of 0.717 kg of CH4 at normal conditions:
V = (0.0285 mol × 8.314 J/mol·K × 273.15 K)/(101325 Pa)
V = 0.667 m3
- Therefore, the amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 is:
Heat evolved = -22.9 kJ/0.667 m3
Heat evolved ≈ 34.3 kJ/m3
- The closest option to this value is option B, which is 3.579×104 kJ. Therefore, the correct answer is B.
Summary
To calculate the amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4, we
To calculate the amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4, we need to use the heat of formation values of CH4, CO2 and H2O.
- The balanced equation for the combustion of CH4 is:
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
- The heat of formation values of the compounds involved in the reaction are:
ΔHf(CH4) = -76.2 kJ/mol
ΔHf(CO2) = -394.8 kJ/mol
ΔHf(H2O) = -241.6 kJ/mol
- We can use the heat of formation values to calculate the heat of reaction, which is the amount of heat evolved or absorbed during a chemical reaction. The heat of reaction (ΔH) for the combustion of CH4 is:
ΔH = ΣnΔHf(products) - ΣnΔHf(reactants)
where n is the number of moles of each compound involved in the reaction.
- In this case, we are burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 at normal conditions, which is equivalent to 0.717 kg (or 0.0285 moles) of CH4. Therefore, the heat of reaction for the combustion of CH4 is:
ΔH = (1 mol CO2 × -394.8 kJ/mol) + (2 mol H2O × -241.6 kJ/mol) - (0.0285 mol CH4 × -76.2 kJ/mol)
ΔH = -802.3 kJ/mol
- The negative sign indicates that the reaction is exothermic, meaning that heat is evolved during the reaction.
- To calculate the amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4, we need to multiply the heat of reaction by the number of moles of CH4 burned:
Heat evolved = ΔH × n
Heat evolved = -802.3 kJ/mol × 0.0285 mol
Heat evolved = -22.9 kJ
- However, we want to express the heat evolved in kJ/m3, so we need to convert the mass of CH4 burned to volume using the ideal gas law:
PV = nRT
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature. At normal conditions (0°C and 1 atm), the ideal gas law becomes:
V = nRT/P
- Using the ideal gas law, we can calculate the volume of 0.717 kg of CH4 at normal conditions:
V = (0.0285 mol × 8.314 J/mol·K × 273.15 K)/(101325 Pa)
V = 0.667 m3
- Therefore, the amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 is:
Heat evolved = -22.9 kJ/0.667 m3
Heat evolved ≈ 34.3 kJ/m3
- The closest option to this value is option B, which is 3.579×104 kJ. Therefore, the correct answer is B.
Summary
To calculate the amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4, we

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ?
Question Description
Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ?.
Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ?.
Solutions for Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ?, a detailed solution for Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ? has been provided alongside types of Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Standard heat of formation of CH4, CO2 and H2O are -76.2, -394.8, -241.6 kJ/mol. Amount of heat evolved by burning 1 cubic metre of CH4 measured at normal conditions is. A) 3.579×10^6. B) 3.579×10^4. C) 6.240×10^4. D) 6.240×10^7 kJ? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















