UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 14th June 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Environment
Emperor Penguins and Climate Change
Source: DTE
Why in News?
Recent studies have highlighted that emperor penguins, a species emblematic of the Antarctic region, are increasingly threatened by climate change due to the shrinking of Antarctic sea ice.
Key Takeaways
- Emperor penguins are the tallest and heaviest species of penguin.
- They are highly adapted to survive in extremely harsh Antarctic conditions.
- This species is categorized as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List.
Additional Details
- Physical Features: Adults display a striking black and white coloration with vibrant orange and yellow accents on the head, neck, and breast. They possess two layers of feathers and a thick layer of fat, which helps in heat retention.
- Breeding and Lifespan: Emperor penguins breed during the winter months (April to November) and have a lifespan ranging from 15 to 20 years.
- Diving Ability: These birds are remarkable divers, capable of reaching depths of approximately 550 meters (1,800 feet) in pursuit of food, making them the deepest-diving birds in the world.
- Habitat: They inhabit the pack ice and marine areas surrounding the Antarctic and spend their entire lives on this ice.
- Weight Variation: Emperor penguins experience rapid weight fluctuations during breeding and feeding seasons; females generally weigh less than males.
As climate change continues to impact their habitat, the emperor penguins face significant challenges that threaten their survival. Conservation efforts are crucial to protect this iconic species and their ecosystem.
GS3/Environment
What is Ocean Darkening?
Source: TOI
 Why in News?
Why in News?A recent study indicates that over one-fifth of the global ocean has significantly darkened in the past two decades, raising concerns about marine ecosystems.
Key Takeaways
- The phenomenon of ocean darkening relates to the shrinking of photic zones, where sunlight penetrates to support photosynthesis.
- Photic layers extend to about 200 meters and are crucial for nearly 90% of the world's marine life.
- Increased darkening affects ocean productivity, climate regulation, and global fisheries.
Additional Details
- Photic Zones: These are the upper layers of the ocean that receive sufficient sunlight for photosynthesis, supporting a vast majority of marine organisms.
- Causes of Darkening:
- In coastal areas, darkening is primarily caused by increased runoff of agricultural nutrients, organic matter, and sediments, leading to algal blooms that obstruct light.
- In the open ocean, factors include changes in plankton dynamics, rising sea surface temperatures, and shifts in ocean circulation patterns.
- The contraction of photic zones could disrupt marine ecosystems, forcing species that rely on sunlight and moonlight for various life processes to compete for limited shallow zones.
- This shift may also disturb marine food webs, which are already stressed by minimal fishing activities.
In summary, the darkening of the ocean poses significant risks to marine life and ecosystems, highlighting the need for further research and monitoring of this critical environmental issue.
GS2/International Relations
The Endgame of a 2,611-Year-Old Jewish-Persian Enmity
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The geopolitical landscape of West Asia experienced a significant escalation on June 13, 2025, with Israel's Rising Lion operation targeting Iran's nuclear and missile infrastructure. This event marked a rare acknowledgment from both Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, highlighting the historical significance of their longstanding enmity.
Key Takeaways
- Israel conducted a meticulously planned military operation against Iran, involving over 200 jets and targeting more than 100 sites.
- Despite official disavowals, there is strong evidence of U.S. covert support for Israel's actions.
- Reactions from the Sunni Arab world are mixed, balancing suspicion towards Iran with concerns over Israeli aggression.
- The operation has potential implications for global economic stability and U.S. foreign policy.
Additional Details
- Historical Context: The current conflict is the latest in a 2,611-year-old enmity, dating back to the destruction of the First Jewish Temple in 586 BCE.
- U.S. Involvement: The withdrawal from the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) and reinstated sanctions under President Trump's administration significantly weakened Iran's position.
- Regional Reactions: Sunni Arab states express ambivalence; they distrust Iran's Shia leadership but are also cautious of Israeli militarism.
- Global Implications: The conflict poses risks to global oil supplies and economic stability, potentially impacting U.S. foreign policy decisions.
In conclusion, the military confrontation between Israel and Iran signifies not just a critical moment in Middle Eastern affairs but also a pivotal juncture in global geopolitics. The repercussions of this conflict are likely to resonate well beyond the region, affecting international security, diplomatic relations, and economic stability for years to come.
GS2/Governance
Centre Sets Up Forest Rights Act (FRA) Cells
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
Under the Dharti Aba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyaan (DAJGUA), the Ministry of Tribal Affairs has approved the establishment of District and State-level Forest Rights Act (FRA) Cells across 18 States and Union Territories to facilitate the implementation of the Forest Rights Act, 2006.
Key Takeaways
- The DAJGUA initiative was launched in October 2024.
- It aims to promote holistic development for tribal communities by addressing infrastructure, livelihoods, education, and health gaps.
- The program covers over 63,843 tribal-dominated villages, benefitting more than 5 crore tribal individuals.
Additional Details
- Funding: The total budget allocated for this initiative is ₹79,156 crore, which includes a central share of ₹56,333 crore and a state share of ₹22,823 crore.
- Inspiration: DAJGUA is modeled after the PM-JANMAN Scheme, which focuses on the welfare of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
- What are FRA Cells? FRA Cells serve as administrative support units to assist in the implementation of the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006.
- Funding Support: These cells are funded directly by the Union Ministry of Tribal Affairs, representing the first structured central government financial support for FRA.
- Objective: The primary goal of FRA Cells is to assist tribal claimants and Gram Sabhas in preparing and submitting forest rights claims, especially in tribal-dominated districts.
In conclusion, the establishment of FRA Cells under the DAJGUA initiative is a significant step towards empowering tribal communities and ensuring their rights over forest lands, ultimately promoting their socio-economic development.
GS3/Environment
Brewing Crisis: How Climate Change is Unraveling India’s Tea Heartland
Source: DTE
Why in News?
North Bengal’s tea gardens are facing a significant crisis, particularly affecting women workers. This crisis is driven by climate change, pest invasions, low wages, and decreased production, resulting in severe economic challenges and heightened gender-based hardships.
Key Takeaways
- Women tea workers face extreme heat and poor working conditions.
- Climate change is leading to declining tea yield and quality.
- Low wages contribute to economic hardship and limited upward mobility for workers.
- Tea estates are adopting climate-resilient practices to combat these challenges.
- The tea sector is often overlooked in policy and climate action discussions.
Additional Details
- Extreme Heat Exposure: Women work under the open sky without shade, enduring high temperatures. For instance, workers often suffer from headaches, vomiting, and exhaustion while plucking leaves during the peak summer months of April and May.
- Lack of Basic Facilities: The absence of crèches, sanitation, and rest shelters forces women to juggle labor and childcare in unsafe conditions. For example, children are hung in cloth cradles tied to trees while mothers continue their work in the gardens.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Climate change is causing wildlife to encroach on tea estates, increasing the risk of attacks. Notably, leopard attacks have injured several women, despite efforts such as using whistles to deter them.
- Declining Tea Yield and Quality: Erratic rainfall patterns disrupt soil moisture and crop cycles, particularly during critical growth months like February and March, leading to reduced yields and degraded leaf quality.
- Economic Hardship: Low daily earnings make it challenging for workers to afford basic necessities, such as food, healthcare, and education. For instance, a worker earning only Rs 250 per day struggles to support their family.
- Climate-Resilient Practices: Some tea estates are transitioning to organic farming, reducing chemical use and enhancing soil health. Techniques such as mulching and intercropping are being implemented to conserve moisture and prevent soil erosion.
- Policy Neglect: The tea sector receives minimal attention in marketing and policy discussions, leading to inadequate support for women workers and insufficient climate funding.
In summary, the challenges faced by women tea workers in North Bengal are multifaceted, involving climate change impacts, economic struggles due to low wages, and inadequate support structures. Addressing these issues through improved working conditions and the promotion of climate-resilient practices is essential for the sustainability of both the tea industry and the livelihoods of its workers.
GS2/International Relations
Israel Strikes Iran’s Nuclear Sites
Source: BBC
 Why in News?
Why in News?On June 13, 2025, Israel executed a significant military operation targeting Iran's nuclear and military installations in Tehran. This strike resulted in the deaths of Iran's Revolutionary Guard chief and two prominent nuclear scientists. This event represents a serious escalation in the ongoing Israel-Iran shadow conflict, raising concerns about a wider regional confrontation in light of Iran's progressing nuclear program.
Key Takeaways
- Israel's strike marks a critical escalation in the Israel-Iran conflict.
- Iran maintains its nuclear program is for civilian purposes, despite international skepticism.
- The IAEA has declared Iran in non-compliance with nuclear non-proliferation obligations.
- The geopolitical landscape has shifted following significant regional events, including the fall of Assad in Syria.
Additional Details
- Iran's Nuclear Programme: Iran asserts that its nuclear activities are solely for civilian and peaceful applications, such as energy generation and medical research. However, the international community remains doubtful, citing a lack of transparency and undeclared nuclear materials.
- IAEA Non-Compliance Declaration: In a notable move, the IAEA Board of Governors indicated that Iran has breached its nuclear obligations, citing insufficient responses regarding its nuclear activities.
- Near-Weapons-Grade Enrichment: Reports indicate that Iran has enriched uranium to as much as 60% purity, approaching the 90% threshold necessary for weapon production, raising alarms globally.
- Regional Dynamics: The geopolitical situation shifted dramatically with the 2023 Hamas attack on Israel and the subsequent fall of President Bashar al-Assad, which diminished Iran’s regional influence and capabilities.
- Impact on Global Oil Prices: The Israeli strike has led to an 8% increase in global oil prices, causing concerns about inflation and supply chain disruptions.
This operation is seen as the culmination of years of planning by Israel, which has consistently opposed Iran's nuclear ambitions and has conducted various covert operations to hinder them. The current situation emphasizes the unpredictable nature of regional politics and its global repercussions.
GS1/Indian Society
Reclaiming Reproductive Autonomy in a Changing Demographic Landscape
Source: WHO
Why in News?
The United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), in its State of the World Population Report 2025, challenges alarmist narratives surrounding declining fertility and demographic transitions. The report emphasizes reproductive agency—the ability of individuals and couples to realize their fertility aspirations—as the primary concern, rather than just focusing on population numbers. This holds significant implications for policymakers, especially in a country like India, where socio-economic and cultural factors greatly influence fertility behavior and population policy.
Key Takeaways
- Global fertility rates have decreased from 5 in 1960 to 2.2 in 2024, with over 50% of countries below the replacement level of 2.1.
- In India, the Total Fertility Rate (TFR) fell from 2.9 in 2005 to 2.0 in 2020, with significant state-level variations.
- 36% of Indian respondents reported unintended pregnancies, highlighting unmet fertility desires.
Additional Details
- Demographic Anxiety: There is rising concern about ageing populations and a shrinking workforce, which fuels fears regarding declining fertility.
- Unmet Fertility Desires: A survey by UNFPA-YouGov revealed that 30% of Indian respondents faced difficulties in conceiving when they desired, indicating both overachieved and underachieved fertility.
- Economic and Social Constraints: Major barriers to reproductive health include financial insecurity, unemployment, and lack of childcare support, which are exacerbated by marriage and domestic responsibilities placed on women.
- Barriers to Reproductive Health: Stigma surrounding infertility and high costs of treatments limit access, while a reliance on female sterilization restricts contraceptive choices.
- Delayed Childbearing: Educated urban couples are postponing childbirth, but often neglect spacing for subsequent children; only 4% of married women report their spacing needs are met.
To secure a demographically resilient future, nations must prioritize reproductive autonomy, dismantle socio-cultural barriers, and implement inclusive policies that reflect the genuine fertility aspirations of individuals. This approach offers a pathway to reshape population policies through a framework that champions dignity, equity, and choice.
GS3/Economy
What is Merchant Discount Rate (MDR)?
Source: AIR
Why in News?
The Finance Ministry has firmly denied recent online rumors suggesting that the government is planning to impose Merchant Discount Rate (MDR) charges on UPI transactions.
Key Takeaways
- MDR is a fee charged to merchants for processing digital payments.
- The government waived MDR on UPI and RuPay card transactions in 2020.
- Merchants cannot pass MDR fees onto customers.
Additional Details
- Overview: MDR refers to the fee charged to merchants by banks or payment service providers for processing digital payments made via credit cards, debit cards, or other digital modes.
- Purpose: It compensates multiple stakeholders involved in a digital transaction, including the issuing bank, acquiring bank, payment gateway, and network operator.
- Fee Structure: MDR is calculated as a percentage of the total transaction amount, typically ranging from 1% to 3%, depending on the transaction and merchant type.
- RBI Regulation: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) regulates MDR, and merchants are not permitted to pass this fee onto customers.
- Discontinuation: To promote cashless payments, the government waived MDR on UPI and RuPay card transactions in 2020, benefiting small merchants and consumers.
- Transaction Flow: When a customer pays digitally, the payment amount is credited to the merchant’s account after deducting the MDR fee. For example, if a customer pays ₹1,000 and the MDR is 2%, the merchant receives ₹980, while ₹20 is distributed among banks and service providers.
- Automatic Deduction: The MDR amount is automatically deducted by the settlement system at the time of transaction processing.
- Variable Rates: MDR rates may vary based on factors such as the type of card used, nature of business, monthly transaction volume, and average transaction value.
- Merchant Agreements: Merchants are required to sign MDR agreements with their banks before they begin accepting digital payments.
- Operational Cost: MDR is treated as part of the merchant’s operational costs when offering customers the convenience of digital payment options.
In summary, the Merchant Discount Rate (MDR) plays a critical role in the digital payment ecosystem, ensuring that all involved parties are compensated for their services while facilitating seamless transactions for merchants and consumers alike.
GS2/Governance
Centre’s FRA Cell Initiative: Boosting Implementation of Forest Rights Act
Source: IBEF
Why in News?
The Union government has initiated funding for structural mechanisms aimed at facilitating the implementation of the Forest Rights Act (FRA), 2006, marking a significant step towards improving the legal rights of forest-dwelling communities.
Key Takeaways
- The government has approved the establishment of over 300 district and state-level FRA cells across India.
- The objective is to assist Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers in exercising their rights over forest land and resources.
Additional Details
- Forest Rights Act (FRA): Enacted in 2006 to address historical injustices faced by tribal and forest-dwelling communities, it decentralizes the recognition of rights to the Gram Sabha, which establishes Forest Rights Committees (FRCs) that collaborate with various committees to process claims.
- Previously, the implementation burden rested solely on state governments and Union Territories, with the Centre providing only advisory support. However, as of March 2025, 14.45% of total claims remain pending due to delays and limited coordination.
- Role of FRA Cells: Established under the Dharti Aba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyaan (DAJGUA), these cells provide technical and administrative support, aiding claimants in preparing documents and tracking claim statuses.
- 324 district-level FRA cells have been approved across 18 states and Union Territories, with funding provided through the Grants-in-Aid General route.
- Concerns: Critics warn that these cells risk creating a parallel implementation mechanism that may confuse responsibilities and undermine the statutory framework established by the FRA.
The DAJGUA initiative aims to integrate various tribal welfare interventions to uplift over 68,000 tribal-majority villages. While the Centre’s direct involvement signifies a pivotal policy shift, the success of FRA cells will depend on clear role delineation and cooperation among authorities to ensure that the integrity of the Forest Rights Act is maintained.
GS3/Science and Technology
What are Black Boxes?
Source: The Hindu
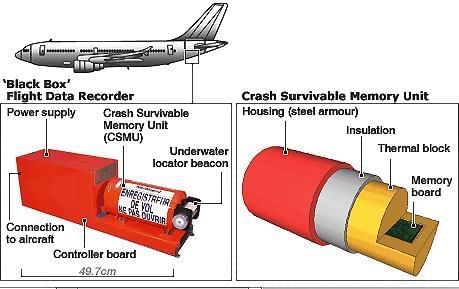 Why in News?
Why in News?Authorities have recovered the black box from the crash site of the recent incident in Ahmedabad, highlighting the importance of these devices in aviation safety and accident investigation.
Key Takeaways
- Black boxes are critical for flight data recording and accident investigation.
- The first practical flight data recorder was developed by Australian scientist David Warren in 1954.
- Despite their name, black boxes are bright orange for visibility.
- Aircraft typically have two types of black boxes: Cockpit Voice Recorder (CVR) and Digital Flight Data Recorder (DFDR).
Additional Details
- Purpose: Black boxes are essential for aiding accident investigations and enhancing flight safety analysis.
- Development: David Warren's invention in 1954 came after his investigations into mid-air explosions.
- Color and Visibility: They are painted bright orange with reflective material to ensure easy visibility post-crash.
- Types: Aircraft usually possess two black boxes: the CVR records cockpit audio, while the DFDR logs flight performance data.
- Single Unit: Some aircraft integrate both functions into a combined unit for efficiency.
- Recording Mechanism: The CVR captures the last 2 hours of cockpit audio, whereas the DFDR stores up to 25 hours of flight data, recording thousands of data points per second.
- Installation Location: Black boxes are generally located in the tail section of the aircraft, which is statistically more likely to survive a crash.
- Durability: They are built with solid-state memory chips and housed in crash-survivable casings to withstand extreme conditions.
- Underwater Locator Beacons (ULBs): Each black box is equipped with a beacon that emits signals for up to 30 days, aiding in recovery efforts after water crashes.
In India, the Aircraft Accident Investigation Bureau (AAIB) conducts crash investigations using black box data as primary evidence. A recent development in April 2025 saw the establishment of India's first dedicated Flight Recorders Laboratory in New Delhi, enhancing the country's ability to analyze crash data independently and effectively.
UPSC 2025
Question: GPS-Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN) uses a system of ground stations to provide necessary augmentation. Which of the following statements is/are correct in respect of GAGAN?
- I. It is designed to provide additional accuracy and integrity.
- II. It will allow more uniform and high-quality air traffic management.
- III. It will provide benefits only in aviation but not in other modes of transportation.
Options: (a) I, II and III (b) II and III only (c) I only (d) I and II only*
|
38 videos|5288 docs|1117 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 14th June 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the major impacts of climate change on Emperor Penguins? |  |
| 2. What is ocean darkening and how does it relate to climate change? |  |
| 3. How does the Forest Rights Act (FRA) benefit indigenous communities? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the Merchant Discount Rate (MDR) in financial transactions? |  |
| 5. What are black boxes and why are they important in aviation? |  |
















