UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 15th April 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS1/History & Culture
History as Battlefield — The Perils of Reversing the Past
Why in News?
In March 2025, India witnessed a notable resurgence in textbook revisions alongside public outrage aimed at Mughal monuments. This situation was exacerbated by viral campaigns that prompted vandalism and calls for renaming or demolishing historical tombs. This reflects a worrying trend of simplifying complex historical narratives into a binary of heroes and villains.
- The revision of history may correct perceived inaccuracies but risks deepening social divisions.
- History should be viewed as a nuanced interpretation rather than a static record.
Additional Details
- History as a Discipline: History requires discernment and should not be manipulated for ideological purposes, as doing so can sow division rather than promote understanding.
- Revisionism vs. Reinterpretation: While reinterpretation involves refining our understanding based on new evidence, revisionism often serves political agendas and distorts historical truths.
- Historical Precedents: Examples such as the Crusades and the European Wars of Religion illustrate how distorted narratives can lead to conflict, rather than reconciliation.
- 20th Century Examples: The rise of Nazi Germany and its use of historical revisionism resulted in catastrophic consequences, including the Holocaust.
- Contemporary Conflicts: Current events, like the Israel-Palestine conflict and Russia's invasion of Ukraine, highlight the ongoing dangers of clashing historical narratives.
In conclusion, history should serve as a guide to foster understanding rather than a tool for vengeance. Acknowledging past injustices is essential, but using them to justify modern conflicts perpetuates cycles of violence. Learning from history through empathy and dialogue is crucial for building a more inclusive future.
GS3/Science and Technology
Novel Silicon Photonics Breakthrough
Why in News?
In a significant advancement, Indian researchers have innovated a novel type of laser that can be directly integrated onto silicon chips, which are fundamental components in modern computing technology.
- New laser technology enhances the capabilities of silicon chips.
- Silicon photonics utilizes light for data transmission, offering superior speed and energy efficiency.
- The integration of lasers onto silicon chips lowers costs and boosts performance.
Additional Details
- Silicon Photonics: This technology employs light (photons) rather than electrical signals to transmit data, enabling faster data transfer with lower energy consumption compared to traditional methods.
- Miniaturized Laser Technology: Researchers have created a laser from gallium arsenide, modified with indium to optimize light emission, facilitating silicon's ability to emit light, which is essential since silicon alone cannot do so effectively.
- This technology is energy-efficient and supports high-performance applications, particularly in sectors requiring rapid data transmission, such as data centers and telecommunications.
- Future improvements aim at enhancing durability for industrial applications, particularly at elevated temperatures.
This breakthrough in silicon photonics not only paves the way for more efficient computing systems but also signifies a leap towards scalable, cost-effective technologies that could transform various industries.
GS2/Polity
Telangana Leads in SC Sub-Categorisation After Supreme Court Nod
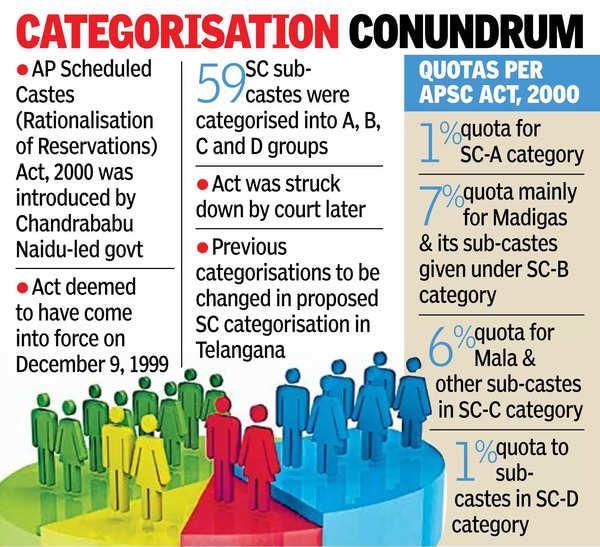 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Telangana government has issued a gazette notification to formally implement Scheduled Caste sub-categorisation, commonly referred to as "reservation within reservation." This marks a significant step in addressing the complexities of caste-based reservations in the state.
- Telangana is the first Indian state to implement sub-categorisation of Scheduled Castes (SCs).
- The initiative follows a Supreme Court ruling that upholds the categorisation of SCs and STs for targeted reservation benefits.
Additional Details
- Telangana Scheduled Castes (Rationalisation of Reservations) Act, 2025: This act, notified on April 14, 2025, coincides with the birth anniversary of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, establishes a new framework for reservation distribution among SCs.
- Group Classification:SCs have been divided into three groups:
- Group I: Reservation Quota: 1%, Sub-Castes Included: 15. Justification: These communities are the most socio-economically and educationally backward among SCs.
- Group II: Reservation Quota: 9%, Sub-Castes Included: 18. These sub-castes have received marginal benefits from existing reservation structures.
- Group III: Sub-Castes Included: 26. These groups have fared relatively better under the current system.
- Despite the internal distribution, the total reservation for SCs remains unchanged at 15%, aiming for equitable access to opportunities among all sub-groups.
The legal basis for this policy is rooted in a landmark Supreme Court judgment delivered by a seven-judge Constitution Bench in August 2024. The court affirmed that states possess the authority to sub-classify SCs and STs, allowing for a more nuanced approach to reservation policies. Key aspects of the judgment include:
- Recognition that reservation benefits were disproportionately accessed by certain sub-castes within SCs.
- Validation of the principle of "reservation within reservation" to uplift the most marginalised sub-groups.
- Clarification that sub-categorisation does not violate Article 14 (Right to Equality) or Article 341 of the Constitution.
The sub-categorisation policy addresses long-standing demands from the Madiga community, which has argued that dominant SC sub-castes such as the Malas have monopolised reservation benefits. The Telangana Government aims to ensure equitable access to education and employment, applying this new classification system to all new recruitment processes.
Looking forward, the Telangana government plans to reassess and potentially enhance reservations after the 2026 Census, contingent on the updated demographic profile of SC communities. Currently, 33 of the 59 SC sub-castes remain in their previous grouping, while only 26 sub-castes have been reshuffled based on recent evaluations.
GS3/Defence & Security
DRDO Successfully Tests Directed Energy Weapon (DEW)
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India’s Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has made significant strides in enhancing the country’s defense capabilities by successfully testing the Mk-II(A) Laser-Directed Energy Weapon (DEW) system. This achievement represents a major milestone in India’s efforts to develop advanced military technologies.
- The Mk-II(A) Laser-DEW system, also known as Sahastra Shakti, has an operational range of 5 km.
- It is designed to neutralize threats such as drones, missiles, and remotely piloted aircraft using a powerful 30-kilowatt laser.
- The system was developed by DRDO’s Centre for High Energy Systems and Sciences (CHESS) in collaboration with various DRDO labs, academic institutions, and Indian industries.
Additional Details
- Operational Mechanism: The Mk-II(A) Laser-DEW system employs radar and Electro-Optic (EO) systems for effective target detection. The laser engages targets at the speed of light, resulting in structural failure or substantial damage.
- Cost Efficiency: The energy required for a few seconds of firing costs as little as a couple of liters of petrol, making it a highly cost-effective defense option.
- The laser system ensures rapid target neutralization while minimizing collateral damage, which is crucial in modern warfare.
The Mk-II(A) Laser-DEW system not only enhances India's defense capabilities but also provides a sustainable, precise, and swift method for addressing evolving aerial threats. This represents a strategic advantage for India in contemporary defense scenarios.
Question: With reference to Indian defence, which one of the following statements is NOT correct?
- (a) With the induction of Prithvi-II, the IAF is the only air force in the world with surface-to-surface ballistic missiles under its command.
- (b) Sukhoi-30 MKI jet fighters can launch air-to-air and air-to-surface precision missiles.
- (c) Trishul is a supersonic surface-to-air missile with a range of 30 km.
- (d) The indigenously built INS Prabal can launch surface-to-surface missiles.
GS2/International Relations
Mehul Choksi Arrested in Belgium
Why in News?
Mehul Choksi, a key accused in the ₹13,500 crore Punjab National Bank (PNB) fraud case, has been arrested in Belgium. India is seeking his extradition to stand trial. Choksi had relocated to Belgium last year for cancer treatment after residing in Antigua and Barbuda since obtaining citizenship there in 2018.
- Choksi is wanted in connection with a significant banking fraud case in India.
- India has initiated extradition proceedings following his arrest in Belgium.
- Extradition processes between countries can be lengthy and complex.
Additional Details
- Extradition Treaty with Belgium: India and Belgium have had an extradition treaty since 1901, allowing extradition based on dual criminality, meaning the offense must be punishable in both nations. Political offenses are exempt from extradition.
- Legal Timeframe: Belgium requires India to provide evidence of Choksi's wrongdoing within two months; otherwise, he could be released.
- Agencies Involved: Choksi's arrest was facilitated by the CBI and the Enforcement Directorate (ED), which are now preparing a legal case that complies with Belgian law.
- Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty (2020): This treaty between India and Belgium aims to enhance cooperation in legal matters, including extradition cases.
- Challenges Ahead: Despite the arrest, the extradition process may be prolonged due to the complexities of European legal procedures.
- Past Precedents: India's previous extradition attempts in Europe, such as those involving Nirav Modi and Vijay Mallya, have experienced significant delays.
- 2021 Dominica Kidnapping Allegation: Choksi's legal team may bring up a 2021 incident where he was allegedly abducted from Antigua to Dominica, raising concerns about his treatment and rights.
- Allegations of Forced Consent: His defense claims that he was coerced into signing a consent document for extradition, potentially undermining his legal protections as an Antiguan citizen.
- Interpol Red Corner Notice Withdrawal: In 2023, Interpol retracted its notice against Choksi due to concerns about his abduction and the risk of an unfair trial in India.
- Human Rights and Health Concerns: Choksi's defense may argue that poor conditions in Indian prisons and health issues could make extradition unsafe.
- Complications Due to Antiguan Citizenship: His citizenship status in Antigua may complicate extradition efforts, as his lawyers might argue that Belgium should consider this before proceeding.
- Expansion Through Gitanjali Group: Choksi expanded his family business, the Gitanjali Group, which operates luxury jewelry stores internationally.
- Fraudulent Use of Bank Credit: From 2014 to 2017, Choksi and his associate Nirav Modi allegedly worked with PNB officials to secure fraudulent Letters of Undertaking to obtain overseas credit.
- LoU Misuse and Loan Defaults: The misuse of Letters of Undertaking led to significant debts when they were rolled over instead of repaid, culminating in a major financial scandal.
- Scale of the Scam: The total fraud is estimated at over ₹13,500 crore, with Choksi individually accused of defrauding PNB of more than ₹6,000 crore.
- ED Action and Fake Assets: The Enforcement Directorate has attached assets valued initially at over ₹5,000 crore, though many were found to be fake, reducing their current estimated value to around ₹2,500 crore.
The situation surrounding Mehul Choksi's arrest and potential extradition is unfolding, with multiple legal and diplomatic hurdles ahead. The outcome may have broader implications for India-Belgium relations and international extradition law.
GS3/Environment
How Governmentality Exacerbates the Problem of Farmers’ Stubble Burning
 Why in News?
Why in News?
A new study by researchers Sujit Raghunathrao Jagadale and Javed M. Shaikh from IIM Amritsar investigates stubble burning, highlighting how government policies and market systems are failing to effectively manage this environmental issue.
- Stubble burning remains a prevalent practice due to economic pressures on farmers.
- Government policies, particularly the MSP, unintentionally encourage practices that exacerbate stubble burning.
- Lack of affordable alternatives and weak enforcement of regulations contribute to the persistence of this practice.
Additional Details
- Cost-Effective Method: Stubble burning is the cheapest technique for farmers to clear fields post-harvest. For instance, farmers burn stubble to quickly prepare their land for the next crop, particularly wheat, without incurring high labor or machinery costs.
- Lack of Affordable Alternatives: There is a scarcity of accessible and efficient methods to manage stubble. Farmers often lack access to technology or subsidies necessary for machines like the Happy Seeder or bio-decomposers.
- Government’s Focus on High-Yield Crops: The Minimum Support Price (MSP) policy promotes the cultivation of wheat and rice, leading to monocropping. For example, farmers are encouraged to continuously grow rice, resulting in excessive stubble that must be disposed of rapidly.
- Debt and Economic Pressure: Many farmers face significant financial burdens, including debt and low crop returns, making stubble burning a means to save time and money. They often sell to middlemen at low prices, leaving them unable to invest in sustainable farming practices.
- Lack of Strong Enforcement or Support: Although stubble burning is punishable by law, enforcement is weak. Farmers feel that there is insufficient governmental support or infrastructure for alternative eco-friendly methods.
In summary, the intersection of economic pressures, governmental policies, and a lack of viable alternatives creates an environment where stubble burning is the most practical solution for many farmers, despite its negative impact on air quality and the environment.
How Does India’s MSP Policy Influence Stubble Burning?
- Encourages Monocropping: The MSP policy incentivizes the cultivation of high-yield crops like rice and wheat, leading to monocropping. Farmers in Punjab frequently grow rice followed by wheat, creating a cycle of stubble that must be burned.
- Limits Crop Diversification: The MSP system prioritizes rice and wheat over other crops, making it economically unfeasible for farmers to transition to more sustainable practices or crops that would reduce stubble burning.
- Financial Constraints: MSP rates for rice and wheat have stagnated, making it more challenging for farmers to invest in alternatives to stubble burning, such as machinery or composting.
What Has the Government Done in This Situation?
- Implemented Subsidies for Machinery: The government has provided subsidies for machinery to help farmers manage stubble without burning. The Punjab government has distributed equipment like straw management machines under the Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization.
- Awareness Campaigns: The government has initiated programs to educate farmers about the harmful effects of stubble burning and promote alternative practices. Campaigns have been launched by the Ministry of Agriculture and local bodies in states like Punjab and Haryana.
- Legal Measures and Penalties: Various state governments have imposed fines on farmers who burn stubble, intending to deter this practice. For example, in Punjab, farmers can face fines of up to Rs 2,500 for violations, although enforcement remains a challenge.
Way Forward
- Promote Crop Diversification: Encourage farmers to transition from paddy to less water-intensive and non-stubble-generating crops with assured procurement and better MSP for alternative crops.
- Strengthen Support and Infrastructure: Enhance access to sustainable stubble management technologies and ensure timely financial and logistic support to small and marginal farmers.
- Expand the availability of solutions like Happy Seeder and bio-decomposer through local cooperatives and custom hiring centers.
Overall, addressing the issue of stubble burning requires a multifaceted approach that includes policy reform, financial support, and education to promote sustainable agricultural practices.
Mains PYQ:
[UPSC 2015] Mumbai, Delhi, and Kolkata are the three Mega cities of the country but the air pollution is a much more serious problem in Delhi compared to the other two. Why is this so?
Linkage: Delhi’s severe air pollution, particularly during certain seasons, results from its geographical location in the Indo-Gangetic Plain, crop stubble burning in nearby states, and weather conditions that trap pollutants.
GS3/Economy
RBI Proposes New Gold Loan Rules
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is set to introduce a new framework for gold loans due to a significant increase in both gold loan outstanding amounts and non-performing assets (NPAs). This surge can be attributed to rising gold prices, which prompted a rise in gold loan disbursals, resulting in NPAs increasing by 28.58% and loan outstanding by 27.26% in the past year.
- Gold loan NPAs increased sharply to ₹6,824 crore as of December 2024 from ₹5,307 crore a year prior.
- RBI has identified and flagged several irregular practices in the gold loan sector.
- New draft guidelines have been issued to enhance regulatory oversight of gold loans.
Additional Details
- Surge in NPAs: The NPAs rose by over ₹1,500 crore, with commercial banks reporting NPAs of ₹2,040 crore, up from ₹1,404 crore in December 2023, while NBFCs reported NPAs of ₹4,784 crore compared to ₹3,904 crore the previous year.
- Gold Loan Outstanding Growth: The total gold loan outstanding for banks and NBFCs reached ₹11,11,398 crore in December 2024, a notable increase from ₹8,73,701 crore the previous year.
- The RBI's review highlighted deficiencies in gold loan practices such as inadequate oversight in third-party sourcing and appraisal, improper valuation, and lack of transparency in auctions.
- RBI Directives: Banks and NBFCs are required to review their gold loan policies, rectify identified gaps, and enhance monitoring of their gold loan portfolios.
- Curbing Evergreening of Loans: The RBI's intervention now mandates full repayment of principal and interest before allowing repledging, making the process more stringent.
The RBI's proposed guidelines also include restrictions on collateral usage, ensuring proper ownership verification, and capping the tenor for bullet repayment loans to a maximum of 12 months. These measures aim to enhance the integrity and stability of the gold loan market amidst growing concerns over NPAs and the overall health of financial institutions involved in gold lending.
GS2/Polity
Unnecessary Amendment: On the RTI Act
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Right to Information (RTI) Act has significantly enhanced accountability among those in power in India since its enactment 20 years ago. However, recent efforts have emerged to undermine some of its crucial provisions, raising concerns among transparency advocates.
- The RTI Act facilitates governmental accountability.
- Amendments proposed in the DPDP Act, 2023 may weaken transparency provisions of the RTI Act.
Additional Details
- Section 8(1)(j) of the RTI Act: This section balances privacy and public interest by allowing denial of personal information only if it does not relate to public activity or causes unwarranted invasion of privacy. For example, while an officer's medical records can be withheld, their salary details are disclosable when serving public interest.
- Public Interest Override: Even personal information must be disclosed if it serves a larger public interest. For instance, a bureaucrat's caste certificate was released when he was accused of using a fake document for a reserved post.
- Accountability of Public Officials: RTI strengthens accountability by enabling scrutiny of officials' actions, qualifications, and benefits. Queries have exposed cases of fraudulent educational degrees among officials.
- Empowerment of Citizens: It enhances democratic participation by allowing citizens access to vital information regarding public functionaries, such as asset declarations of elected representatives.
- Prevention of Blanket Denial: The RTI ensures that authorities cannot reject requests merely by labeling information as 'personal'; they must justify how it affects privacy against public interest.
However, the recent Section 44(3) of the DPDP Act, 2023 raises concerns for transparency advocates by:
- Removing Public Interest Safeguard: This amendment eliminates the provision allowing disclosure of personal information in public interest, which could shield cases like fake caste certificates from scrutiny.
- Enabling Blanket Denial: The vague definition of 'personal information' allows authorities to classify numerous public-relevant data as private, leading to potential denial of educational qualifications and property disclosures.
- Undermining RTI as a Transparency Tool: It restricts access to information that previously helped expose corruption and misconduct.
Impact of the DPDP Amendment
The DPDP amendment deviates from the intent of the K.S. Puttaswamy judgment, which recognized the right to privacy but emphasized the need to balance it with transparency:
- Ignoring the Balancing Principle: The amendment disregards the need for a public interest test, allowing personal information to be withheld even when it concerns corruption or fraud.
- Democratic Accountability: The judgment did not suggest overriding transparency laws like the RTI; instead, it implied that restrictions on information access should be minimal and necessary.
- Distorting Informed Citizenry: The amendment may prevent access to information essential for holding public officials accountable, such as property details or caste certificates.
Potential Denials Under Amended RTI Provisions
- Educational Qualifications: Information about public servants' academic backgrounds may now be classified as personal, leading to denials of RTI queries regarding fake degrees.
- Caste and Community Certificates: Data related to caste status could be withheld, even when crucial for verifying eligibility for reservation benefits.
- Property and Financial Disclosures: Disclosures about government employees' assets may be denied under the guise of personal information.
Way Forward
- Restore Public Interest Safeguard: Amend the DPDP Act to reinstate the public interest clause from Section 8(1)(j) of the RTI Act.
- Define 'Personal Information' Clearly: Provide a precise definition to prevent misuse and ensure critical public accountability data remains accessible.
The discussion surrounding the RTI Act and its amendments highlights ongoing concerns regarding the autonomy and independence of the Information Commission, emphasizing the need for vigilance in maintaining transparency in governance.
GS3/Science and Technology
KATRIN Experiment
Why in News?
The KATRIN (Karlsruhe Tritium Neutrino Experiment) has achieved a significant milestone by measuring the mass of neutrinos with unprecedented precision, contributing to our understanding of these elusive particles.
- The KATRIN experiment is based at the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT) in Karlsruhe, Germany.
- It aims to measure the mass of the electron antineutrino with a precision of less than 0.45 eV/c².
- The experiment utilizes the beta decay of tritium, a radioactive isotope of hydrogen, to infer neutrino mass by analyzing emitted electrons' energy.
- The findings set a new upper limit on neutrino mass, which is nearly twice as precise as previous measurements made in 2022.
Additional Details
- Technological Setup: The experiment features a 70-meter-long beamline with a powerful tritium source and a 10-meter-wide spectrometer designed to measure emitted electrons' energy with high accuracy.
- Data Collection: The data was gathered over five campaigns from 2019 to 2021, totaling 250 days of observations.
- Neutrinos and Their Properties: Neutrinos are extremely light subatomic particles that rarely interact with matter, making detection challenging. They play a crucial role in cosmic structure formation, including galaxies and clusters.
- Neutrinos are produced in processes such as nuclear reactions and beta decay, and trillions of them pass through the human body every second.
The KATRIN experiment represents a leap forward in neutrino research, enhancing our understanding of fundamental particles and their role in the universe.
GS2/Polity
Ambedkar Jayanti Reflection - Judicial Overreach and the Evolving Indian Constitutional Order
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Indian Constitution, which was once a pillar of deliberation and balance, is now perceived to be under transformation—not by the Parliament or the Executive, but by the Judiciary. This shift raises concerns about the integrity of constitutional governance, necessitating a re-examination of the Constitution in the context of B.R. Ambedkar's legacy, which emphasizes limited governmental powers, checks and balances, and democratic accountability. This reflection is particularly relevant on Ambedkar Jayanti, observed on April 14.
- The Supreme Court's recent ruling in the State of Tamil Nadu vs Governor of Tamil Nadu case has significant implications for the federal structure.
- The ruling has been criticized for eroding the separation of powers and undermining the constitutional procedure.
- The potential for judicial overreach risks altering the fundamental principles of governance as envisioned by B.R. Ambedkar.
Additional Details
- Judicial Action: The Supreme Court invoked Article 142 to set time limits for gubernatorial assent to Bills and asserted that the President "ought" to consult the Court under Article 143, which marks a significant departure from traditional legislative processes.
- Separation of Powers: The judgment has been perceived as a violation of Article 74, which mandates that the President acts on the advice of the Council of Ministers. By asserting judicial authority over executive functions, the Supreme Court has blurred the lines between the legislative and judicial branches.
- Federalism Concerns: The ruling affects all states without proper representation in the proceedings, challenging the principles of federal consultation and cooperative federalism.
- Judicial Conduct: The decision, issued by a two-judge bench, raises questions regarding procedural adherence to Article 145(3), which calls for a constitution bench for significant constitutional questions, potentially setting a dangerous precedent.
In conclusion, the ongoing developments in judicial interpretations and actions pose a serious challenge to the constitutional order envisioned by Ambedkar. The judiciary must reflect on its role: Are they upholding the Constitution, or are they in the process of rewriting it? On this Ambedkar Jayanti, it is crucial to reaffirm the commitment to the foundational principles of democracy and governance.
GS2/Polity
Feminism for Polarised Times
Why in News?
The implementation of the Women’s Reservation Bill, 2023, represents a pivotal change in India’s socio-political environment, marking a significant advancement in gender equity. This bill has elevated feminist issues to the forefront of political discussions, yet it has also introduced complexities that challenge the engagement with feminism in contemporary society.
- The Women’s Reservation Bill signifies a transformative shift in gender equity within Indian politics.
- Feminist discourse is becoming increasingly polarized and may overlook the emotional complexities of lived experiences.
- Understanding the intersection of structural and interpersonal dynamics is essential for a nuanced feminist framework.
- Micro-level changes and daily negotiations play a critical role in advancing gender equality.
Additional Details
- Feminism’s Two Terrains:The two primary areas of feminism are:
- Structural: Institutional frameworks that marginalize women, such as political representation and economic opportunity.
- Interpersonal: Dynamics within relationships and family settings that influence gender roles.
- Complicated Interactions: Many men engage in sacrifices for their families that reflect care and duty, complicating the narrative of patriarchal oppression.
- Social Change: Significant reforms often arise from everyday negotiations, emphasizing the importance of recognizing contributions from men acting as allies.
- Challenges in Feminist Discourse: There is a tendency to oversimplify experiences in feminist rhetoric, which can alienate potential allies and misrepresent realities.
- Compassionate Feminism: A more inclusive approach that acknowledges the struggles of all genders, aiming for solidarity rather than division.
In conclusion, while it is essential to confront systemic injustices, a compassionate and nuanced approach to feminism that embraces complexity and promotes understanding can lead to more effective and equitable relationships and societal transformation.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 15th April 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the implications of reversing historical narratives in the context of political discourse? |  |
| 2. How does the recent breakthrough in silicon photonics impact technology development? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of Telangana's leadership in SC sub-categorization after the Supreme Court's approval? |  |
| 4. What advancements have been made in directed energy weapon (DEW) technologies by DRDO? |  |
| 5. How does governmentality contribute to the issue of farmers' stubble burning in India? |  |
















