UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 23rd July 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/International Relations
Universities Everywhere Are in Crisis
Why in News?
In recent years, universities have faced significant challenges, becoming targets of political and economic pressures that threaten their autonomy and ability to foster open debate. A notable example is the attack on Harvard University's federal funding in July 2024, representing a broader trend where right-wing governments globally are attempting to exert ideological control over higher education.
Key Takeaways
- Universities are increasingly under siege from political and economic forces, undermining their independence.
- Notable cases illustrate how funding and policies are weaponized to impose ideological conformity.
Additional Details
- United States: Elite institutions like Harvard and Columbia are accused of promoting anti-American sentiment. The Trump administration's policies, including visa restrictions for international students and threats to defund universities, have highlighted the fragility of academic freedom.
- Australia: The government has vetoed humanities research deemed contrary to national interests, resulting in self-censorship among scholars on sensitive topics like politics and climate change.
- Global Patterns: Countries like India and Hungary illustrate how political populism suppresses academic freedom. Universities face punitive actions for challenging government narratives.
- Neoliberal Changes: The transformation of universities into corporate entities has prioritized market metrics over critical inquiry, diminishing the relevance of humanities and social sciences.
The ongoing crisis in academia is driven by both ideological and economic factors, posing a threat to the intellectual independence necessary for addressing global challenges. Defending academic freedom is essential not only for the integrity of educational institutions but also for the health of democratic societies.
GS3/Defence & Security
MiG-21s to Retire by September 2025
Why in News?
The Indian Air Force's longest-serving combat aircraft, the Russian-origin MiG-21 (Mikoyan and Gurevich), is scheduled for retirement by September 2025 after decades of service.
Key Takeaways
- The MiG-21 has been a crucial part of the IAF since its induction in 1963.
- Safety concerns have led to its nickname as a "flying coffin" due to frequent crashes.
- It is set to be replaced by the indigenous Tejas Mark-1A fighter aircraft.
Additional Details
- About MiG-21:
- Type: Single-engine, single-seater, multi-role fighter and ground attack aircraft.
- Origin: Initially inducted as an interceptor and later upgraded for multi-role capabilities.
- Key Indian Variants: Type-77, Type-96, MiG-21 BIS, and MiG-21 Bison (the most advanced variant with upgraded radar, avionics, and missile systems).
- Safety Concerns: The aircraft has a high accident rate, especially in recent decades, leading to significant pilot fatalities.
- Combat Features: The MiG-21 is known for its high speed, agility, and rapid climb capability, and it can deploy both air-to-air and air-to-ground missiles.
- War Record: The aircraft played key roles in the 1965 War with Pakistan, the 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War, and the 1999 Kargil Conflict.
- In a notable operation in 2019, a MiG-21 Bison, piloted by Group Captain Abhinandan Varthaman, shot down a Pakistani F-16 during aerial combat.
- Induction Timeline: The aircraft was inducted into the IAF in 1963, with the first units assembled in India at Chandigarh with Soviet assistance. Over 700 MiG-21s were procured, forming the backbone of the IAF for decades.
- Currently, three MiG-21 Bison squadrons remain operational, each with 16-18 aircraft.
- Replacement: The MiG-21s will be replaced by the Tejas Mark-1A, a single-engine, fourth-generation multirole light fighter aircraft developed under the Light Combat Aircraft program launched in the 1980s.
- Indigenous Content: The Tejas aircraft boasts 59.7% indigenous components by value and 75.5% of the line replaceable units are produced domestically.
In conclusion, the retirement of the MiG-21 marks the end of an era for the Indian Air Force, paving the way for modern advancements in aerial combat capabilities with the introduction of the Tejas Mark-1A.
UPSC 2024 Question:
Consider the following aircraft:
- Rafael
- MiG-29
- Tejas MK-1
How many of the above are considered fifth generation fighter aircraft?
- Options: (a) Only one (b) Only two (c) All three (d) None*
GS3/Environment
Empowering Urban India for Climate Resilience
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India's urban areas are experiencing rapid growth, which presents significant challenges in adapting to the impacts of climate change. A recent report by the World Bank, titled “Towards Resilient and Prosperous Cities in India,” in collaboration with the Union Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), underscores the urgent need for improved urban climate resilience. The report advocates for greater autonomy for Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) and highlights the necessity of an estimated $2.4 trillion investment by 2050 to address these challenges.
Key Takeaways
- The necessity for urban autonomy in climate governance is emphasized, with evidence indicating that cities with decision-making power have better climate resilience.
- The report highlights the financial and population projections essential for urban climate adaptation.
- Best practices in Indian cities are cited as models for resilience against climate change.
- Conclusive recommendations for national and local governments aim to improve urban climate readiness.
Additional Details
- Urban Autonomy: The World Bank stresses the importance of implementing the 74th Constitutional Amendment Act of 1992 to enhance local governance structures, enabling better resource mobilization, accountability, and revenue generation.
- Climate Risks:Urban India faces two primary risks:
- Pluvial flooding due to inadequate drainage systems and excessive concretization.
- Extreme heat stress exacerbated by the urban heat island effect.
- The report estimates that annual flood-related losses could reach $5 billion by 2030 and $30 billion by 2070, while heat-related fatalities may double to over 300,000 annually by 2050.
Financial and Population Projections
- It is projected that $2.4 trillion will be necessary by 2050 to build resilient urban infrastructure and services.
- An investment of at least $150 billion is required over the next 15 years to enhance flood resilience in 60% of high-risk cities.
- India's urban population is expected to nearly double to 951 million by 2050, with cities generating 70% of new employment by 2030.
Best Practices Cited in India
- Ahmedabad: Developed a Heat Action Plan model to strengthen early warning systems, enhance healthcare readiness, increase green cover, and adjust work schedules for outdoor laborers.
- Kolkata: Implemented a city-level flood forecasting and warning system.
- Indore: Invested in a modern solid waste management system, improving cleanliness and generating green jobs.
- Chennai: Adopted a climate action plan focused on risk assessment and promoting both adaptation and low-carbon growth.
Recommendations of the Report
- For National and State Governments: Develop a financing roadmap and establish standards to boost municipal capacity while involving the private sector in climate-resilient infrastructure development.
- For Cities and ULBs: Assess climate risks locally and mobilize capital for adaptation and mitigation through methods like cool roofs, early warning systems, urban greening, and adjusted working hours to reduce heat stress.
- Implement urban planning strategies that minimize impervious surfaces and enhance stormwater management.
The World Bank–MoHUA report emphasizes the critical need to empower cities through enhanced autonomy, targeted investments, and necessary institutional reforms. These steps are essential for ensuring that India's urban future is not only climate-resilient but also economically vibrant and socially inclusive.
GS3/Environment
IUCN World Conservation Congress 2025
Why in News?
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) World Conservation Congress 2025 is set to take place in Abu Dhabi, focusing on the utilization of genetic tools in conservation efforts.
Key Takeaways
- The IUCN World Conservation Congress is the largest global assembly of nature conservation experts, leaders, and decision-makers.
- This event occurs every four years and will shape the future priorities for nature conservation and climate change.
Additional Details
- Components of the Congress:The Congress consists of three major components:
- Forum: A vast knowledge marketplace for conservation and sustainable development science, practices, and innovations.
- Exhibition: A space where IUCN members, businesses, and academia can host pavilions, booths, and events.
- Member’s Assembly: The highest decision-making body of IUCN, where members vote on critical conservation and sustainable development issues.
- Theme of 2025 Congress: The theme, "Powering transformative conservation," will address five essential themes aimed at driving significant changes for a sustainable future for nature and humanity.
- Overview of IUCN: Founded in 1948, the IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) is the largest and most diverse environmental network, comprised of government and civil society organizations. It leverages knowledge and resources for conservation.
- Governance Structure:
- The IUCN Council is the primary governing body between Congress sessions, overseen by the IUCN President.
- The Members’ Assembly, as IUCN’s highest governing body, discusses strategic topics, adopts motions, approves programs, and elects the IUCN Council.
The IUCN World Conservation Congress serves as a critical platform for addressing pressing environmental issues, enhancing collaboration, and guiding global conservation efforts.
GS3/Defence & Security
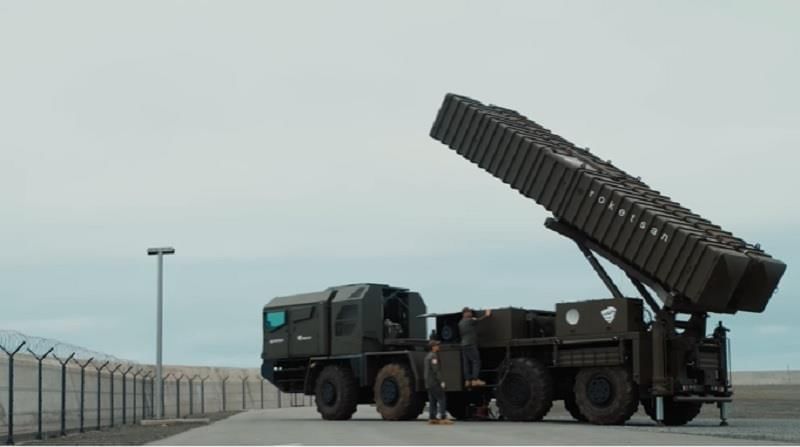
Tayfun Block-4: Turkey's Hypersonic Ballistic Missile
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Turkey has recently introduced its first hypersonic ballistic missile, the Tayfun Block-4, during a ceremony held in Istanbul, marking a significant milestone in its defense capabilities.
Key Takeaways
- The Tayfun Block-4 is Turkey's longest-range nationally produced ballistic missile.
- It is classified as a hypersonic missile, capable of speeds exceeding Mach-5 (five times the speed of sound).
- Developed by the Turkish defense firm Roketsan, it features advanced technology for enhanced performance.
Additional Details
- Dimensions and Weight: The missile measures 6.5 meters in length and has a total weight of approximately 2,300 kilograms.
- Speed and Maneuverability: It is designed for high speed and advanced maneuverability, allowing it to evade enemy defenses effectively.
- Operational Range: The operational range extends up to 800 kilometers, with future plans to enhance this range to 1000 kilometers.
- Guidance System: The missile utilizes a sophisticated guidance system that integrates GPS, GLONASS technologies, and inertial navigation (INS), ensuring high accuracy with a maximum deviation of only 5 meters per shot.
- Warhead Type: Equipped with a fragmentation warhead, the missile employs 'solid composite' fuel, enabling rapid and effective strikes on critical targets such as air defense systems, command centers, and essential infrastructure.
The introduction of the Tayfun Block-4 signifies Turkey's entry into the hypersonic ballistic missile era, enhancing its strategic defense capabilities and reinforcing its position in regional security dynamics.
GS3/Science and Technology
Winter Fog Experiment (WiFEX)
Why in News?
The Winter Fog Experiment (WiFEX) has achieved a significant milestone, marking ten years of extensive research focused on the dense winter fog in North India.
Key Takeaways
- Launched in winter 2015 at Indira Gandhi International Airport, New Delhi.
- Led by the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology in collaboration with various governmental bodies.
- One of the few long-term experiments worldwide dedicated to studying fog phenomena.
Additional Details
- Objectives: The primary goals of WiFEX include enhancing the now-casting (next 6 hours) and forecasting capabilities for winter fog across different time and spatial scales.
- Impact: Aims to mitigate the adverse effects of fog on transportation, aviation, and the economy, as well as to reduce accidents caused by poor visibility.
- Methodology: Utilizes advanced instruments such as micrometeorology towers, ceilometers, and high-frequency sensors to gather comprehensive data on various atmospheric parameters, constructing a unique dataset that helps in understanding the formation and dissipation of dense fog.
- Forecasting Model: The insights gained have contributed to the creation of a high-resolution (3 km) probabilistic fog prediction model, recognized as one of the most sophisticated forecasting tools in the region.
The model has demonstrated over 85% accuracy in predicting the onset, density, duration, and clearance of very dense fog (visibility below 200 meters), thereby significantly improving operational forecasting capabilities.
GS2/International Relations
China, India, and the Conflict Over Buddhism
 Why in News?
Why in News?
As international focus centers on China's naval expansion in the Indo-Pacific and India's strategic responses, a significant but quieter contest is emerging in the Himalayas. This conflict revolves around the spiritual and cultural influence of Himalayan Buddhism, transforming a tradition of peace into a geopolitical battleground.
Key Takeaways
- The geopolitical struggle between India and China is deeply intertwined with the influence of Buddhism.
- China employs Buddhism as a tool of statecraft, while India's response has been slower and more fragmented.
- The succession crisis of the Dalai Lama could create a schism in Tibetan Buddhism, impacting regional loyalties.
Additional Details
- Buddhism as a Tool of Statecraft: China has aggressively sought to control Tibetan religious life since the 1950s, marginalizing independent lamas and asserting authority over reincarnation processes. In 2007, state approval became mandatory for all Living Buddhas, placing spiritual legitimacy under political control.
- India's Buddhist Diplomacy: While India has hosted the Dalai Lama since 1959, it has only recently begun to promote its Buddhist heritage actively. Efforts include investing in pilgrimage circuits, but these initiatives still lag behind China's well-coordinated strategies.
- The Dalai Lama Succession Crisis: The current Dalai Lama has expressed intentions to reincarnate outside Chinese control, likely in India. This could lead to two competing figures recognized by different communities, potentially dividing Tibetan Buddhism and influencing geopolitical allegiances.
- Cultural Influence of China: China is expanding its influence through cultural narratives and investments in Buddhist infrastructure, asserting territorial claims in regions like Arunachal Pradesh and Nepal, where it argues for historical and spiritual legitimacy.
The ongoing conflict over Himalayan Buddhism reveals that geopolitics extends beyond territory and military strength. As India and China vie for regional dominance, the future of Asia may hinge not only on strategic deterrence but also on spiritual succession. The Himalayas, often viewed as a remote frontier, are becoming a critical arena where religion and realpolitik intersect.
GS3/Economy
What are Stable Coins?
Why in News?
The US House of Representatives has recently passed the Genesis Act, which aims to regulate US dollar-pegged stablecoins, highlighting the growing importance of stablecoins in the financial landscape.
Key Takeaways
- Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies whose value is pegged to other assets like fiat currencies or gold.
- They aim to reduce the volatility associated with cryptocurrencies, making them more suitable for everyday transactions.
- There are three main types of stablecoins: fiat-collateralized, crypto-collateralized, and non-collateralized (algorithmic).
Additional Details
- Definition: Stablecoins are a type of cryptocurrency designed to maintain a stable price by being pegged to an asset, such as a fiat currency or commodity. They are intended to provide a less volatile option in the cryptocurrency market.
- Types of Stablecoins:
- Fiat-Collateralized: These stablecoins are backed by reserves of fiat currency. For example, one US dollar might equal one stablecoin, secured by actual dollar reserves held by the issuer.
- Crypto-Collateralized: These stablecoins are backed by other cryptocurrencies. They often require over-collateralization to account for the volatility of the backing assets.
- Non-Collateralized (Algorithmic): These stablecoins use algorithms to control the supply based on market demand, without backing by any physical assets.
- While stablecoins aim for price stability, their value can fluctuate in secondary markets, and there may be no guarantee that reserves are adequate to cover all redemptions.
In conclusion, stablecoins represent a significant development in the world of digital currencies by providing a bridge between traditional finance and the volatile crypto market, although their stability is not guaranteed.
GS1/Indian Society
Realities Behind the Global Experiment of ‘Remote Work’
Why in News?
A recent “Global Survey of Working Arrangements” (2024–25) conducted by the Ifo Institute and Stanford University highlights the increasing disparity between employees' wishes for remote work and its actual availability on a global scale.
Key Takeaways
- There is a significant gap between the desire for remote work and its implementation.
- Employers express reluctance due to concerns about team dynamics and productivity.
- Cultural biases and inadequate home infrastructure hinder remote work adoption in many regions, particularly in Asia.
Additional Details
- Employer Reluctance Due to Team Dynamics: Many employers believe that remote work diminishes collaboration, innovation, and team bonding. For instance, in India's tech sector, companies like TCS and Infosys have enforced office returns to preserve team culture.
- Cultural Bias Toward Presenteeism: In several Asian countries, physical presence at work is associated with loyalty and productivity. In Japan, employees are often expected to stay late, even without substantial work output, as a demonstration of dedication.
- Inadequate Home Infrastructure: Many people lack essential home setups for remote work, such as reliable internet and quiet spaces. For example, a worker in Mumbai might struggle to concentrate due to living in a cramped 1BHK apartment with family.
- Health and Mental Well-being Concerns: Prolonged remote work can lead to issues like backaches, eye strain, and increased mental stress from isolation and blurred work-life boundaries. A Microsoft report indicated rising burnout levels among remote workers during the pandemic.
Overall, while remote work offers flexibility, various cultural and infrastructural barriers continue to limit its widespread adoption, especially in Asian countries.
GS3/Environment
Threat of Ambrosia Beetle to Rubber Plantations in Kerala
Why in News?
Rubber plantations in Kerala are facing a significant challenge due to the attack of ambrosia beetles, which form a detrimental alliance with fungi, leading to severe leaf fall and rapid drying of trees.
Key Takeaways
- Ambrosia beetles are primarily associated with ambrosia fungi.
- These beetles are native to Central and South America and were first reported in India in 2012.
- The beetles attack stressed, dead, or infected trees, leading to economic losses in rubber production.
Additional Details
- Ambrosia Beetle: This beetle gets its name from the fungi it cultivates. It has a mutualistic relationship with two fungal species: Fusarium ambrosia and Fusarium solani.
- Effects on Rubber Trees: The ambrosia beetles bore tunnels, known as galleries, in the bark of trees, where they introduce fungi. The fungi weaken the wood, enabling deeper penetration. This relationship can lead to severe structural damage, leaf fall, trunk drying, and even tree death, significantly affecting latex production.
- Prevention Techniques: To mitigate the impact of this beetle-fungus duo, experts recommend using antifungal agents, removing infected tree parts, and employing traps designed for ambrosia beetles.
Continued monitoring and preventive actions are essential to safeguard rubber plantations from this invasive threat.
GS2/Governance
PRATIBHA Setu Initiative
Why in News?
The Union Public Service Commission (UPSC) has initiated the PRATIBHA Setu program to leverage the capabilities of civil service aspirants who reach the interview stage but do not make it to the final merit list.
Key Takeaways
- The initiative aims to connect candidates who passed the UPSC interview but were not selected with verified employers.
- It was launched with the results of the Civil Services Examination (CSE) 2023, evolving from the Public Disclosure Scheme established in 2018.
Additional Details
- Purpose: The initiative seeks to provide alternate career pathways for high-performing candidates who have demonstrated their capabilities through the rigorous UPSC selection process.
- Talent Pool: The program boasts a talent pool of over 10,000 high-performing candidates, allowing employers access to a well-evaluated group of potential hires.
- Eligibility: Candidates from various services such as Civil Services, Indian Forest Service, Engineering Services, and Central Armed Police Forces are included, while the National Defence Academy and Naval Academy candidates are excluded.
- Recruiter Access: Organizations can register through the Ministry of Corporate Affairs portal using their Corporate Identification Number (CIN).
- Platform Tools: Employers have access to a dashboard for shortlisting candidates and can view candidates' educational profiles and contact details digitally.
- Impact: This initiative not only opens new career paths for UPSC aspirants but also facilitates transparent and efficient hiring processes for employers.
In summary, the PRATIBHA Setu initiative enhances the relevance of the UPSC selection process beyond just final appointments, benefiting both candidates and employers in India.
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 23rd July 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the main factors contributing to the crisis in universities? |  |
| 2. How does the retirement of MiG-21s impact national defense? |  |
| 3. What steps can urban India take to enhance climate resilience? |  |
| 4. What is the significance of the IUCN World Conservation Congress? |  |
| 5. What are stable coins and how do they function in the cryptocurrency market? |  |





















