UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 24th May 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS1/Geography
A Good Monsoon
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?This May has been notably wet, with India experiencing 68.4% more rainfall than average. Additionally, there have been no extreme temperatures or significant heatwaves across most regions of the country.
Key Takeaways
- India received 68.4% more rainfall than usual for May.
- Western disturbances and moisture-laden winds contributed to continuous showers.
- No major heatwaves were reported during this period.
Additional Details
- Above-Normal Rainfall: India witnessed one of the wettest months in recent years, with 27 out of 36 meteorological subdivisions reporting over 20% surplus rain.
- Frequent Moisture-Laden Winds: The combination of western disturbances from the Mediterranean and incursions from the Bay of Bengal and Arabian Sea caused intermittent thunderstorms, particularly in northern and eastern India.
- Suppression of Heatwaves: Each thunderstorm contributed to lower temperatures, preventing the formation of heatwaves; central and northern India did not experience any significant heatwave events in May.
Importance of Heat Lows in Northwest India
- Creates Suction for Moist Winds: Heat lows operate like a vacuum, attracting moisture-laden southwesterly winds from the Indian Ocean into the subcontinent. For example, strong heat lows over Rajasthan can trigger early monsoon onset in central India.
- Drives Monsoon Circulation: These low-pressure areas are crucial for initiating and sustaining the monsoon trough, which facilitates widespread rainfall. The absence of heat lows can delay or weaken the monsoon in northwest and central regions.
- Influences Rainfall Intensity and Spread: Proper development of heat lows ensures uniform and timely rainfall, which is essential for agriculture. For instance, weak heat lows in 2015 led to a patchy and deficient monsoon season.
Effects of El Niño and IOD on Monsoon
- El Niño Weakens Monsoon Winds: Warmer waters in the Pacific Ocean associated with El Niño can suppress the Indian monsoon by weakening the low-pressure system over the subcontinent. For example, the 2015 El Niño resulted in a 14% rainfall deficit in India.
- Positive IOD Strengthens Monsoon: A positive Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) leads to warmer waters near Africa and cooler waters near Indonesia, enhancing monsoon winds and rainfall in India. For example, in 2019, a strong positive IOD mitigated El Niño's effects, resulting in above-normal rainfall.
Impact of Monsoon on Food Inflation
- Good Monsoon Boosts Crop Yields: Adequate rainfall supports timely sowing and healthy harvests, leading to better food availability and stable prices. For instance, a normal monsoon in 2022 helped moderate the rise in cereal prices.
- Reduces Dependency on Imports: Sufficient domestic production of staples like wheat and pulses decreases the need for costly imports, helping to control food inflation. In 2024, surplus wheat stocks due to favorable rainfall alleviated price pressures.
- Stabilizes Rural Demand and Supply Chains: A healthy monsoon boosts rural incomes, enhancing supply consistency and reducing volatility in food prices. For example, a robust kharif output in 2021 contributed to lower vegetable prices.
Way Forward
- Strengthen Climate-Responsive Agriculture: Encourage the development of drought- and flood-resistant crop varieties and expand irrigation to reduce reliance on erratic monsoons.
- Enhance Weather Forecasting and Storage Infrastructure: Improve real-time weather alerts and expand storage facilities to minimize post-harvest losses and stabilize food prices.
Mains PYQ
[UPSC 2024] What are the causes of persistent high food inflation in India? Comment on the effectiveness of the monetary policy of the RBI to control this type of inflation.
Linkage: Understanding the dynamics of food inflation is crucial for appreciating the significant positive economic contributions that a favorable monsoon can make by potentially increasing agricultural output and stabilizing food prices.
GS3/Economy
RBI Dividend Transfer to the Union Government
Source: The Hindu
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has approved the transfer of a substantial surplus of ₹2.69 lakh crore to the Union Government as a dividend for the financial year 2024-25. This transfer is significant as it represents a key non-tax revenue source for the government, aiding in fiscal management.
Key Takeaways
- The RBI's dividend transfer is aimed at bolstering the Union Government's finances.
- This year's surplus is 27% higher than the previous year's transfer of ₹2.10 lakh crore.
- Dividends are determined under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
Additional Details
- What is a Dividend in Public Finance: A dividend refers to a portion of profits returned by a corporation or institution to its shareholders. In the case of the RBI, the Government of India is the sole shareholder.
- Significance of RBI Dividends: Dividends serve as a non-tax revenue source for the government, helping bridge fiscal deficits.
- Dividend Yield: This is a measure of the return from dividends relative to the stock price, calculated as: Dividend Yield = (Annual Dividend per Share) / (Current Market Price of Share).
- The RBI's surplus for 2024-25 is attributed to:
- Increased sales of foreign exchange reserves, particularly in January 2025.
- Higher interest income from investments in government securities and foreign assets.
- Gains from forex transactions amid global market volatility.
- The transferable surplus was calculated as per the Revised Economic Capital Framework (ECF), which determines how much surplus the RBI can safely transfer while maintaining adequate capital to absorb financial shocks.
This remarkable increase in the RBI's earnings highlights its robust financial management and strategic operations in the face of fluctuating global economic conditions.
GS2/International Relations
Northeast India as a Gateway for Trade with Southeast Asia
Source: The Hindu
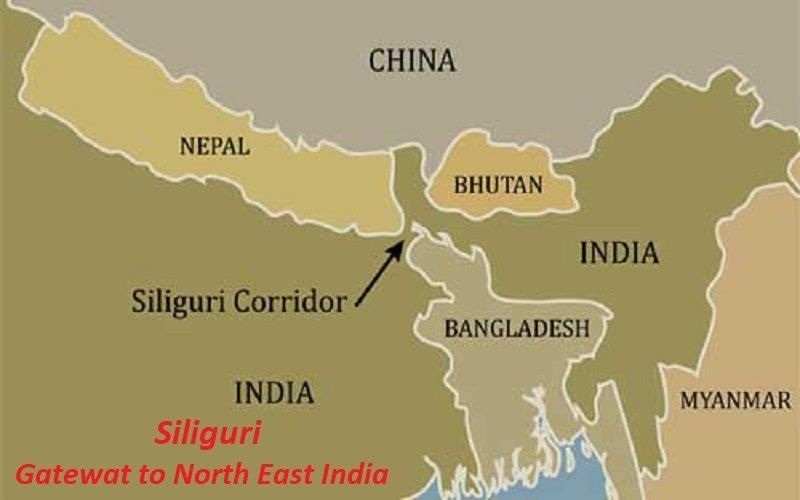 Why in News?
Why in News?The Prime Minister recently stated that the eight states of India's Northeast are now at the forefront of development and growth. He has urged investors to explore potential opportunities in this region.
Key Takeaways
- The Northeast is now seen as a "frontrunner of growth" rather than a "frontier region."
- Strategic projects aim to connect the Northeast with Southeast Asia, enhancing trade opportunities.
- The region is rich in natural resources, positioning it as an energy powerhouse.
- Cultural and economic diversity drives innovation in sectors like tourism and crafts.
Additional Details
- Strategic Importance: The Prime Minister highlighted the Northeast’s strategic location, which facilitates connections with Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, and Vietnam under the Act East Policy.
- Economic Contributions: Each of the eight states, referred to as "Ashta Lakshmis," uniquely contributes to India's prosperity, supported by initiatives like NESIDS to unlock economic strengths.
- Closure of Land Ports: The Directorate General of Foreign Trade ordered the closure of land ports with Bangladesh to level the playing field for local producers and boost internal supply chains.
India is focused on enhancing infrastructure and connectivity, positioning the Northeast as a trade gateway to Southeast Asia. This includes investment in border trade hubs and logistics parks, alongside promoting local industries and skill development to foster economic growth in the region.
GS3/Science and Technology
INSPIRE Scheme Overview
Source: Frontiners
Why in News?
Research scholars across India have expressed their concerns regarding delays in the disbursement of INSPIRE fellowships funded by the Department of Science and Technology (DST). These delays have lasted between 8 to 13 months, prompting significant attention to the scheme's administration.
Key Takeaways
- The INSPIRE scheme is a flagship initiative by DST aimed at enhancing India's scientific research capabilities.
- It was launched in 2008 to build a robust human resource base in science and technology.
- Unlike other scholarship schemes, INSPIRE selects candidates based on merit without entrance exams.
Additional Details
- INSPIRE Fellowship: This fellowship is a part of the INSPIRE scheme, designed to encourage research careers in basic sciences. It aims to attract top-performing students towards scientific research instead of more lucrative fields like engineering or finance. Approximately 1,000 scholars are chosen each year based on their academic performance and the quality of their research proposals.
- Eligibility Criteria: Candidates must be first-rank holders in postgraduate courses in science, applied sciences, or engineering, or be INSPIRE scholars with at least 70% aggregate marks in their undergraduate and postgraduate studies. They should also have been among the top 1% in Class XII board exams or excelled in national level examinations like IIT-JEE. A screening committee evaluates applications before awarding the fellowship.
- Key Features:The INSPIRE scheme has a total financial outlay of ₹1,979 crore during the 11th Plan and ₹2,200 crore in the 12th Plan. It includes three main components:
- SEATS (Scheme for Early Attraction of Talent): Designed to foster interest in science among school students.
- SHE (Scholarship for Higher Education): Aimed at undergraduate and postgraduate science students.
- AORC (Assured Opportunity for Research Careers): Encompasses INSPIRE Fellowships and Faculty Awards.
The INSPIRE scheme is crucial for nurturing scientific talent in India, and the recent delays in fellowship disbursement highlight the need for efficient management to ensure the continued support of aspiring researchers.
GS3/Environment
6 New Sites Added to Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS)
Source: Global Times
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) has acknowledged six traditional farming systems from Brazil, China, Mexico, and Spain, recognizing them as Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS).
Key Takeaways
- Recognition of six traditional farming systems by FAO.
- These systems promote biodiversity and sustainable agricultural practices.
About the Newly Recognised GIAHS Systems
- Deqing Pearl Mussel Fishery (China): An 800-year-old integrated system combining pearl farming, rice, and silk, enhancing ecotourism and water purification.
- Fuding White Tea Culture (China): Diverse tea gardens tied to local rituals and livelihoods, supporting 18 tea and 41 vegetable varieties.
- Gaolan Pear Orchards (China): A 600-year-old dryland system along the Yellow River that produces 2 million kg of pears through native crop-livestock integration.
- Erva Mate Agroforestry (Brazil): Indigenous agroforestry practices under Araucaria forests that preserve ecology and culture through erva-mate farming.
- Metepantle Terraces (Mexico): A 3,000-year-old Nahua terrace farming system that ensures food sovereignty and conserves over 140 native species.
- Lanzarote Sand Farming (Spain): Utilization of volcanic and sea sand techniques to cultivate crops without irrigation in one of Europe’s driest regions.
About GIAHS
- Definition: GIAHS are living and evolving agricultural systems where communities maintain strong ties to their land through agrobiodiversity, traditional knowledge, resilient ecosystems, and cultural heritage.
- Purpose: The program aims to identify, support, and safeguard agricultural systems that preserve genetic diversity, rural livelihoods, and maintain cultural landscapes.
- Origins: The concept was initiated in 2002 at the World Summit on Sustainable Development in Johannesburg, led by the United Nations.
Program Implementation
- Global level: Identification, selection, and formal recognition of GIAHS.
- National level: Policy support and capacity building for recognized systems.
- Local level: Community empowerment and technical assistance for sustainable resource use.
India’s GIAHS-Recognized Farming Systems
- Koraput Traditional Agriculture (Odisha): This system, practiced by tribal communities in the Eastern Ghats, conserves over 1,200 indigenous rice varieties and integrates millets and pulses through shifting and terraced cultivation.
- Kuttanad Below Sea Level Farming System (Kerala): The only below-sea-level farming system in India, utilizing polders and bunds for paddy cultivation, rice-fish rotation, and seasonal flood management with indigenous water control systems.
- Saffron Heritage of Kashmir (UT of Jammu & Kashmir): Cultivated on the Pampore plateau at elevations of 1,600–1,800 metres, this saffron is renowned for its high crocin content, aroma, and color strength, contributing significantly to the local economy and cultural heritage.
Question:
The FAO accords the status of ‘Globally Important Agricultural Heritage System (GIAHS)’ to traditional agricultural systems. What is the overall goal of this initiative?
- 1. To provide modern technology, training in modern farming methods, and financial support to local communities of identified GIAHS to greatly enhance their agricultural productivity.
- 2. To identify and safeguard eco-friendly traditional farm practices and their associated landscapes, agricultural biodiversity, and knowledge systems of the local communities.
- 3. To provide Geographical Indication status to all the varieties of agricultural produce in such identified GIAHS.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
- (a) 1 only
- (b) 2 only*
- (c) 2 and 3 only
- (d) 1, 2 and 3
This recognition highlights the importance of preserving traditional agricultural practices that maintain biodiversity and cultural heritage, ensuring sustainable agriculture for future generations.
GS3/Environment
Keoladeo National Park: A Sanctuary for Birds and Turtles
Source: ETV Bharat
 Why in News?
Why in News?Keoladeo National Park, renowned as the 'paradise of birds', is gaining recognition not only for its avian diversity but also as a sanctuary for turtles, offering refuge to eight out of ten turtle species found in Rajasthan.
Key Takeaways
- Located in Bharatpur, Rajasthan, Keoladeo National Park is also known as Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary.
- Founded as a hunting preserve in the late 19th century, it became a bird sanctuary in 1956 and was designated a national park in 1981.
- The park hosts over 360 species of birds, especially during the migratory season from October to March.
Additional Details
- History: Established by Suraj Mal, the maharaja of Bharatpur, the park was named Keoladeo after an ancient temple dedicated to the Hindu god Shiva.
- Area: Spanning 29 sq. km, the park features diverse ecosystems, including woodlands, swamps, and wet grasslands.
- Significance: It is recognized as a Ramsar site and a UNESCO World Heritage Site, strategically positioned in the Central Asian migratory flyway.
- Flora: The vegetation primarily consists of dry deciduous forests with trees such as kadam, jamun, babul, and kair.
- Fauna: The park is home to a variety of mammals and reptiles, including pythons, deer, blackbucks, and fishing cats.
In summary, Keoladeo National Park is not only a vital habitat for countless bird species but also serves as an important sanctuary for turtles, making it a critical site for biodiversity conservation.
GS3/Environment
Zudpi Jungles are Forest Land: Supreme Court Ruling
Source: Live Law
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Supreme Court of India has made a significant ruling regarding the Zudpi Jungle lands in Eastern Vidarbha, Maharashtra. The court has determined that approximately 86,400 hectares of these lands should be classified as forest land. However, it has permitted the continuation of existing structures such as schools, homes, graveyards, and government offices that were established before December 12, 1996.
Key Takeaways
- The Zudpi Jungle lands are crucial for ecological balance, functioning as wildlife corridors.
- These lands have been recognized as forest-like areas by the Maharashtra government since the 1980s.
Additional Details
- About Zudpi Jungles: The Zudpi Jungles are located in the eastern Vidarbha region of Maharashtra. The term "Zudpi" in Marathi refers to shrubs or bushes.
- Vegetation and Soil: The land features low-quality vegetation, primarily consisting of shrubs and dry plants. The soil, known as Murmadi soil, is arid and unsuitable for large trees due to its gravelly nature.
- Ecological Role: Despite the sparse growth, these lands are ecologically significant as they serve as wildlife corridors, facilitating safe movement for animals between forest patches.
- Geographic Spread: The Zudpi Jungles are found across six districts in Vidarbha: Nagpur, Wardha, Bhandara, Gondia, Chandrapur, and Gadchiroli.
- Conservation Status: The Maharashtra government has recognized these lands as forests since the 1980s and sought exemption from the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980, acknowledging their forest-like characteristics.
- Biodiversity Importance: Environmental experts emphasize that small forest patches like the Zudpi Jungles are vital for maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance.
Legal Context
- Definition of Forests: The Supreme Court's ruling in the T.N. Godavarman v. Union of India case in 1996 expanded the definition of 'forest' to include all areas with forest-like features, regardless of formal classification.
- Legal Protection: The ruling established that all such lands are protected under the Doctrine of Public Trust, mandating the government to safeguard natural resources for future generations.
- Constitutional Links: The court linked environmental protection to Article 21 (Right to Life) and Article 48A, which requires the State to protect forests and wildlife.
- Impact: This decision has brought millions of hectares under forest protection laws, promoting a uniform standard for forest classification and conservation efforts.
This ruling emphasizes the importance of recognizing ecological value in land classifications and highlights the role of judicial intervention in environmental protection.
GS3/Economy
Self-Reliant India (SRI) Fund Scheme
Source: Financial Express
Why in News?
The Self-Reliant India (SRI) Fund has made significant investments totaling approximately ₹10,979 crore in 577 Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) across India as of March 2025. The highest concentration of investee firms is found in Karnataka (151), followed by Maharashtra (144) and Delhi (69).
Key Takeaways
- The SRI Fund aims to support MSMEs through equity funding.
- It was launched in 2020 as part of the Atmanirbhar Bharat Package.
- The total target corpus of the fund is ₹50,000 crore, with ₹10,000 crore from the Government of India.
Additional Details
- Structure and Management: The fund operates as a Category-II Alternative Investment Fund (AIF) registered with SEBI. It employs a two-tier structure consisting of a Mother Fund managed by NSIC Venture Capital Fund Limited (NVCFL) and 60 empanelled Daughter Funds that make direct investments in MSMEs.
- Funding Type: The SRI Fund provides equity or quasi-equity support, aimed at reducing MSMEs’ reliance on debt and promoting long-term growth.
- Sectoral Focus: The fund prioritizes investments in manufacturing, services, and high-growth MSMEs, particularly those engaged in innovation, research and development, and exports.
- Addressing Credit Gap: The fund plays a crucial role in bridging the estimated ₹30 lakh crore credit gap faced by MSMEs in India by complementing credit guarantee schemes with equity-based support.
- Revised Eligibility: With the turnover limit raised to ₹500 crore, a larger number of companies now qualify for SRI and related MSME support.
In summary, the Self-Reliant India Fund is a pivotal initiative aimed at empowering MSMEs, fostering innovation, and enhancing economic self-reliance in India.
GS3/Environment
State of the World’s Animal Health Report
Source: DTE
Why in News?
The inaugural State of the World’s Animal Health report, released by the World Organisation for Animal Health (WOAH), highlights the alarming spread of infectious animal diseases to new regions and species. Notably, nearly half of these diseases (47 percent) are capable of zoonotic transmission, posing significant threats to human health.
Key Takeaways
- 47 percent of infectious animal diseases are zoonotic.
- Bird flu caused the loss of over 630 million birds in the last two decades.
- Peste des petits ruminants (PPR) has re-emerged in Europe.
- African swine fever (ASF) has reached Sri Lanka, traveling over 1,800 km.
- In 2024, there were 3,517 cases of Bluetongue reported in 23 countries.
- New cases of New World screwworm reported in Mexico and Nicaragua.
Additional Details
- Zoonotic Diseases: Diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans, posing health risks globally.
- Climate Change and Trade: Factors such as climate change and increased trade are influencing the spread of animal diseases.
- Prevention Measures: Many diseases are preventable through vaccination, improved hygiene, and biosecurity. However, access to vaccines is uneven worldwide.
- Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR): If not addressed, AMR could cause significant livestock losses and threaten food security, impacting two billion people by 2050.
- Despite a reduction in antimicrobial use from 2020 to 2022, one in five countries still uses them as growth promoters, which is discouraged by WOAH.
This report underscores the critical need for enhanced disease prevention strategies to reduce reliance on antibiotics and combat the rise of drug-resistant diseases. The importance of global cooperation in animal health cannot be overstated, as it directly impacts human health and food security.
GS3/Science and Technology
What is a Binary Star System?
Source: Nature
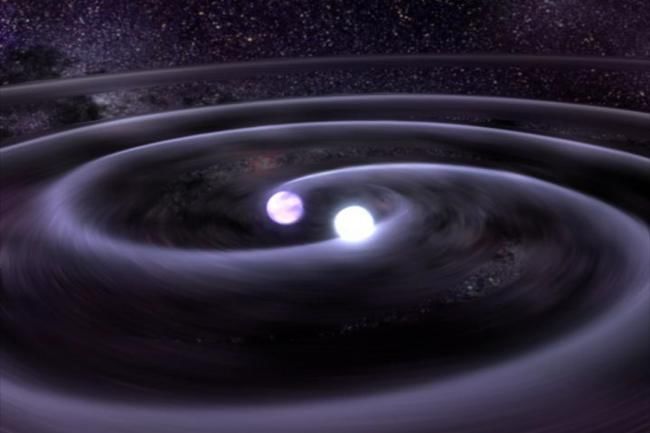 Why in News?
Why in News?A large team of astronomers and astrophysicists from various institutions in China has recently discovered a binary star system that includes a millisecond pulsar and a helium-rich companion star. This finding enhances our understanding of stellar dynamics and evolution.
Key Takeaways
- A binary star system consists of two stars bound by gravity, orbiting a common center of mass.
- Not all double stars are binary; some may appear close together in the sky but are not gravitationally linked.
- Approximately 85% of stars are thought to exist within binary or multiple star systems.
Additional Details
- Binary Stars: These systems include a primary star (the larger one) and a secondary star (the smaller companion). The characteristics of these stars can vary greatly in terms of mass, size, and brightness.
- Optical Doubles: Some star pairs seen from Earth may not be part of a binary system; these are termed optical doubles and are far apart in space.
- Stellar Remnants: Binary systems can also consist of a normal star and a remnant, such as a white dwarf, neutron star, or black hole, formed after a star exhausts its nuclear fuel.
- In certain binary systems, stars can transfer mass between one another, especially when their radii are comparable to the distance separating them.
This discovery highlights the complexity and diversity of stellar systems, offering valuable insights into the life cycles of stars and their interactions.
GS3/Economy
Bitcoin Hits Record $110K After Major U.S. Crypto Reform
Why in News?
Bitcoin has surpassed the $110,000 milestone for the first time, fueled by renewed investor enthusiasm following advancements in a significant cryptocurrency bill in the U.S. Senate — the GENIUS Act (Guiding and Establishing National Innovation for US Stablecoins). This bill aims to regulate stablecoins and has garnered bipartisan support, with some Democrats who previously opposed the legislation now backing it. The proposed reforms are anticipated to enhance market confidence and support the growth of crypto businesses. However, concerns have arisen regarding potential conflicts of interest, particularly involving former President Trump and Melania, who are engaged in the crypto space and could benefit from the bill's effects on the market.
Key Takeaways
- Bitcoin's price has reached an all-time high of $110,000.
- The GENIUS Act aims to regulate stablecoins and has gained bipartisan support.
- Concerns exist regarding conflicts of interest involving the Trump family in the crypto industry.
Additional Details
- GENIUS Act: This legislation focuses on the regulation of stablecoins, which are cryptocurrencies pegged to stable assets like the U.S. dollar. It represents a significant shift in policy by allowing large tech corporations to issue their own stablecoins.
- Key Provisions of the Bill:
- Mandatory Compliance: Issuers must comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and anti-terrorism laws, as well as privacy regulations under existing banking norms.
- Full Reserve Requirement: Stablecoins are required to be backed 1:1 by fiat currency or high-quality liquid assets.
- Separation of Funds: Issuers must maintain reserves separate from their operational funds.
- Transparency & Audits: Regular third-party audits and public disclosures of reserves are mandated.
- Political & Ethical Concerns: Some lawmakers have expressed worries about the potential for personal gain for the Trump family from this legislation and questioned the level of oversight involved.
- Broader Implications: The act is viewed as a pioneering federal effort to introduce stability and accountability to the fast-evolving crypto sector while legitimizing stablecoins in the U.S. economy.
- Inadequate Consumer Protections: Critics argue that the act does not offer consumers the same protections as traditional payment systems, which may leave users vulnerable.
- Risks of Illicit Use: With stablecoins being implicated in over 60% of unlawful crypto transactions, the rapid growth without adequate safeguards could exacerbate their use in illegal activities and destabilize financial markets.
- Big Tech Involvement: The bill's provisions allowing major tech firms to issue stablecoins could blur the lines between banking and commerce, raising concerns about regulatory loopholes and competitive fairness.
This legislative initiative represents a critical juncture in the regulation of cryptocurrencies, aiming to balance innovation with the need for consumer protections and market integrity.
GS3/Science and Technology
Alicella gigantea
Source: MSN
Why in News?Recent research has uncovered that the rare giant shrimp Alicella gigantea is more widespread than previously thought, inhabiting 59% of the world's oceans.
Key Takeaways
- Alicella gigantea is a giant amphipod crustacean that can reach lengths of up to 34 cm.
- This species was once believed to be extremely rare, with few documented sightings since its discovery.
- New findings indicate it has been recorded in 75 locations across the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian Oceans.
Additional Details
- Taxonomy: Alicella gigantea belongs to the amphipod group, which includes over 10,000 known species of shrimp-like crustaceans.
- Habitat:This species thrives in deep-sea environments, particularly in:
- Abyssal depths (between 3,000 to 6,000 m)
- Hadal zones (greater than 6,000 m)
- It has been discovered at depths up to 6,746 m, notably in regions like the Murray Fracture Zone.
- The Pacific Ocean is the most significant habitat, with 75% of its suitable seafloor area falling within the depth range favorable for Alicella gigantea.
The compilation of 195 records from diverse locations establishes Alicella gigantea as a globally distributed species rather than a localized rarity, highlighting its ecological significance.
|
38 videos|5258 docs|1111 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 24th May 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the key highlights of the RBI dividend transfer to the Union Government? |  |
| 2. How does Northeast India serve as a gateway for trade with Southeast Asia? |  |
| 3. What is the INSPIRE scheme and its significance? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of the newly added sites to the Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS)? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the Supreme Court ruling regarding Zudpi jungles as forest land? |  |





















