UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 23rd December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS1/History & Culture
Rann Utsav
Source: Mint
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Prime Minister of India has extended an invitation to the public to experience the Rann Utsav, an ongoing cultural festival that will continue until March 2025.
- The Rann Utsav is an annual cultural festival organized by the Gujarat Tourism Department.
- It takes place in the Great Rann of Kutch, the largest salt desert in India.
- The festival showcases the rich cultural and artistic heritage of Kutch and attracts both domestic and international tourists.
About the Rann of Kutch
- Location: The Rann of Kutch is a vast area of salt marshes located along the India-Pakistan border, primarily in the Kutch district of Gujarat.
- Divisions: The Great Rann stretches east to west, bordered by the Thar Desert to the north and Kutch Hills to the south.
- Little Rann of Kutch: Situated southeast of the Great Rann, this area extends towards the Gulf of Kutch.
- Geographical Features: The region lies close to sea level, connected to the Arabian Sea via Kori Creek.
- Unique Ecosystem: It is recognized as the only large flooded grassland zone in the Indomalayan realm, supporting diverse flora and fauna.
Climate
- Summer: Temperatures can soar to an average of 44°C, with peaks reaching up to 50°C.
- Winter: The region experiences freezing temperatures during the winter months.
Ecological Significance
- Flora and Fauna: The Great Rann is home to the endangered Indian Wild Ass (Khur) and features ecosystems such as mangroves, desert vegetation, and grass-covered patches vital for local wildlife.
- Wildlife Sanctuary: The region is part of the Wild Ass Wildlife Sanctuary, which is India’s largest wildlife sanctuary.
- Biodiversity: The juxtaposition of desert and sea fosters unique plant and animal life.
Historical and Cultural Significance
- The Rann has a rich history, having been home to neolithic settlements and later an important center for the Indus Valley Civilization.
- It has been part of various historic empires, including the Mauryas and the Guptas, reflecting its historical lineage.
- Kutch Desert: This expansive desert area is bordered by Sindh (Pakistan) to the northwest and Rajasthan to the northeast.
- The region serves as an example of Holocene sedimentation, showcasing geological and environmental diversity.
The Rann Utsav not only highlights the cultural richness of Kutch but also emphasizes the ecological and historical significance of the Rann of Kutch, making it a unique destination for travelers.
GS2/Governance
Understanding Dark Patterns and Consumer Protection Initiatives
Source: The Statesman
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Department of Consumer Affairs is set to launch the 'Jago Grahak Jago App,' 'Jagriti App,' and 'Jagriti Dashboard' on National Consumers Day, December 24, 2024, aimed at protecting consumers from deceptive practices known as dark patterns.
- Dark Patterns: Deceptive design practices in user interfaces that mislead consumers.
- Consumer Protection Initiatives: New apps and tools to identify and report dark patterns.
Additional Details
- What are Dark Patterns? Dark patterns refer to deceptive design strategies that manipulate users into actions they did not intend to take. Coined by Harry Brignull in 2010, these patterns undermine consumer autonomy and can lead to misleading advertisements and unfair trade practices.
- Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA): In 2023, the CCPA issued guidelines for the prevention and regulation of dark patterns, identifying 13 specific types, including false urgency, basket sneaking, and trick wording.
- Jago Grahak Jago App: This app offers crucial information about e-commerce URLs, alerting users to potentially unsafe sites.
- Jagriti App: Users can report URLs suspected of containing dark patterns, which will be processed as complaints by the CCPA.
- Jagriti Dashboard: This tool generates real-time reports on e-commerce URLs to detect dark patterns effectively.
The implementation of these applications is significant in aiding the CCPA to identify and eliminate dark patterns, thereby expediting the resolution of consumer complaints and enhancing consumer rights protection.
GS3/Economy
Indian Rupee Falling Against the US Dollar
Source: The Hindu
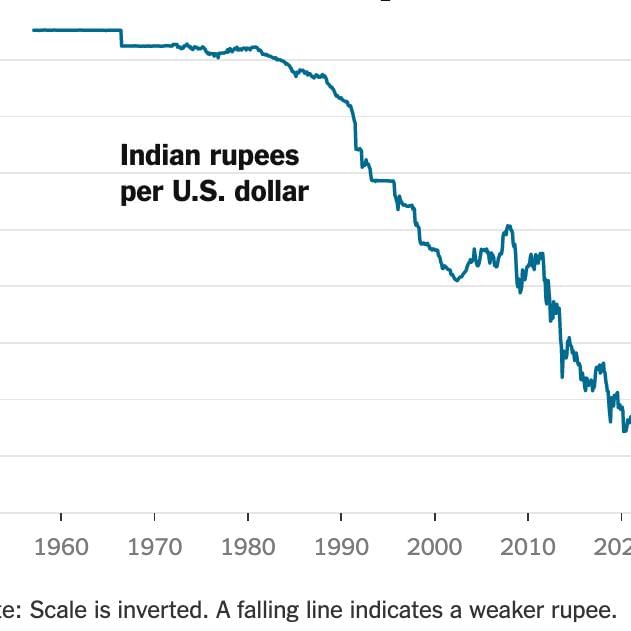 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Indian rupee has recently depreciated against the US dollar, surpassing the 85 mark. In April, the exchange rate was around 83, and a decade ago, it was approximately 61. This trend indicates a consistent decline in the rupee's value relative to the dollar.
- The exchange rate is currently affecting the rupee, which has seen fluctuations over the years.
- Various factors determine the demand for the rupee compared to the dollar, impacting its exchange rate.
- Policy recommendations are suggested to address the falling rupee.
Additional Details
- Understanding Exchange Rates: The Indian rupee is used for domestic transactions but must be exchanged for foreign currencies like the US dollar for international purchases. The exchange rate specifies how many rupees are necessary to obtain one unit of a foreign currency.
- Factors Influencing Exchange Rates: Exchange rates are primarily driven by the dynamics of demand and supply. If the demand for US dollars exceeds that for Indian rupees, the dollar strengthens, leading to a weaker rupee.
- Trade in Goods: A higher import rate from the US compared to exports leads to increased demand for dollars, thus weakening the rupee.
- Inflation Differences: Higher inflation in India compared to the US diminishes the rupee's value, prompting investors to withdraw investments.
- The rupee recently fell to 85.11 against the dollar due to a stronger dollar, not necessarily a weaker rupee.
The depreciation of the rupee has significant repercussions, particularly on inflation, as India imports a large portion of its crude oil requirements. This increase in import costs can exacerbate the trade and current account deficits, further pressuring the exchange rate. However, a weaker rupee may enhance the attractiveness of remittances and benefit some exporters, provided they do not rely heavily on imported raw materials.
GS3/Economy
What Can the Budget Do for Agriculture
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
The upcoming Union Budget 2025-26 presents a pivotal moment to transform India's agricultural sector, which is essential for the nation's economy. This budget must focus on strategic initiatives that enhance productivity, improve farmer incomes, and address environmental challenges.
- India's agriculture faces significant threats from climate change, necessitating resilient agricultural systems.
- A substantial increase in agricultural research and development (agri-R&D) investment is essential.
- Adopting sustainable farming practices is crucial to restoring soil health and enhancing productivity.
- Reforming fertilizer subsidies and export policies can improve farmer incomes and market conditions.
Additional Details
- Climate Change Impact: The agriculture sector is experiencing a 0.7°C rise in temperature and a 6% reduction in monsoon precipitation, adversely affecting crop yields.
- Investment in Agri-R&D: Currently, India invests less than 0.5% of its agricultural GDP in R&D. Doubling this investment to at least 1% would support the development of climate-resilient crops and innovative farming practices.
- Sustainable Farming Practices: Strategies such as organic amendments and crop rotation can restore soil health and increase carbon sequestration, contributing to climate mitigation.
- Fertilizer Use Balance: The government's Natural Farming Mission must integrate both bio-fertilizers and chemical fertilizers to meet the nutritional needs of a growing population.
- Technological Innovations: Encouraging the use of advanced fertilizers like nano-urea can enhance nutrient efficiency, reducing environmental impact.
- Modernizing Subsidies: Transitioning to direct income transfers based on landholding size can improve resource efficiency and align with farmers' economic interests.
- Building Agri-Value Chains: Creating comprehensive food systems that ensure farmers retain a larger share of consumer spending, similar to the dairy sector, can enhance income stability.
- Market Reforms: Reforming export policies to eliminate bans on key commodities is necessary to ensure fair prices and support farmers' profitability.
In conclusion, the Union Budget 2025-26 must prioritize agricultural reforms that address climate challenges, rationalize subsidies, and enhance value chains. By adopting a sustainable and market-oriented approach, India can ensure food security, improve farmer livelihoods, and protect its natural resources.
GS3/Science and Technology
Understanding Speed Guns
Source: First Post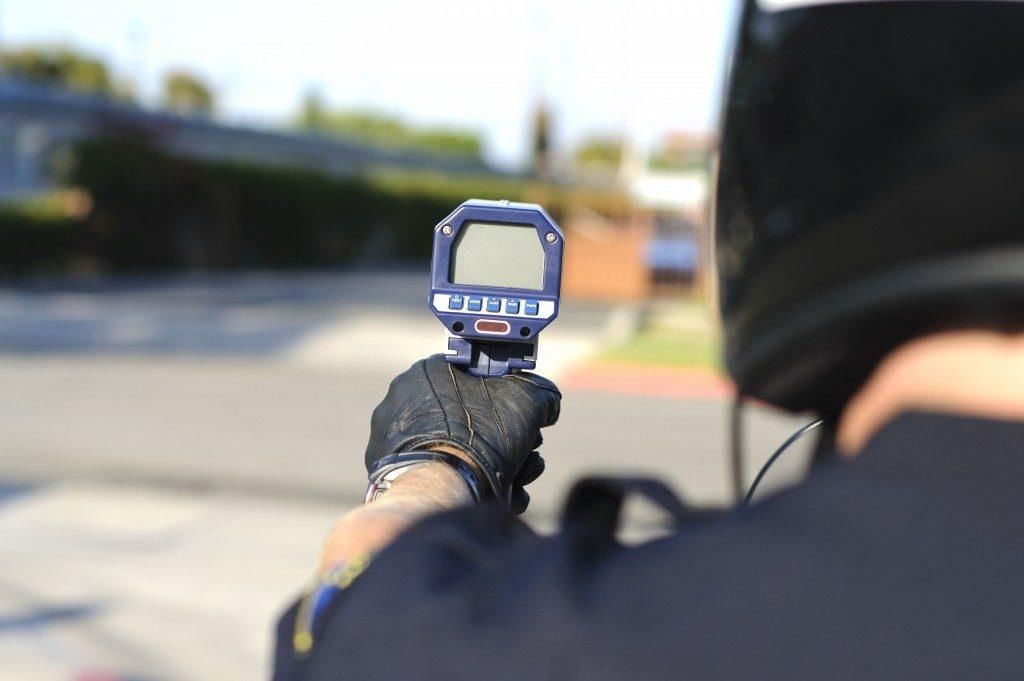 Why in News?
Why in News?
Speed guns are essential tools used by law enforcement and various industries to accurately measure the speed of moving objects without physical contact. Their significance has grown in traffic monitoring and sports performance assessment.
- Speed guns utilize the Doppler effect to determine the speed of an object.
- Originally developed for military applications during World War II, speed guns operate using radio waves.
- They are widely used in traffic enforcement, sports coaching, and other industries requiring precise speed measurements.
Additional Details
- How Speed Guns Work: Speed guns contain a radio transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter emits radio waves that bounce off a moving object. The receiver detects the returning waves, and a built-in computer calculates the object’s speed by analyzing the frequency change.
- Doppler Effect: The principle behind speed measurement is the Doppler shift, which occurs when the frequency of the waves changes as the object moves towards or away from the speed gun. The difference in frequency is used to accurately determine the speed.
- Speed Calculation: The speed of an object is calculated using the formula: (difference in frequency * c) / (emitted frequency * 2), where c represents the speed of light (approximately 299,792,458 m/s).
In summary, speed guns are crucial tools for various applications, providing accurate speed measurements through advanced technology. Their reliable operation over diverse distances makes them invaluable in many fields.
GS3/Economy
On Kisan Diwas: Why Terms of Trade Have Improved More for Farm Workers Than Farmers
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recent trends indicate that crop prices have not kept pace with rising production costs, while agricultural wages for workers have increased faster than inflation over the past two decades. This has led to significant shifts in the economic landscape for both farmers and agricultural laborers.
- Wages for agricultural laborers have risen substantially compared to the stagnant incomes of farmers.
- Government policies have enhanced the bargaining power and income stability of farm workers.
- There is a noticeable shift in economic power dynamics within rural areas, impacting social structures.
Additional Details
- Terms of Trade (ToT): ToT measures the relative prices of goods and services a country exports against those it imports. In agriculture, it assesses the prices farmers receive for their produce against their input costs, such as seeds and fertilizers. A favorable ToT indicates higher profitability for farmers.
- Wage Growth: Agricultural laborers have seen their Index of Prices Received (IPR) increase over threefold, from 49.1 to 151.4 between 2004-05 and 2013-14. In contrast, their Index of Prices Paid (IPP) rose only from 76.4 to 129.3, leading to a significant improvement in their ToT from 64.2% to 117.1%.
- Stagnation of Farmer Incomes: Farmers’ IPR rose by just 56.3% from 2013-14 to 2022-23, while their IPP increased by 58.4%. This resulted in a decline in their ToT from 98.6% to 97.2%, indicating economic pressure as input prices outpace their product prices.
- Economic Diversification: The growth of employment opportunities outside agriculture has empowered laborers to pursue better-paying jobs, increasing their wage rates and negotiating power.
The implications of these changes for the agricultural sector indicate a potential for greater social mobility among laborers, but they also reveal the vulnerabilities faced by farmers. As laborers gain better wages, there may be labor shortages in farming, leading to increased challenges for farmers who may find it difficult to hire workers. Moreover, disparities in economic conditions could foster social tensions, necessitating policy reforms to address these inequities.
Way Forward
- Enhance Farmer Profitability: Implement policies that ensure fair crop pricing, reduce input costs through targeted subsidies, and promote crop diversification and value addition to improve farmers’ income and ToT.
- Strengthen Rural Employment: Expand employment opportunities in rural non-farm sectors and align government schemes like MGNREGA with skill development programs to sustain wage growth for agricultural laborers while addressing labor shortages in farming.
In conclusion, addressing these evolving economic dynamics is crucial for fostering a balanced agricultural sector that supports both farmers and agricultural workers, ensuring sustainable growth and stability in rural economies.
GS2/International Relations
Order of Mubarak Al-Kabeer
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The Prime Minister of India has recently been awarded the Wisam Mubarak Al-Kabeer, also known as the Order of Mubarak the Great, by Sheikh Meshal Al-Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah, the Amir of Kuwait. This prestigious honor highlights the diplomatic relations between India and Kuwait.
- The Order of Mubarak Al-Kabeer is Kuwait's highest national award.
- It is awarded to Heads of State, foreign sovereigns, and members of royal families as a symbol of friendship.
- The award was established in 1974 to commemorate the reign of Mubarak Al Sabah.
Additional Details
- Order of Mubarak Al-Kabeer: This honor represents the highest level of recognition by the Kuwaiti government, bestowed to signify goodwill and diplomatic ties.
- Historical Background: The award was instituted in 1974 in memory of Mubarak Al Sabah, who ruled Kuwait from 1896 to 1915. His leadership was pivotal in granting Kuwait greater autonomy from the Ottoman Empire and establishing a British protectorate in 1899.
- Notable Recipients: The award has also been presented to several prominent figures, including Queen Elizabeth II, former U.S. Presidents George H.W. Bush and Bill Clinton, King Salman of Saudi Arabia, and former French President Nicolas Sarkozy.
- The design of the award was updated in 1992 following Kuwait's liberation from Iraq.
This award not only honors the recipients but also strengthens international relations and showcases Kuwait's commitment to recognizing global leaders and fostering diplomatic ties.
GS3/Science and Technology
What is Starlink?
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?Elon Musk, the founder of SpaceX, recently denied claims regarding the use of his Starlink satellite internet technology by militants in Manipur, India. This statement followed the seizure of Starlink devices and weapons by the Indian Army and police, raising concerns about the potential misuse of the technology by non-state actors.
- Starlink is a satellite internet service developed by SpaceX.
- It aims to provide broadband internet through a network of low Earth orbit satellites.
- Currently, Starlink is not operational in India due to regulatory restrictions.
Additional Details
- Starlink Project: This initiative uses a large constellation of satellites equipped with phased array and parabolic antennas to ensure low latency and high-speed internet connections.
- SpaceX plans to launch a total of 42,000 satellites to create a mega-constellation that will provide global coverage.
- Starlink has received regulatory approval in more than 60 countries, including neighboring nations like Bangladesh and Bhutan, where operations are expected to start in 2025.
In conclusion, while Starlink represents a significant advancement in satellite internet technology, its potential applications in India remain limited by regulatory frameworks. The recent allegations regarding its misuse underscore the need for careful oversight as satellite technologies continue to evolve.
GS2/Polity
Fourth Branch Institutions Shouldn’t be Retirement Homes for Civil Servants, Judges
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?Recently, Supreme Court judge Justice P S Narasimha emphasized that fourth branch institutions in India should not serve as retirement homes for civil servants and judges. He made this statement during the second edition of the Justice ES Venkataramiah Centennial Memorial Lecture organized by the National Law School of India University in Bengaluru.
- Fourth branch institutions are crucial for maintaining accountability in governance.
- Justice Narasimha highlighted the need for merit-based appointments in these institutions.
- Concerns regarding the autonomy and effectiveness of key institutions like the Election Commission and the CAG were raised.
Additional Details
- Fourth Branch Institutions: These are constitutionally or statutorily created bodies that function independently of the executive, legislature, and judiciary. Their primary role is to uphold accountability, transparency, and democracy. Examples include the Election Commission of India (ECI), Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG), Central Information Commission (CIC), and Central Vigilance Commission (CVC).
- Significance: Institutions like the ECI ensure free and fair elections, which is fundamental to democracy. The CAG’s audits have exposed significant irregularities, prompting public discourse on corruption.
- Concerns: Allegations of partisanship have emerged against the ECI, particularly regarding delayed action on violations of the Model Code of Conduct. The CAG has faced criticism for audit delays and overestimating losses. Additionally, the CIC struggles with vacancies and delays in processing appeals, which undermines its effectiveness.
- Strengthening Institutions: It is essential to enhance these institutions to safeguard democracy. This includes implementing transparent appointment processes, ensuring adequate funding, and protecting them from political interference.
- Justice Narasimha's Emphasis: He underscored the critical role of fourth branch institutions, such as the EC and CAG, in ensuring accountability and governance, as envisioned by the Constitution's framers. He warned against allowing these bodies to become mere retirement homes for civil servants and judges, advocating for appointments based on merit.
In conclusion, the independence and effectiveness of fourth branch institutions are vital for restoring public trust and ensuring accountability within the government. By addressing challenges such as capacity building and diversity in composition, these institutions can significantly enhance governance in India's democratic framework.
GS2/International Relations
Panama Canal: Importance and Current Geopolitics
Source: International Monetary Fund
Why in News?The Panama Canal has recently been in the news due to comments made by US President-elect Donald Trump, who criticized Panama for high charges imposed on US ships using the canal and hinted at a potential US takeover.
- The Panama Canal is a vital waterway located in Central America, connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean.
- It has significant historical importance and continues to play a crucial role in global trade.
- Geopolitical concerns have arisen regarding China's increasing influence in the region, particularly through infrastructure investments linked to the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Additional Details
- Geographical Location: The canal is approximately 80 km long and traverses the Isthmus of Panama. It utilizes a system of locks to elevate ships up to 85 feet (26 meters).
- Historical Significance: Construction began in 1881 by the French under Ferdinand de Lesseps but was completed by the US in 1914, led by engineers George Washington Goethals and John Stevens. The control of the canal was handed over to Panama in 1999 as per the Torrijos-Carter Treaties of 1977.
- Present Significance: The canal is essential for global trade, significantly shortening travel time between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans, and is a major source of revenue for Panama through tolls and trade-related activities.
- Current Geopolitical Context: Trump's remarks highlight concerns over China's growing influence in Panama, especially after the 2018 signing of the BRI, which has led to increased Chinese investment in local infrastructure, raising US geopolitical concerns.
In summary, the Panama Canal remains a critical asset for both international trade and geopolitical strategy, with ongoing developments affecting its operation and regional influence.
GS3/Environment
Union Minister Releases India State of Forest Report, 2023
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?The India State of Forest Report 2023 (ISFR 2023) was recently released by the Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change at the Forest Research Institute in Dehradun. This report is crucial as it provides a comprehensive overview of the country’s forest and tree resources, highlighting changes and developments over the past two years.
- India's total forest and tree cover stands at 827,357 sq km, accounting for 25.17% of the geographical area.
- There has been an increase of 1,445 sq km in total forest and tree cover since 2021.
- The states with the most significant increases in forest cover include Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Odisha, and Rajasthan.
- India's total mangrove cover is now 4,992 sq km, reflecting ongoing conservation efforts.
- The total carbon stock is estimated at 7,285.5 million tonnes, with a notable increase of 81.5 million tonnes.
Additional Details
- India's State of Forest Report: This biennial report, published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI) since 1987, utilizes satellite data and field surveys to assess the country’s forest resources.
- Technological Advancements: The FSI has adopted advanced technology for real-time fire alerts, enhancing forest management practices.
- Growing Stock and Bamboo Resources: The total growing stock has increased by 262 million cubic meters, with bamboo-bearing areas expanding by 5,227 sq km.
- Way Forward: Focus on strengthening conservation efforts and management practices, utilizing technological innovations for monitoring forest health.
The ISFR 2023 serves as a vital tool for understanding forest dynamics in India and emphasizes the need for sustainable management and conservation practices to tackle challenges such as deforestation and biodiversity loss.
|
44 videos|5257 docs|1109 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 23rd December 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of Rann Utsav in Indian culture? |  |
| 2. How do dark patterns affect consumer behavior online? |  |
| 3. What factors contribute to the depreciation of the Indian Rupee against the US Dollar? |  |
| 4. How can government budgets impact the agricultural sector? |  |
| 5. What is the role of civil servants and judges in fourth branch institutions? |  |





















