UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 11th February 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Polity
What is Euthanasia?
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
The Supreme Court has recently agreed to consider a petition regarding the implementation of passive euthanasia for patients suffering from rabies.
- Euthanasia is the practice of hastening the death of a patient to alleviate suffering.
- The term originates from the Greek phrase "eu thanatos," meaning "good death."
- Euthanasia is classified into two main categories: Active and Passive Euthanasia.
- In India, passive euthanasia has been legalized, while active euthanasia remains illegal.
Additional Details
- Active Euthanasia: This method involves taking direct actions to end a patient's life, such as administering a lethal dose of medication through an intravenous line. It is sometimes referred to as "aggressive euthanasia."
- Passive Euthanasia: This involves intentionally causing a patient's death by withholding or withdrawing life-sustaining treatments, like a ventilator, from terminally ill patients.
- Legality in India: In the landmark ruling of the Common Cause vs. Union of India case (2018), the Supreme Court recognized the right to die as part of the right to life. This ruling allows for the creation of a "living will" for terminally ill patients, enabling them to refuse medical treatment or life support, thus ensuring a dignified exit.
Overall, while passive euthanasia is legally permitted in certain circumstances in India, active euthanasia is still considered a crime. This distinction is crucial in understanding the ongoing legal and ethical debates surrounding euthanasia in the country.
GS3/Environment
Burmese Pythons
Source: DTE
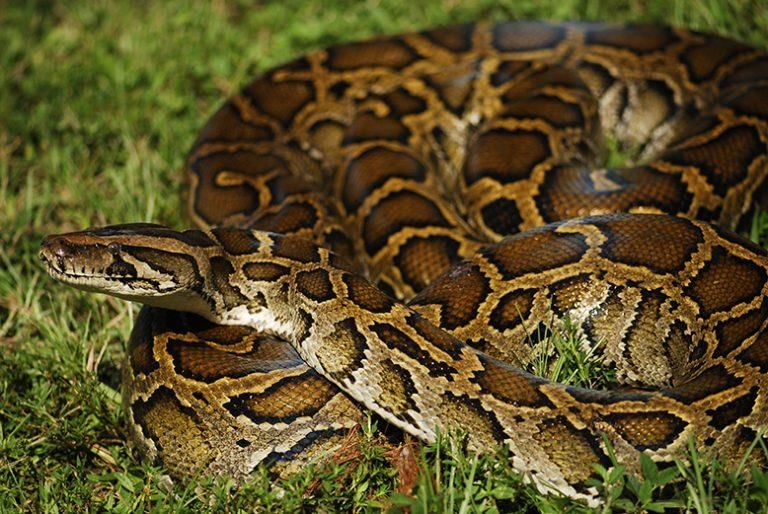 Why in News?
Why in News?Scientists at the University of Florida have conducted a statistical analysis of extensive data collected by contractors working to manage Burmese pythons. This research has provided essential insights into the most effective methods for removing these invasive reptiles.
- Burmese pythons are among the largest snake species, reaching lengths of up to 20 feet and weights exceeding 250 pounds.
- They are non-venomous, solitary, and primarily nocturnal, residing in various habitats including forests and wetlands.
- This species is now recognized as distinct from Python molurus, following a taxonomic update in 2009.
Additional Details
- Habitat: Burmese pythons thrive in diverse environments such as grasslands, marshes, swamps, rocky areas, caves, woodlands, rainforests, mangrove forests, and river valleys.
- Distribution: They are native to the tropical and subtropical forests of eastern and northeastern India, Myanmar, southern China, Southeast Asia, and parts of the Indonesian archipelago. Their presence in Florida is attributed to the pet trade, where they have become an invasive species.
- Conservation Status: The IUCN classifies Burmese pythons as Vulnerable, indicating they face threats in their natural habitats.
This research underscores the importance of understanding Burmese pythons' behaviors and habitats to formulate effective removal strategies, which are crucial for preserving local ecosystems in Florida.
GS2/Polity
Article 22 of the Indian Constitution
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The Supreme Court recently ruled that informing an arrested person of the grounds of their arrest is a mandatory constitutional obligation and not merely a formality. Failure to comply with this requirement renders the arrest illegal, thus violating Articles 22(1) and 21 of the Constitution, which are fundamental for protecting individual rights and personal liberty.
- Article 22 provides protection against arbitrary arrest and preventive detention.
- Informing an arrested person of the grounds for their arrest is a fundamental right.
- Failure to comply can lead to the arrest being deemed invalid.
Additional Details
- Protection in Ordinary Arrests:
- The arrested individual must be informed of the grounds of arrest as soon as possible.
- They have the right to consult and be defended by a lawyer of their choice.
- They must be presented before a magistrate within 24 hours.
- Preventive Detention Provisions:
- Preventive detention without trial is limited to 3 months, unless extended by an Advisory Board.
- The government may withhold reasons for detention if it affects public interest.
- Parliament can extend detention beyond 3 months in special cases.
- The Supreme Court emphasized that the grounds of arrest should ideally be provided in writing, as per the ruling in Pankaj Bansal vs Union of India (2023).
- In case of non-compliance with Article 22(1), the accused must be released, and violation of this article can be a basis for bail.
In conclusion, the recent judgment by the Supreme Court highlights the importance of adhering to constitutional provisions regarding arrest, ensuring that fundamental rights are upheld, and that due process is followed in the criminal justice system.
GS2/Polity
Centre vs Delhi Government: The Constitutional Tussle
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?The governance of Delhi, India's national capital, has been a significant point of contention, resulting in ongoing legal disputes between the Aam Aadmi Party (AAP)-led Delhi Government and the BJP-led Central Government. The primary source of conflict is Delhi's unique constitutional status as a Union Territory (UT) with its own legislature, which has implications for administrative control and governance.
- The legal battles revolve around who has authority over bureaucratic appointments, law enforcement, and governance powers in Delhi.
- Multiple Supreme Court interventions have sought to clarify the powers of the Delhi Government versus those of the Central Government.
Additional Details
- Constitutional Status of Delhi: Defined by Article 239AA of the Indian Constitution, Delhi has a legislative assembly with the authority to make laws on various subjects, excluding police, public order, and land.
- Legal Battles:
- In 2015, the Union Home Ministry issued a notification asserting L-G control over bureaucratic services, which was challenged by the Delhi Government.
- In 2016, the Delhi High Court ruled that the L-G had overriding powers, but a 2018 Supreme Court judgment established that the L-G must act on the "aid and advice" of the elected government in most matters.
- A 2023 Supreme Court ruling reaffirmed the 2018 judgment, emphasizing that the Delhi Government has control over administrative services.
- Central Government's Legislative Response: In May 2023, the Government of National Capital Territory of Delhi (Amendment) Act extended the L-G's powers over bureaucratic appointments, leading to further legal challenges from the Delhi Government.
- Political Context: The ongoing legal struggles have delayed policymaking and led to accusations from the AAP regarding the Centre's obstruction of development programs.
The conflict between the Centre and the Delhi Government is not only a legal and constitutional issue but also a political one that has significant implications for governance in the national capital. As the legal battles continue, the outcomes will affect the administrative autonomy of Union Territories with legislatures, setting important precedents for future governance in similar regions.
GS2/Governance
PM-AJAY Scheme
Source: Economic Times
Why in News?
The Union Minister for Social Justice and Empowerment recently chaired a meeting of the Central Advisory Committee for the PM-AJAY scheme, highlighting its ongoing initiatives aimed at improving the socio-economic conditions of Scheduled Castes (SC) communities.
- The PM-AJAY scheme is a 100% Centrally Sponsored initiative aimed at reducing poverty among SC communities.
- This scheme merges three previous schemes: PM Adarsh Gram Yojana (PMAGY), Special Central Assistance to Scheduled Castes Sub Plan (SCA to SCSP), and Babu Jagjivan Ram Chhatrawas Yojana (BJRCY).
Additional Details
- Objectives:The primary goals include:
- Increasing the income of the target population through various income-generating schemes, skills development, and infrastructure improvement.
- Reducing poverty among the target population and helping them rise above the poverty line.
- Eligibility Criteria:
- Scheduled Castes individuals living below the poverty line can benefit from this scheme.
- Villages with 50% or more SC population are eligible for infrastructure development grants.
- Implementation:The scheme has been in effect since 2021-22 and consists of three main components:
- Development of SC dominated villages into an 'Adarsh Gram' component.
- Grants-in-aid for district/state-level projects aimed at the socio-economic betterment of SCs.
- Construction of hostels for higher educational institutions.
This comprehensive approach aims to foster inclusive growth and uplift SC communities through targeted initiatives and support.
GS2/Polity
Autonomous District Council Elections in Meghalaya
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?The elections for the Khasi Hills Autonomous District Council and the Jaintia Hills Autonomous District Council are set to take place on February 21. This event is significant within the framework of local governance in tribal areas in India.
- The elections are scheduled for February 21 in Meghalaya.
- Autonomous District Councils (ADCs) are established under the Sixth Schedule of the Indian Constitution.
- Each ADC has a term of five years and consists of a maximum of 30 members.
Additional Details
- Sixth Schedule: This constitutional provision outlines the governance of tribal areas in India, specifically in states like Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura, and Mizoram.
- Membership: Each ADC can have up to 30 members, which includes 4 nominated members by the governor and 26 elected representatives through adult franchise.
- Functions of ADCs: ADCs have the authority to make laws regarding land management, inheritance, marriage, and also manage local education and health facilities.
- Revenue Sources: The main revenue for ADCs comes from taxes on professions, vehicles, market entry, and maintenance fees for local services.
The establishment and functioning of Autonomous District Councils play a crucial role in empowering tribal communities and ensuring localized governance in Meghalaya.
GS2/International Relations
Exercise Cyclone 2025
Source: PIB
Why in News?
The joint military exercise, Exercise Cyclone 2025, is scheduled to take place from February 10 to 23 in Rajasthan, involving the armed forces of India and Egypt. This exercise marks a significant step in enhancing military cooperation between the two nations.
- Exercise Cyclone 2025 is the third edition of the joint military exercise between India and Egypt.
- The exercise aims to improve coordination and tactical skills between the two armies.
- Focus areas include counter-terrorism, high-intensity combat, and survival techniques in desert conditions.
Additional Details
- Objective: The primary goal of Exercise Cyclone 2025 is to enhance military collaboration and operational effectiveness through joint training sessions that simulate real-world scenarios.
- Motto: The motto for this year's exercise is “Together we train, together we excel,” reflecting the spirit of cooperation.
- Previous Editions: The first edition took place in India in 2023, followed by the second edition in Egypt in 2024.
- The exercise will involve the special forces of both countries, allowing them to operate together in simulated combat situations.
The increasing military cooperation between India and Egypt underscores a mutual commitment to strengthening security measures and fostering strategic partnerships in the region.
GS2/International Relations
India as a Bridge between the Global North and South
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
India's recent diplomatic initiatives reflect its ambition to advocate for the interests of the Global South. Prime Minister Narendra Modi's addresses at significant events, such as the 18th Pravasi Bharatiya Divas Convention and the 3rd Voice of Global South Summit, underscore India's dedication to creating an inclusive global governance framework. Unlike its historical engagement in the Non-Alignment Movement (NAM), India's current strategy aims to position itself as a facilitator between the Global North and South, raising questions about the motivations behind this proactive stance and its potential impact on global development.
- India is redefining its role as a mediator between developed and developing nations.
- The strategic competition with China plays a significant role in India's diplomatic ambitions.
- India aims to establish itself as a self-reliant power advocating for equitable economic structures.
Additional Details
- The China Factor: India is motivated by the need to provide an alternative to China's state-led development model, which heavily relies on loans and investments. India promotes equal partnerships and sustainable growth, positioning itself as a viable alternative for developing nations.
- Self-Reliance: India's aspiration to be a self-reliant power involves addressing the economic challenges faced by developing nations, particularly those burdened by debt and restrictive policies from international financial institutions.
- Development Cooperation: India's commitment to a collaborative development approach through initiatives like the 'Global Development Compact' aims to foster mutual learning and respect among partner nations.
- Human-Centric Development Model: Initiatives such as Mission LiFE ('Lifestyle for Environment') highlight India's focus on sustainable development, while also emphasizing skill development and entrepreneurship to build human capital in developing countries.
- Institutional Strengthening: India's advocacy for the African Union's inclusion in the G-20 illustrates its commitment to enhancing the representation of the Global South in international governance.
In conclusion, India stands at a crucial juncture in global politics, with the opportunity to redefine its influence as a leader of the Global South. By advocating for inclusive economic frameworks, promoting sustainable development, and strengthening its institutional capacities, India can effectively emerge as a key global development partner. However, to truly be the 'Voice' of the Global South, India must listen to the needs and aspirations of its partner countries.
GS3/Science and Technology
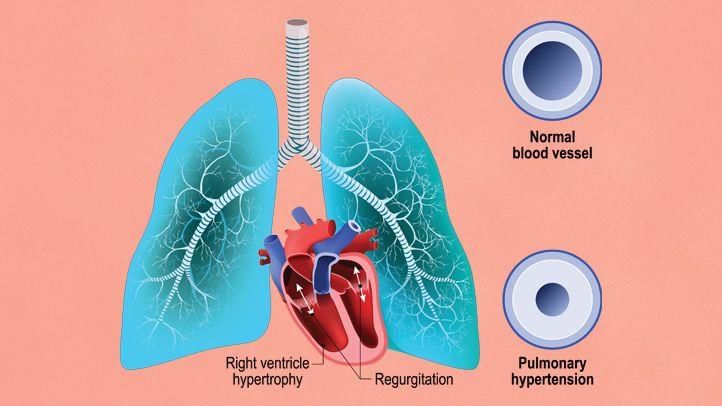
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Source: Nature
 Why in News?
Why in News?Natco Pharma has recently received final approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for its Bosentan tablets for oral suspension, which is the generic version of Actelion Pharmaceuticals' pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) drug, Tracleer.
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) is a specific type of pulmonary hypertension.
- Recent FDA approval for a generic version of a leading PAH treatment.
Additional Details
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH): PAH occurs when the small arteries in the lungs become thickened and narrowed, obstructing blood flow and raising blood pressure in the lungs.
- Causes:The exact cause of PAH is not clearly understood but is believed to result from injury to the cells lining lung blood vessels, leading to vascular disease. It may also be linked to other medical conditions, such as:
- Congenital heart disease
- Liver disease
- HIV
- Connective tissue diseases (e.g., scleroderma, lupus)
- Drug Use: PAH can be associated with past or present drug use, including methamphetamine and certain diet pills.
- Symptoms:Symptoms of PAH include:
- Blue fingers or lips
- Chest pain
- Dizziness or fainting
- Fatigue
- Worsening shortness of breath
- Treatment: Although treatment options exist for managing PAH, there is currently no known cure.
In summary, the recent FDA approval of Bosentan for PAH highlights significant progress in the treatment of this serious condition. While effective management options are available, ongoing research is essential to find a definitive cure.
GS1/History & Culture
Renaming of Fort William
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
In an effort to remove colonial symbols and practices from the Indian Armed Forces, Fort William in Kolkata, which serves as the headquarters of the Eastern Army Command, has been renamed Vijay Durg.
- Fort William was originally constructed by the British in 1773 and named after King William III of England.
- It is situated on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River in Kolkata, West Bengal, and functioned as a crucial British military stronghold during the colonial era.
- The fort's first version was established by the English East India Company in 1696, which included an inner bastion that was notorious as a prison, leading to the term "Black Hole of Calcutta."
Additional Details
- Black Hole of Calcutta Incident: This incident in 1756 involved the alleged imprisonment of British prisoners by Nawab Siraj-ud-Daulah, resulting in many suffocating due to overcrowding and poor ventilation.
- Following the Battle of Plassey in 1757, Robert Clive commanded the fort's demolition, and a new structure was completed later.
- Fort William College: Established by Lord Wellesley in 1800 to train civil servants in Indian languages and customs, it was closed in 1802.
- The current fort is octagonal, constructed of brick and mortar, and spans 70.9 acres. It is now overseen by the Indian Army as the headquarters of the Eastern Command.
The significance of the renaming lies in its homage to Vijay Durg Fort in Maharashtra, an important naval fort under Chhatrapati Shivaji, symbolizing India's indigenous military history. This renaming reflects India's broader initiative to eliminate colonial influences and promote native military traditions.
In September 2022, the Indian Navy updated its ensign, replacing the British-era design with a new octagonal one inspired by Chhatrapati Shivaji’s royal seal.
GS3/Economy
SASCI Scheme Overview
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The Government of India has approved 40 projects across 23 states, allocating ₹32,95.76 crore under the ‘Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment (SASCI) Scheme’ for the Financial Year 2024-25. This scheme is significant as it aims to bolster state capital expenditure and promote economic growth.
- The SASCI Scheme was launched in FY 2020-21 as a measure for post-COVID recovery.
- It has been expanded for FY 2023-24 with an allocation of ₹1.3 lakh crore.
- The scheme supports a variety of projects, including infrastructure development, urban reforms, tourism, and sustainability initiatives.
Additional Details
- Structural Mandate:The scheme comprises eight components based on states' share of central taxes:
- General Capital Assistance: ₹1 lakh crore allocated according to states' share of central taxes.
- Vehicle Scrappage & Testing Facilities: Provides incentives for phasing out old vehicles and establishing automated testing centers.
- Urban Planning Reforms: Encourages modern land-use planning and governance improvements.
- Urban Finance Reforms: Aims to strengthen municipal revenue models and financial sustainability.
- Housing for Police Personnel: Funds residential units for police and their families.
- Cultural & Economic Development: Promotes initiatives like One District One Product (ODOP), Make in India, and supports local entrepreneurship.
- Digital Libraries at Panchayat/Ward Levels: ₹5,000 crore allocated for enhancing library infrastructure and digital learning access.
- Development of Iconic Tourist Centres: Focuses on branding and improving infrastructure for major tourism hubs.
- Features & Significance:The scheme aims to:
- Boost capital investment to stimulate demand and create jobs.
- Encourage reforms in urban governance, infrastructure, and sustainability.
- Promote responsible tourism and enhance global branding of iconic destinations.
- Strengthen local industries through initiatives like ODOP.
- Improve public services such as policing, water supply, and rural roads.
Overall, the SASCI Scheme is pivotal in facilitating state-level economic growth and enhancing infrastructure across various sectors, thereby contributing to the broader objective of national development.
|
38 videos|5288 docs|1117 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 11th February 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is euthanasia and what are the different types of euthanasia? |  |
| 2. What is the ecological impact of Burmese pythons in their non-native habitats? |  |
| 3. What is Article 22 of the Indian Constitution and what rights does it provide? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the PM-AJAY Scheme in India? |  |
| 5. How does the Centre vs Delhi Government case reflect the constitutional tussle in India? |  |





















