UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 22nd October 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
eShram - One Stop Solution
Source: Financial Express

Why in news?
Recently, the Union Ministry of Labour & Employment and the Ministry of Youth Affairs & Sports introduced the eShram One Stop Solution in New Delhi. This initiative aims to streamline the access of various Social Security Schemes for unorganised workers who are registered on the eShram portal.
About eShram - One Stop Solution:
- The eShram platform is designed to facilitate seamless access to multiple government welfare schemes for unorganised workers.
- It aims to simplify the registration process for these workers, making it easier for them to benefit from government schemes.
- This platform serves as a connection between workers and the numerous benefits provided by the government, ensuring a more straightforward and transparent registration process.
- It consolidates and integrates data from various Central Ministries and Departments into a unified repository.
- Key welfare schemes such as One Nation One Ration Card, Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, National Social Assistance Programme, National Career Service, and Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maandhan have been integrated into eShram.
What is eShram Portal?
- Launched by the Ministry of Labour and Employment in 2021, the eShram portal aims to create a comprehensive National Database of Unorganised Workers.
- Registration on the portal is fully Aadhaar verified and requires Aadhaar seeding.
- Any unorganised worker can register on the portal based on self-declaration.
- The portal allows for registration under 400 different occupations spanning across 30 broad sectors.
GS3/Environment
Nilgiri tit Butterfly
Source: The Hindu

Why in news?
Recently, butterfly enthusiasts in the Nilgiris have documented the first instance in India of the Nilgiri tit Butterfly (Hypolycaena nilgirica) using a large terrestrial orchid as a host plant.
About Nilgiri tit Butterfly:
- This butterfly belongs to the family Lycaenidae.
- It was first identified in 1884 in Coonoor, located in the Nilgiris, and has also been recorded in Sri Lanka.
- Additional sightings have occurred in the Kalakkad Mundanthurai Tiger Reserve, Chinnar Wildlife Sanctuary in Idukki district, and Silent Valley National Park in Palakkad district, Kerala.
Appearance:
- The male Nilgiri tit is characterized by a dark reddish purple-brown coloration on its upper side.
- It features two black spots that are rimmed in orange near its tails.
- In contrast, the female is a pale brown color.
Habitat:
- This butterfly is typically found in forested areas and lush gardens, particularly those containing orchids.
- It has been observed laying its eggs on the inflorescence of the larval host plant, Eulophia epidendraea, which is a species of terrestrial orchid.
- This marks the first documented instance of the Nilgiri tit utilizing this specific type of plant as a host.
- The terrestrial orchid is commonly found on rocky slopes in humid environments.
Conservation Status:
- This endemic butterfly is classified under Schedule II of the Wildlife Protection Act, indicating its need for protection and conservation efforts.
Significance:
- The discovery of the Nilgiri tit Butterfly utilizing a new host plant highlights the importance of biodiversity and the need for continued research and conservation in the Nilgiris region.
GS3/Environment
What is the Nature Restoration Law (NRL)?
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The Nature Restoration Law (NRL), enacted by the European Union (EU), serves as a significant model for addressing India's environmental challenges.
About Nature Restoration Law (NRL):
- It is a legislative measure aimed at addressing the interconnected crises of climate change, biodiversity loss, and environmental degradation.
- This law represents the first comprehensive, continent-wide initiative of its type.
- The NRL is a crucial component of the EU Biodiversity Strategy, which establishes binding objectives for the restoration of degraded ecosystems.
- Its focus is on ecosystems that have the highest potential for carbon capture and storage, as well as minimizing the impacts of natural disasters.
- Member States are required to restore a minimum of 20% of the EU's land and marine areas by the year 2030.
- This restoration mandate encompasses various environments, including terrestrial, coastal, freshwater, forest, agricultural, and urban areas.
- By 2050, the restoration efforts are expected to cover all ecosystems classified as "requiring restoration."
- The NRL sets forth obligations to enhance urban green spaces, restore free-flowing rivers by removing artificial barriers, increase pollinator populations, and contribute to the goal of planting 3 billion additional trees across the EU.
- Member States must develop "restoration plans" that outline strategies for meeting these targets and ensuring that restored areas do not significantly deteriorate.
- While crafting these Nature Restoration Plans, it is essential for Member States to assess socio-economic impacts and benefits, as well as estimate the financial resources necessary for implementation.
GS2/International Relations
What is the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)?
Source: International Atomic Energy Agency

Why in News?
The 2024 edition of the IAEA’s Climate Change and Nuclear Power report has been released, highlighting the need for a significant increase in investment to achieve goals for expanding nuclear power.
About International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA):
- The IAEA serves as the primary intergovernmental platform for scientific and technical collaboration in the nuclear sector.
- It is commonly referred to as the "Atoms for Peace and Development" organization and operates within the framework of the United Nations.
- The agency is dedicated to ensuring the safe, secure, and peaceful application of nuclear science and technology.
History:
- Established as an autonomous entity through its own international treaty known as the IAEA Statute.
- Despite its independent status, the IAEA reports to both the United Nations General Assembly and the Security Council.
- The agency's headquarters is located in Vienna, Austria, and it currently comprises 178 member states.
Structure:
- General Conference: This assembly includes all member states and meets annually to approve budgets, programs, and discuss the IAEA's policies.
- Board of Governors: Comprising 35 members, this board convenes approximately five times a year to execute statutory functions, endorse safeguards agreements, and appoint the Director General.
- The IAEA’s daily operations are managed by the Secretariat, led by the Director General.
Functions of IAEA:
- The agency collaborates with member states and various global partners to advocate for the safe and peaceful use of nuclear technologies.
- It implements nuclear safeguards involving monitoring, inspecting, and analyzing information to ensure nuclear activities are solely peaceful.
- The IAEA works to detect and prevent the diversion of nuclear materials for weapons purposes.
- It plays a critical role in fulfilling the mandates established by the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), which acts as a primary defense against the spread of nuclear weapons.
- Additionally, the IAEA aids member states by promoting the exchange of scientific and technical knowledge.
- It enhances capabilities at national, regional, and international levels to effectively respond to nuclear and radiological emergencies, which is vital for minimizing their impact.
GS3/Environment
What are Hornets?
Source: Forbes

Why in News?
According to a recent study, a species of hornet that often munches on foods containing alcohol can hold its liquor, without any side effects, at levels that no other known animal can tolerate.
About Hornets:
- Hornets are a type of social wasp, living in large, organized colonies.
- They consist of around 20 species, primarily found in Asia, Europe, and Africa, with one species introduced in North America.
- Hornets belong to the Vespidae family, which includes various wasp species such as yellow jackets and paper wasps.
- Typically, hornets have a coloration of black or brown with yellow or yellowish markings.
- Due to their size, hornets are often perceived as more dangerous than other wasp species, although they are not necessarily more aggressive.
- They release more venom per sting than any other stinging insect.
- The northern giant hornet, also known as the Asian giant hornet (V. mandarinia), is recognized as the largest wasp species globally.
- Hornets prefer to build their nests in elevated locations.
Diet
- Hornets have a diverse diet, primarily consisting of sugars and proteins.
- They prey on various insects, including honeybees and other social wasps.
- Hornets chew their prey into a paste to feed their larvae.
GS2/International Relations
Z-Morh project in Kashmir
Source: Indian Express

Why in news?
On October 20, a violent attack occurred involving suspected militants targeting workers of APCO Infratech, the company responsible for constructing the Z-Morh tunnel along the Srinagar-Sonamarg highway in Jammu and Kashmir. This incident resulted in the deaths of seven workers, marking the first militant strike against a significant infrastructure project in the area. Previously, such targets had not been a focus for militants in Jammu and Kashmir.
About
- The Z-Morh tunnel spans 6.4 kilometers and connects the Sonamarg tourist resort with Kangan town located in central Kashmir's Ganderbal district.
- Situated near Gagangir village, not far from Sonamarg, this tunnel aims to provide all-weather access to the popular tourist destination along the Srinagar-Leh highway.
- The name "Z-Morh" is derived from the Z-shaped road configuration at the site of the construction.
Commencement of the project
- The Z-Morh tunnel project was initially drafted by the Border Roads Organisation (BRO) in 2012 and was first awarded to Tunnelway Ltd.
- Subsequently, the project was transferred to the National Highways & Infrastructure Development Corporation Limited (NHIDCL).
- Although its completion was anticipated by August 2023, the project encountered several delays.
- A soft opening occurred in February 2024, but the official inauguration was postponed due to the Model Code of Conduct related to the Jammu and Kashmir Assembly elections.
Need for the tunnel
- The tunnel is being constructed at an altitude exceeding 8,500 feet, an area vulnerable to snow avalanches during winter.
- This leads to the closure of access roads to Sonamarg for most of the winter season.
Strategic importance of the Z-Morh tunnel
- The Z-Morh tunnel is part of the broader Zojila tunnel project, designed to ensure year-round connectivity between Srinagar and Ladakh.
- The Zojila tunnel will connect Sonamarg to Drass in Ladakh, with an expected completion date of December 2026.
- While the Z-Morh tunnel will enhance access to the Sonamarg health resort, it is also critical for providing prompt military access to Ladakh.
- This tunnel is essential for establishing all-weather road connectivity between Srinagar, Drass, Kargil, and Leh, reducing reliance on air support for military operations.
- Improved connectivity will assist in troop and supply transport, decrease costs, and prolong the operational lifespan of aircraft used by the Indian Air Force.
- This project is vital for the Indian defense forces stationed in Siachen and Eastern Ladakh, where ongoing tensions with Pakistan and China exist.
Recent terror attack on infra project in J&K and the exposing of vulnerabilities
- The attack on APCO Infratech workers signifies a notable event in Jammu & Kashmir, highlighting a resurgence of terrorism.
- This incident indicates a larger strategy aimed at exposing vulnerabilities within the region.
- It suggests a calculated attempt by Pakistan’s deep state to undermine peace and stability, particularly following the peaceful elections and the establishment of a democratic government in Srinagar.
- The term "deep state" refers to an alleged clandestine network of unelected officials and private entities operating outside the law to influence government policy.
Pakistan’s Deep State and its Role
- The Pakistani deep state appears intent on reinstating its influence in Jammu & Kashmir by instigating violent incidents.
- Its objective is to thwart India's efforts to stabilize Jammu & Kashmir, especially after the abrogation of Article 370.
- Strategic terror events like this attack are perceived as means to prevent the establishment of peace dividends in the region.
Targeting Peripheral Areas and Infrastructure Projects
- While urban areas such as Srinagar, Anantnag, and Baramulla remain heavily secured, attackers have shifted their focus to less protected peripheral regions.
- The Z-Morh tunnel, as a flagship infrastructure initiative, necessitates a substantial workforce and specialized skills.
- This attack may signal a broader threat to infrastructure projects in Jammu & Kashmir’s peripheral areas, including the Kishanganga project and railway endeavors in Banihal and Qazigund.
Possible Chinese angle
- The People’s Anti-Fascist Front (PAFF), a Pakistani terror organization, released a statement commending The Resistance Front (TRF), an offshoot of Lashkar-e-Taiba, for the recent attack in Jammu and Kashmir that resulted in seven civilian fatalities.
- PAFF characterized the attack as "strategic," claiming it was designed to disrupt Indian military deployments towards the eastern border while invoking the support of "Chinese friends" in their justification.
- Despite the historical strategic ties between China and Pakistan, there is currently no evidence implicating Beijing in this incident.
Broader Pattern of Unusual Activities
- The attack may be part of a larger scheme aimed at undermining India’s developing strategic confidence.
- Recent occurrences, including bomb hoaxes, unusual explosions, and diplomatic pressure over transnational issues, appear interconnected, indicating a broader effort to place India on the defensive.
Conclusion
- The proxy conflict in Jammu & Kashmir is ongoing. Despite a reduction in violence frequency, it is crucial to remain vigilant.
- Efforts should concentrate on combating terror networks, addressing financing, and tackling drug mafias to maintain stability in the region.
GS3/Demography
How South India Deals with its Aging Population?
Source: Indian Express
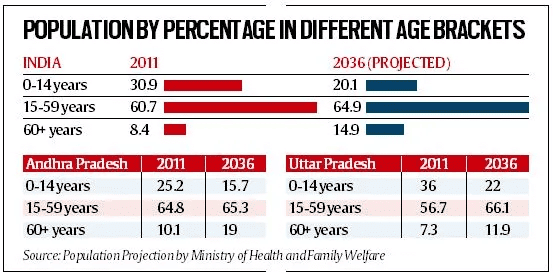
Why in news?
In a recent development, Andhra Pradesh Chief Minister N. Chandrababu Naidu announced plans for a law designed to encourage families to have more children. His decision stems from worries about the state's shrinking younger population, as fertility rates have fallen below the replacement level. The Chief Minister expressed that having fewer than two children could lead to a swift decline in the youth demographic, which may have long-term consequences for the state.
Context & Concerns of Southern States:
- Naidu's comments reflect a larger discussion on demographic trends in Southern India.
- States like Tamil Nadu and Kerala have successfully reduced their fertility rates over the years.
- This decline in birth rates has contributed to an aging population, raising concerns about future political representation in the Indian Parliament.
- Tamil Nadu's Chief Minister M.K. Stalin has voiced concerns about a potential decrease in South India's parliamentary seats due to low population growth.
India's Aging Population and Fertility Trends:
- The 2021 Census has been delayed, so the latest population data comes from a 2020 report by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- The report shows that the percentage of individuals aged 60 and above is expected to rise significantly across India.
- This trend is particularly pronounced in Southern states, which achieved low fertility rates earlier than Northern states.
- For instance, Uttar Pradesh will not reach the replacement fertility rate of 2.1 children per woman until 2025, over two decades after Andhra Pradesh.
- From 2011 to 2036, India's population is projected to increase by around 31 crore individuals.
- Half of this growth is expected to occur in five states: Bihar, Maharashtra, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh.
- Conversely, the five Southern states (Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Telangana) will contribute only about 2.9 crore to this growth during the same timeframe.
- The elderly population (aged 60+) is expected to more than double from 10 crore in 2011 to 23 crore by 2036.
- This means nearly one in four people could be over 60 by 2036, while Northern states are projected to retain a younger demographic with only 12% of their population in the 60+ age bracket.
Why is an Aging Population a Concern?
- An aging population presents distinct challenges separate from a decreasing overall population.
- The dependency ratio—representing those not in the workforce (under 15 and over 60)—is a major concern.
- A high dependency ratio indicates that a larger segment of the population relies on the working-age group for economic support.
- This situation may necessitate increased investments in healthcare and social security for the elderly.
- Moreover, a smaller population relative to other states could affect political representation in the Lok Sabha.
- Southern states, having undergone earlier demographic transitions, fear losing parliamentary seats to Northern states where population growth remains robust.
Do Pro-Natalist Policies Work?
- CM Naidu referenced examples from nations like Japan and China, where governments have tried to boost fertility rates to counter aging populations.
- Experts suggest that pro-natalist policies—measures encouraging larger families—have seen limited success.
- Such policies often falter in prosperous and educated societies.
- While Scandinavian countries have managed to stabilize fertility rates through family support systems and gender equality measures, others, such as France and South Korea, have not achieved significant success despite financial incentives.
Why CM Naidu’s Comments Matter?
- Naidu’s statements mark a notable shift in political dialogue surrounding population issues.
- In the past, India faced challenges of overpopulation and high fertility rates, prompting efforts to control population growth.
- Andhra Pradesh achieved a replacement fertility rate of 2.1 children per woman back in 2004, even having laws that restricted individuals with more than two children from contesting local elections—laws that have since been repealed.
- With declining fertility rates, India now holds the title of the world’s most populous country, prompting a new conversation focused on balancing population control with the need for enough young people to fuel economic growth.
What is the Way Forward?
- Experts suggest that ineffective pro-natalist policies should be complemented by strategies such as migration to address demographic challenges.
- Internal migration from Northern to Southern states could help mitigate the workforce shortage in the South.
- Southern states could benefit from absorbing working-age migrants, thus avoiding the costs associated with raising and educating a younger population.
- This approach mirrors the model of the United States, where immigration has sustained economic growth by providing a steady influx of working-age individuals.
- Economists advocate for focusing on improving labor productivity rather than merely increasing population numbers.
- By leveraging the ongoing demographic dividend—where a significant portion of the population is of working age—India can maximize its economic potential.
In conclusion, as discussions about incentivizing larger families emerge, the broader debate on demographic challenges intensifies. While the state grapples with the real issue of a declining younger population, global evidence suggests that simply encouraging larger families may not be the optimal solution. Instead, a multifaceted approach emphasizing labor productivity and addressing demographic needs may better balance India's population dynamics and economic requirements.
GS3/Defence & Security
Dealing with Fake Bomb Threats in Aviation
Source: Indian Express

Why in News?
Over the past week, nearly 100 fake bomb threats, mainly originating from anonymous social media accounts, have raised significant concerns about aviation safety in India. Although all the threats were hoaxes, they resulted in widespread disruptions for airlines, passengers, and crew members. In light of these events, it is essential to analyze the security protocols in place when a flight receives a bomb threat, as well as the efforts of the government and the Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA) to handle and prevent similar situations in the future.
Bomb Threat Response Protocol:
- Mid-air bomb threat:
- When a bomb threat is received during a flight, the Bomb Threat Assessment Committee (BTAC) is convened to assess the threat's credibility.
- Pilots collaborate with Air Traffic Control (ATC) to decide whether to head back to the departure airport, proceed to the destination, or divert to the nearest airport.
- Pre-departure bomb threat:
- If a bomb threat is reported before take-off, the aircraft is moved to a secure area for comprehensive checks, in coordination with the BTAC.
- International flights:
- For bomb threats targeting international flights outside Indian airspace, Indian agencies coordinate with international ATC and security agencies to divert the flight to the nearest airport.
Response to Recent Spate of Fake Bomb Threats Targeting Indian Airlines:
- Swift response from airlines:
- Airlines promptly activated anti-terrorism protocols and reached out to the MoCA for support. Despite stringent security measures, all threats were treated with utmost caution.
- Inter-Ministerial coordination:
- The MoCA, Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA), and agencies like the Bureau of Civil Aviation Security (BCAS) are collaborating closely to address the surge in threats.
- Enhanced security:
- In response to the threats, airport security has been intensified, with a 10% increase in security checks.
- Expanded CCTV coverage has been implemented to ensure that no suspicious items are brought on board.
- The MoCA is actively working to upgrade security protocols.
- Deterrence and investigation efforts:
- The BCAS and airport-specific BTACs are taking a proactive approach to evaluate each threat based on recent incidents.
- While focusing on passenger safety, the committees aim to minimize disruptions by refining their assessment processes.
- Tracking culprits:
- The government is striving to identify those behind the fake threats, but the use of VPNs and anonymous social media accounts complicates tracking efforts.
- Efforts are underway to collaborate with social media platforms and VPN providers to pinpoint the culprits.
Legislative Action to Curb Fake Bomb Threats:
- Current arrangement:
- Currently, hoax bomb threats are managed under the country's criminal laws, as there are no specific legal provisions addressing bomb threats to aircraft.
- Amendments to Aircraft Security Rules:
- The government plans to revise the Aircraft Security Rules (governed by the Aircraft Act 1934) to include individuals responsible for hoax bomb threats in the no-fly list, thus barring them from boarding flights.
- This list currently applies only to unruly passengers onboard but will expand to encompass those issuing threats through social media or other means.
- Changes to SUASCA Act, 1982:
- Amendments to the Suppression of Unlawful Acts against Safety of Civil Aviation (SUASCA) Act are being proposed.
- Presently, the Act addresses in-flight incidents, but the government seeks to broaden its scope to include bomb threats even when aircraft are grounded, making such offenses cognizable under the law.
- This would potentially lead to severe fines and prison sentences for offenders.
Conclusion:
The increase in hoax bomb threats is significantly disrupting Indian airlines and placing immense pressure on aviation security. The government is implementing measures to tighten regulations, yet the challenges of responding to and mitigating such threats continue to burden the system.
GS3/Science and Technology
Caenorhabditis elegans
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
Recently, while accepting the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine this year, molecular biologist Gary Ruvkun spent a few minutes lauding his experimental subject: a tiny worm named Caenorhabditis elegans.
About Caenorhabditis elegans:
- Caenorhabditis elegans is a nematode worm, known for being a small, simple, and highly organized organism.
- This worm matures from a fertilized egg to an adult, measuring approximately one millimeter, within just 3-5 days.
- It has significantly contributed to our understanding of human biology and various biological processes.
- It was the first multicellular organism to have its entire genome sequenced and its neural connections mapped.
- Caenorhabditis elegans has two distinct sexes: hermaphrodites and males.
- The hermaphrodite can be seen as a female that produces a small number of sperm and can reproduce either through self-fertilization using its own sperm or through cross-fertilization by mating with a male.
- Self-fertilization allows a single heterozygous worm to create homozygous offspring.
What are Nematodes?
- Nematodes belong to the phylum Nematoda and are among the most numerous animals on the planet.
- They exist in a variety of habitats, acting as parasites in both plants and animals or as free-living organisms found in soil, freshwater, marine environments, and even in unconventional locations such as vinegar, beer malts, and deep crustal water-filled cracks.
Features
- Nematodes exhibit bilateral symmetry and have an elongated body that typically tapers at both ends.
- Many species possess a pseudocoel, which is a fluid-filled cavity situated between the digestive tract and the body wall.
GS3/Defence & Security
India’s fourth nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN)
Source: Mint

Why in News?
India has successfully launched its fourth nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine (SSBN) at the Ship Building Center (SBC) in Visakhapatnam, significantly bolstering its nuclear deterrence capabilities.
Details about the fourth SSBN:
- The fourth SSBN is designated as S4*.
- This submarine features approximately 75 percent indigenous components.
- It is armed with K-4 ballistic missiles, which have a striking range of 3,500 km and are deployed through vertical launch systems.
- In contrast, the first SSBN, INS Arihant, is equipped with K-15 nuclear missiles that have a range of 750 km.
- INS Arighaat and INS Aridhaman, the subsequent submarines, are enhancements of INS Arihant and are exclusively armed with K-4 ballistic missiles.
- The launch of S4* comes after the commissioning of INS Arighaat in August 2024, while INS Aridhaman is anticipated to be commissioned next year.
- INS Arihant and INS Arighaat are already conducting deep-sea patrols.
Naming Convention:
- India's first leased nuclear attack submarine was named INS Chakra, designated as S1.
- INS Arihant was designated S2, INS Arighaat S3, and INS Aridhaman S4.
- S4* is the most recent addition and awaits a formal name.
Significance of SSBNs:
- SSBNs are advanced military assets utilized by a limited number of countries, including the United States, Russia, China, the United Kingdom, France, and India.
- These submarines are equipped with submarine-launched nuclear ballistic missiles.
- SSBNs are designed to ensure a reliable second-strike capability, reinforcing strategic stability through the principle of mutual assured destruction.
- They offer unlimited range and endurance, with operational limits dictated primarily by food supplies, crew fatigue, and maintenance needs.
Conclusion:
- The launch of S4* enhances India's strategic capabilities, contributing to national security.
- Continued investments in indigenous military technology are crucial for India's defense posture.
GS3/Environment
What is Crepidium assamicum?
Source: Assam Tribune
Why in News?
A recently identified species of orchid, Crepidium assamicum, has been discovered in Dibru Saikhowa National Park.
About Crepidium assamicum:
- It belongs to the genus Crepidium.
- This species was found in Dibru Saikhowa National Park, located in Assam.
- Dr. Jintu Sarma and Khyanjeet Gogoi, both assistant professors from the Department of Botany at Guwahati College, made the discovery. Dr. Gogoi is well-known as the Orchid Man of Assam.
- With the addition of this species, the total number of Crepidium species in India has risen to 19, while the global count has reached 281.
- Scientific studies indicate that there are approximately 27,000 diverse species of orchids worldwide, with India hosting around 1,265 species, and Northeast India accounting for about 800 of these. Assam alone is home to around 414 orchid species.
Key Facts about Dibru Saikhowa National Park:
- Dibru Saikhowa National Park is also recognized as a biosphere reserve, situated across the Dibrugarh and Tinsukia districts.
- The park is bordered by the Brahmaputra and Lohit Rivers to the north and the Dibru River to the south.
- Vegetation: The forest types within Dibru Saikhowa include:
- Semi-evergreen forests
- Deciduous forests
- Littoral and swamp forests
- Patches of wet evergreen forests
- This park features the largest Salix swamp forest in northeastern India.
- Climate: The area experiences a tropical monsoon climate characterized by:
- Hot and humid summers
- Cool and generally dry winters
- Flora: Dominant plant species found in the park include:
- Dillenia indica
- Bischofia javanica
- Bombax ceiba
- Lagerstroemia parviflora
- Fauna: The park is home to a variety of wildlife, including:
- Tigers
- Elephants
- Leopards
- Jungle Cats
- Bears
- Small Indian Civets
- Squirrels
- Gangetic Dolphins
- Hoolock Gibbons
- Feral Horses
|
38 videos|5275 docs|1115 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 22nd October 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the eShram portal and its significance for workers in India? |  |
| 2. What are the key features of the Nilgiri tit butterfly and its habitat? |  |
| 3. What does the Nature Restoration Law (NRL) aim to achieve? |  |
| 4. What is the role of the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)? |  |
| 5. What are hornets and how do they differ from other wasps? |  |





















