NEET Exam > NEET Questions > When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heat...
Start Learning for Free
When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved is
- a)SO₂
- b)NH₃
- c)CO₂
- d)CO
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the g...
Potassium hexacyanoferrate(II) react with sulfuric acid and water to produce potassium sulfate, iron(II) sulfate, ammonium sulfate and carbon monoxide. Sulfuric acid - concentrated solution. The reaction takes place in a boiling solution.
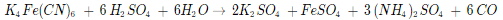
View all questions of this test
Most Upvoted Answer
When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the g...
Heating potassium ferrocyanide crystals with conc. H₂SO₄ results in the evolution of a gas. The gas evolved is CO (carbon monoxide).
Explanation:
- Potassium ferrocyanide is a salt with the chemical formula K₄[Fe(CN)₆]. It is also known as yellow prussiate of potash.
- When heated with conc. H₂SO₄, the salt undergoes a reaction known as destructive distillation or dry distillation.
- In this reaction, the salt is decomposed into its constituent elements, i.e., potassium, iron, carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen.
- The decomposition of potassium ferrocyanide can be represented by the following equation:
K₄[Fe(CN)₆] + 6H₂SO₄ → 2KHSO₄ + K₂SO₄ + FeSO₄ + 6CO + 6H₂O + N₂
- As we can see from the equation, the gas evolved is CO (carbon monoxide).
- Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas that is odorless, tasteless, and colorless. It is formed by incomplete combustion of carbon-containing compounds.
- Carbon monoxide is a potent poison that can cause headaches, dizziness, nausea, and even death in high concentrations.
In conclusion, when potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc. H₂SO₄, the gas evolved is CO (carbon monoxide), which is a toxic gas that can be harmful to human health.
Explanation:
- Potassium ferrocyanide is a salt with the chemical formula K₄[Fe(CN)₆]. It is also known as yellow prussiate of potash.
- When heated with conc. H₂SO₄, the salt undergoes a reaction known as destructive distillation or dry distillation.
- In this reaction, the salt is decomposed into its constituent elements, i.e., potassium, iron, carbon, nitrogen, and hydrogen.
- The decomposition of potassium ferrocyanide can be represented by the following equation:
K₄[Fe(CN)₆] + 6H₂SO₄ → 2KHSO₄ + K₂SO₄ + FeSO₄ + 6CO + 6H₂O + N₂
- As we can see from the equation, the gas evolved is CO (carbon monoxide).
- Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas that is odorless, tasteless, and colorless. It is formed by incomplete combustion of carbon-containing compounds.
- Carbon monoxide is a potent poison that can cause headaches, dizziness, nausea, and even death in high concentrations.
In conclusion, when potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc. H₂SO₄, the gas evolved is CO (carbon monoxide), which is a toxic gas that can be harmful to human health.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the g...

Attention NEET Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed NEET study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in NEET.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved isa)SO₂b)NH₃c)CO₂d)COCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved isa)SO₂b)NH₃c)CO₂d)COCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved isa)SO₂b)NH₃c)CO₂d)COCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved isa)SO₂b)NH₃c)CO₂d)COCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved isa)SO₂b)NH₃c)CO₂d)COCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for NEET 2024 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved isa)SO₂b)NH₃c)CO₂d)COCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved isa)SO₂b)NH₃c)CO₂d)COCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved isa)SO₂b)NH₃c)CO₂d)COCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved isa)SO₂b)NH₃c)CO₂d)COCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved isa)SO₂b)NH₃c)CO₂d)COCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved isa)SO₂b)NH₃c)CO₂d)COCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved isa)SO₂b)NH₃c)CO₂d)COCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice When potassium ferrocyanide crystals are heated with conc.H₂SO₄, the gas evolved isa)SO₂b)NH₃c)CO₂d)COCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























