UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 13th December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Environment
D. Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary
Source: Northeast Today
 Why in News?
Why in News?A recent stakeholders' coordination meeting was held to discuss the reintroduction of rhinoceroses to the D. Ering Wildlife Sanctuary (DEWS) located in the East Siang District of Arunachal Pradesh.
- The sanctuary was established in 1976 and was previously known as Lali Wildlife Sanctuary.
- It was renamed to D. Ering in 1986 after the declaration of Lali Reserve Forest as a sanctuary.
- DEWS features a tropical climate with rainfall from both northeast and southwest monsoons.
- The Siang River, one of Arunachal Pradesh's major rivers, flows through the sanctuary.
Additional Details
- Flora: The sanctuary mainly consists of riverine plains with a significant presence of thatch and grasses, along with scattered patches of trees such as Termenelia myriocarpa, Dillenia indica, Albizia spp., and Bombax ceiba.
- Fauna: DEWS is home to diverse wildlife including Hog Deer, Wild Pig, Tiger, and Elephant. It also hosts more than 150 species of birds, including endangered species like the White-Winged Wood Duck and Bengal Florican.
This meeting marks a significant step forward in conservation efforts for the rhinoceros population and highlights the importance of protecting the rich biodiversity of the D. Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary.
GS3/Environment
Assessment of Water Resources of India, 2024 by CWC
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
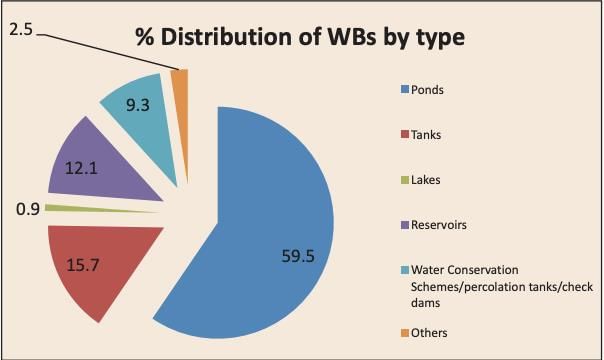
Why in News?The Central Water Commission (CWC) has recently published its report titled ‘Assessment of Water Resources of India, 2024’. This report provides critical insights into the water availability in India from 1985 to 2023, estimating the average annual water availability at 2,115.95 billion cubic meters (BCM).
- Average annual water availability is estimated at 2,115.95 BCM.
- Top three basins by water availability are:
- Brahmaputra Basin: 592.32 BCM
- Ganga Basin: 581.75 BCM
- Godavari Basin: 129.17 BCM
- Bottom three basins by water availability are:
- Sabarmati Basin: 9.87 BCM
- Pennar Basin: 10.42 BCM
- Mahi Basin: 13.03 BCM
- Water availability has increased from 1,999.2 BCM in 2019 due to the inclusion of contributions from Bhutan and Nepal.
- Current per capita water availability is 1,513 cubic meters, up from 1,486 cubic meters in 2021, yet still indicates water stress.
Additional Details
- Utilizable Water Resources: The report indicates that out of the total water availability, approximately 690 BCM is utilizable surface water. Notably, smaller basins tend to have a higher proportion of utilizable water compared to larger basins like the Brahmaputra.
- Central Water Commission (CWC): Established in 1945 as the Central Waterways, Irrigation and Navigation Commission (CWINC), CWC operates under the Ministry of Jal Shakti. It serves as a statutory advisory body for water resource development and management, headquartered in New Delhi.
- The Chairman of CWC also serves as the Ex-Officio Secretary to the Government of India, overseeing various responsibilities including control, conservation, and utilization of water resources, maintaining the National Register of Large Dams (NRLD), and conducting hydrological surveys.
In conclusion, the CWC’s report highlights crucial data regarding India’s water resources, emphasizing both the availability and the challenges faced in water management. Despite improvements in figures, the country continues to grapple with issues related to water stress.
GS1/History & Culture
Durgadi Fort: History and Cultural Significance
Source: MSN
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Kalyan civil court has ruled that Durgadi Fort is owned by the Maharashtra government, dismissing claims made by the Majlis-E-Mushawarat Trust. This Trust initially filed its claim in 1976, asserting that the fort contains a mosque and an idgah (prayer hall) alongside a temple dedicated to Goddess Durga.
- Durgadi Fort dates back to the 16th century and is part of the Bijapur-based Adil Shahi Sultanate.
- The fort has been referenced in British documents since 1570.
- In 1760, after the Marathas captured Kalyan, they constructed a wooden temple for Durgadevi and renamed the fort Durgadi Killa.
- Control of the fort passed to the British in 1818, leading to the temple's cessation of operations.
- By 1876, the idol of Goddess Durga was reported stolen.
Additional Details
- Historical Significance: The fort is not only a military structure but also houses a tomb and a prayer space, reflecting its multi-religious history.
- Geographical Location: Situated in Thane district, approximately 50 km northeast of Mumbai, the fort is perched on elevated ground, providing scenic views of the Ulhas River.
- Cultural Impact: Durgadi Fort has played a crucial role in the religious dynamics of Maharashtra, originally featuring a mosque and later modified to include a Durga temple. This reflects the complex interplay of religious identities and historical heritage, leading to communal tensions.
This ruling and the historical significance of Durgadi Fort underscore its importance in understanding the cultural and religious landscape of Maharashtra.
GS3/Environment
Malayan Night Heron Sighted in Madurai
Source: Times of India
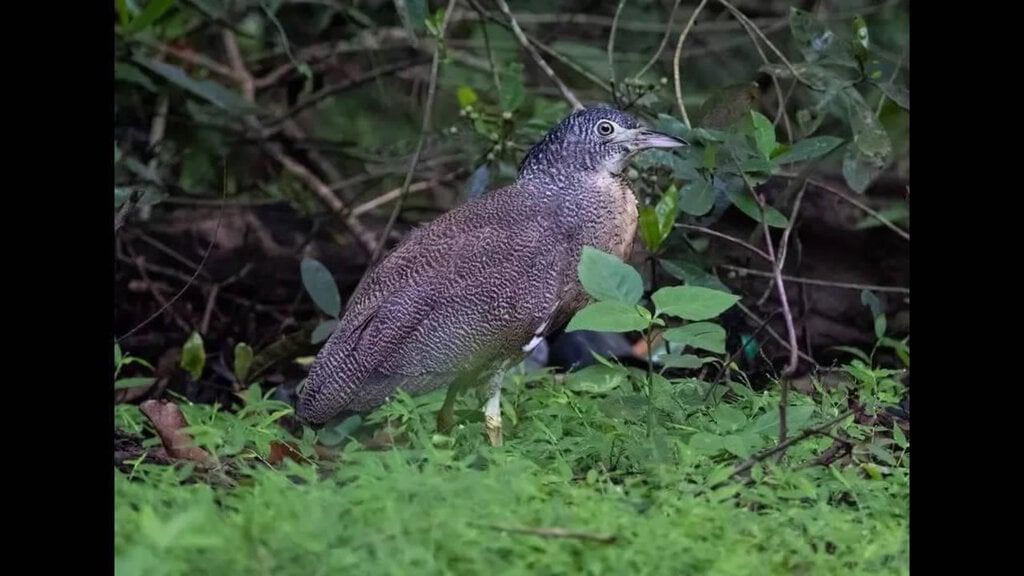 Why in News?
Why in News?The Malayan Night Heron, a migratory bird native to Southeast Asia, has been officially recorded in Madurai for the first time, near the Alagar Kovil hills. This sighting marks an important event for ornithology in the region.
- The Malayan Night Heron is also known as the Malaysian night heron or tiger bittern.
- This bird is medium-sized and primarily nocturnal, making it unique among herons.
Additional Details
- Appearance: The Malayan Night Heron is characterized by its rufous neck, barred chestnut back, a black cap with a crest, and white-tipped primaries.
- Habitat: It thrives in dense subtropical forests, utilizing various wetland areas such as streams, marshes, and swamps, as well as evergreen forests, secondary scrub, and reservoirs at moderate elevations.
- Distribution: This bird is predominantly found across India, East Asia, the Philippines, and the East Indies. Its native range includes Myanmar, Thailand, and Malaysia, from where it migrates to India during the winter months. It is commonly observed in northern Tamil Nadu and typically seen in Kerala and Karnataka.
- Diet: The Malayan Night Heron primarily feeds on earthworms and beetles, showcasing its preference for invertebrates.
- Conservation Status (IUCN): It is currently classified as Least Concern, indicating a stable population.
The sighting of the Malayan Night Heron in Madurai is significant as it highlights the ecological diversity of the region and the importance of conserving migratory bird habitats.
GS2/Polity
Athlete Biological Passport (ABP)
Source: Times of India
Why in News?The World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) has authorized the National Dope Testing Laboratory (NDTL) as an Athlete Passport Management Unit (APMU) to oversee the management of the Athlete Biological Passport (ABP). This initiative aims to enhance anti-doping measures in sports.
- The ABP is a sophisticated anti-doping tool that tracks an athlete's biological markers over time.
- It identifies variations in blood and steroid profiles to ensure fair play and protect clean athletes.
- The ABP supports targeted testing and serves as indirect evidence in doping cases.
Additional Details
- Haematological Module: This module gathers data on markers indicative of blood doping, focusing on substances that enhance oxygen transport.
- Steroidal Module: It measures markers of steroid doping in urine and serum, including endogenous anabolic androgenic steroids (EAAS) that are administered exogenously.
- Endocrine Module: This module monitors the use of human growth hormone (hGH) and its analogs.
- The ABP enables targeted, conventional anti-doping tests for athletes with abnormal profiles and serves as corroborative evidence in anti-doping rule violations.
The implementation of the ABP signifies a crucial step in the fight against doping in sports, promoting integrity and fairness while safeguarding the health of athletes.
GS3/Science and Technology
IndiaAI Future Skills Platform
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Union Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology has recently announced that 8.6 lakh candidates have enrolled in the IndiaAI Future Skills platform, highlighting the growing interest in AI education across the country.
- The IndiaAI Future Skills platform is part of the seven foundational pillars of the IndiaAI Mission.
- The initiative aims to enhance India’s readiness for an AI workforce by reducing entry barriers to AI programs.
- It plans to increase the availability of AI courses at undergraduate, postgraduate, and Ph.D. levels.
Additional Details
- Establishment of Data and AI Labs: The initiative will set up Data and AI Labs in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities across India, providing foundational level courses to foster inclusive access to AI education.
- The initiative is developed in collaboration with industry partners, ensuring that training programs are aligned with evolving industry demands.
- AI Data Labs are being launched in cities such as Gorakhpur, Lucknow, Shimla, Aurangabad, Patna, Buxar, and Muzaffarpur to promote technological advancements beyond urban centers.
This initiative aims to democratize access to AI education, ensuring that opportunities are available to a broader segment of the population, thus contributing to a more robust AI talent pipeline in India.
GS3/Science and Technology
Manganese Contamination and Its Health Implications
Source: Nature
Why in News?Recent research indicates that contamination of water with manganese (Mn) is linked to cancer cases in the Gangetic plains of Bihar, raising significant health concerns in the region.
- Manganese is the fifth-most abundant metal on Earth, found in various forms such as oxides, carbonates, and silicates.
- It plays a crucial role in the growth of plants and the assimilation of nitrates.
- Excessive manganese intake can lead to severe toxicity in humans.
Additional Details
- Manganese Properties: Manganese is typically too brittle to be used as a pure metal and is primarily utilized in alloys, particularly steel. Common minerals include pyrolusite (manganese dioxide) and rhodochrosite (manganese carbonate).
- Biological Role: As an essential trace element, manganese is vital for maintaining body homeostasis. It is a component of many enzymes found in all known living organisms.
- Manganese can oxidize when exposed to air and is prone to rusting in moist environments.
- The primary sources of manganese ores are located in countries such as Australia, South Africa, China, Gabon, and Brazil.
Understanding the implications of manganese contamination is crucial for public health, particularly in areas like Bihar where water sources may be compromised. Continuous monitoring and remedial actions are essential to mitigate these health risks.
GS3/Environment
Beijing’s War Against Air Pollution
Source: The Hindu
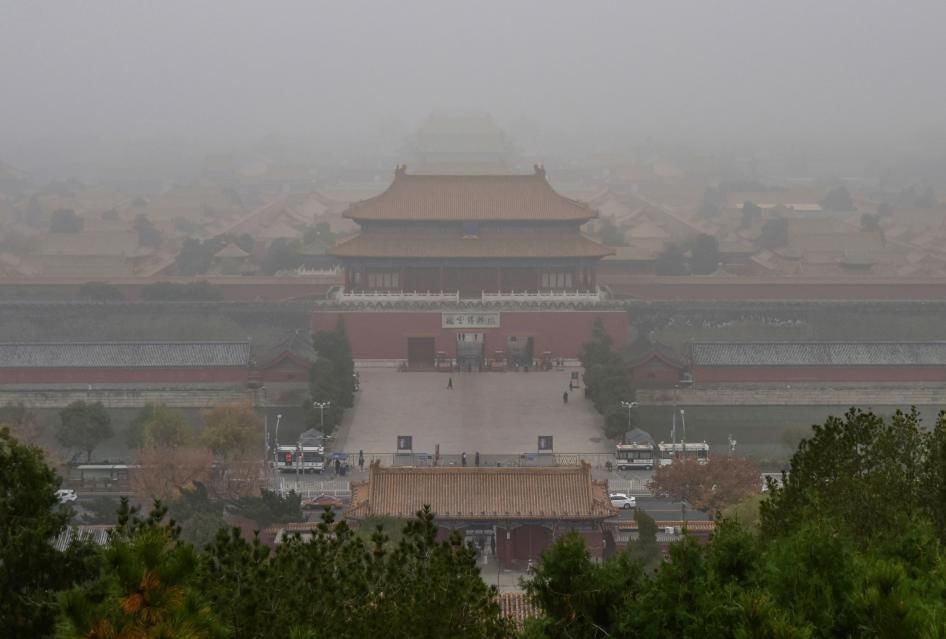 Why in News?
Why in News?Beijing has made significant strides in reducing its air pollution levels, dropping from an average air quality index (AQI) of 144 in 2015 to a third lower by 2017. In comparison, Delhi's current AQI stands at 155 in 2024, indicating a need for similar efforts in the Indian capital.
- Beijing's pollution levels were comparable to Delhi's current state.
- Beijing implemented a long-term, phased anti-pollution strategy.
- Strong political will and community involvement were crucial to Beijing's success.
- Delhi can learn from Beijing's strategies for urban pollution management.
Additional Details
- Similarities between Beijing and Delhi:
- Rapid Urbanization and Economic Growth: Both cities have faced increased emissions due to industrialization and urban growth.
- Heavy Reliance on Fossil Fuels: Energy generation and transportation in both cities heavily depend on fossil fuels.
- Regional Impact: Both cities experience pollution from surrounding areas, particularly in winter.
- Beijing's Successful Strategies:
- Long-Term Planning: Beijing's 20-year program included three phases: 1998-2008, 2009-2012, and 2013-2017, focusing on gradual implementation with public participation.
- Targeted Pollution Sources: The city identified key pollution sources, including energy and coal combustion, transportation, and construction.
- Transportation Improvements: Retrofitting vehicles and expanding public transport, such as subways and buses, contributed to significant emissions reductions.
- Industrial Regulations: Tightened environmental requirements and penal actions against violators were implemented to improve industrial practices.
- Regional Cooperation: The final phase emphasized collaboration with neighboring provinces for comprehensive pollution control.
- Lessons for Delhi:
- Political Will: Strong leadership is essential for enforcing effective policies.
- Public Transport System: Delhi needs an integrated and efficient bus-metro system to reduce reliance on private vehicles.
- Vehicle Scrappage: Implementing a subsidy-for-scrap program for old vehicles is crucial.
- Urban Planning: Enhancing connectivity between residential and work areas can reduce travel needs.
- Energy Overhaul: Transitioning to cleaner energy sources, such as solar, is necessary for sustainable electricity supply.
- Regional Coordination: Delhi should engage with surrounding regions to tackle cross-border pollution issues.
In conclusion, Beijing's comprehensive approach to tackling air pollution offers valuable insights for Delhi. By adopting similar strategies, focusing on strong political commitment, and fostering regional cooperation, Delhi can work towards improving its air quality and public health outcomes.
GS3/Science and Technology
Disease X – Science & Technology
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?The recent outbreak reported in early December 2024 in the Democratic Republic of Congo has raised alarms as it has resulted in over 400 fatalities. This incident remains unclassified, leading to concerns that it may represent an instance of Disease X.
- Disease X serves as a placeholder for a hypothetical and unpredictable pathogen that could potentially lead to a global health crisis.
- The term was introduced by the World Health Organization (WHO) in 2018 to prepare for unforeseen outbreaks.
- The COVID-19 pandemic exemplifies Disease X, as it was an unknown pathogen that required a rapid global response.
Additional Details
- Forecasting Challenges: Predicting the emergence of Disease X is complex, as it relies on various unpredictable factors.
- Zoonotic Diseases: These diseases are often the source of major epidemics, highlighting the risk posed by pathogens that can jump from animals to humans.
- Other potential origins of Disease X include pathogen mutations to evade treatment, laboratory accidents, or even biological attacks.
This outbreak emphasizes the significance of being prepared for unpredictable health threats and the necessity for ongoing vigilance and research into emerging diseases.
GS1/Indian Society
Pandupol Hanuman Temple
Source: Law Advice
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Supreme Court has recently highlighted the importance of balancing wildlife protection in the Sariska Tiger Reserve with the religious sentiments of devotees visiting the Pandupol Hanuman Temple.
- The Pandupol Hanuman Temple is a sacred site with a rich historical and cultural significance.
- It is located within the Sariska Tiger Reserve, which is known for its diverse flora and fauna.
- The temple is associated with Hindu mythology, particularly the epic Mahabharata.
Additional Details
- About Pandupol Hanuman Temple:
This temple is believed to be over 5000 years old and is located in the Sariska Tiger Reserve in Alwar, Rajasthan. It is significant in Hindu mythology as it is thought that the Pandavas, during their exile, visited this area, formerly known as Viratnagar. It is here that Bhima is said to have encountered Lord Hanuman. The temple's name reflects its connection to the Pandavas and honors Lord Hanuman.
- Reclining Statue of Lord Hanuman:
The temple's main attraction is the reclining statue of Lord Hanuman, which the Pandavas are believed to have established.
- Sariska Tiger Reserve:
This reserve spans an area of 800 sq km within the Aravali Hills and was established as a natural reserve in 1955 and later as a national park in 1979. It is notable for being the first reserve in the world to successfully relocate tigers.
- Flora and Fauna:
The Sariska Tiger Reserve is characterized by Northern Tropical Dry Deciduous and Thorn Forests, with trees such as dhok, salar, and kadaya. It hosts a variety of wildlife, including leopards, sambhar, chital, and nilgai.
The Pandupol Hanuman Temple serves not only as a site of religious significance but also plays a crucial role in conservation discussions, emphasizing the need to harmonize spiritual practices with environmental preservation.
GS3/Defence & Security
Dark Eagle Anti-Missile System
Source: Eurasian Times
Why in News?The United States has developed a new anti-missile system known as the Dark Eagle, which is approaching operational readiness following a successful test flight.
- Long-range hypersonic anti-missile system.
- Capable of intercepting various missile types including ballistic, cruise, and hypersonic missiles.
- Operational range exceeds 2,775 kilometers (1,724 miles).
- Equipped with a hypersonic glide warhead (C-HGB) capable of reaching speeds of Mach 17.
Additional Details
- Hypersonic Glide Warhead (C-HGB): This component allows the missile to achieve extreme speeds, specifically between 3,000 and 3,700 meters per second, making it particularly challenging to intercept.
- The system is designed to potentially outmatch Russian air defense systems, including the S-300V4, S-400, and S-500.
The Dark Eagle represents a significant advancement in missile defense technology, enhancing the ability to counter threats from adversaries and ensuring strategic superiority.
GS2/Polity
Principles of Judicial Conduct
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The recent comments by Justice Shekhar Kumar Yadav of the Allahabad High Court regarding the Muslim community during an event organized by the Vishwa Hindu Parishad's legal cell have sparked significant public outrage.
- The “Restatement of Values of Judicial Life” serves as the primary ethical guideline for judicial behavior, adopted by the Supreme Court in 1997.
- This code consists of 16 key principles designed to maintain public confidence in the judiciary's impartiality.
Additional Details
- Restatement of Values of Judicial Life: This document emphasizes that justice must not only be done but must also be perceived to be done, reinforcing public trust in the judiciary.
- Judges are prohibited from engaging in various activities that could compromise their impartiality, such as:
- Running for election in any club or society.
- Close personal associations with members of the bar practicing in their court.
- Allowing family members who are lawyers to appear before them.
- Hearing cases involving family members or close relations.
- Bangalore Principles of Judicial Conduct, 2002:Formulated under the auspices of the United Nations, these principles were adopted to provide a universal framework for judicial conduct, emphasizing six core values:
- Independence: Judges must remain free from external pressures.
- Impartiality: Judges are to remain unbiased and avoid any conflicts of interest.
- Integrity: Upholding moral and ethical standards is crucial for maintaining public trust.
- Propriety: Judges must conduct themselves in a manner that upholds the dignity of the judiciary.
- Equality: Ensuring fair treatment irrespective of background.
- Competence and Diligence: Continuous improvement of legal knowledge and effective case management are expected.
These principles collectively aim to ensure that judges conduct themselves in a manner that reflects the high standards expected of their office, thereby fostering public confidence in the judicial system.
|
38 videos|5258 docs|1111 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 13th December 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of the D. Ering Memorial Wildlife Sanctuary in India? |  |
| 2. How does the Central Water Commission (CWC) assess water resources in India? |  |
| 3. What historical events are associated with Durgadi Fort? |  |
| 4. Why is the sighting of the Malayan Night Heron in Madurai important? |  |
| 5. What are the implications of manganese contamination on health? |  |
















