UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 28th December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Science and Technology
Upper Siang Hydropower Project
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
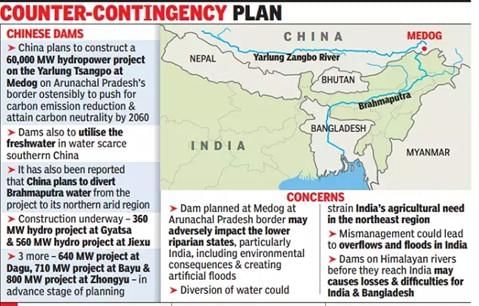
Why in News?The proposed Upper Siang Hydropower Project is significant as India seeks to counter China's ambitious plans to construct the world's largest dam. Strategically located in Arunachal Pradesh, this project aims to bolster India's energy capacity while addressing regional security concerns.
- The project is designed to have an installed capacity of 11,000 MW.
- It will be developed on the Siang River, which is known as the Brahmaputra in Arunachal Pradesh.
- This initiative serves as a counter to China's proposed 60,000 MW Yarlung Tsangpo dam.
Additional Details
- Developers: The project is a collaborative effort between the National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC) and the North Eastern Electric Power Corporation (NEEPCO).
- Reservoir Storage: It will feature a reservoir with a capacity of 9 billion cubic meters (BCM).
- Estimated Cost: The total cost of the project is projected to be around ₹1,13,000 crore.
- The region is primarily home to the Adi Tribe, who depend on pani kheti (settled agriculture along riverbanks) for their livelihood.
The Adi Tribe has a rich cultural heritage, speaking Tibeto-Burman languages and tracing their roots back to southern China in the 16th century. They are renowned for their craftsmanship in cane and bamboo products. Major festivals celebrated by the Adi include:
- Solung: A harvest festival that involves animal sacrifices.
- Aran: A festival centered around hunting.
- Motor or Pator system: A unique ritual where villages undergo lockdowns to search for wild herbs during epidemics.
This project not only aims at enhancing India's energy security but also highlights the cultural significance of the region and its indigenous communities.
GS2/International Relations
Canary Islands Migration Deaths
Source: Hindustan Times
 Why in News?
Why in News?In 2024, over 10,000 migrants tragically lost their lives while attempting to reach Spain by sea, marking it as one of the most fatal years for migration attempts.
- The Canary Islands are situated approximately 62 miles west of Morocco and are part of the European Union's outermost regions.
- In 2024, a record number of 10,457 migrant deaths were reported while crossing the perilous Atlantic migration route.
Additional Details
- About the Canary Islands: The Canary Islands, a Spanish archipelago, includes major islands such as Lanzarote, Fuerteventura, Gran Canaria, Tenerife, La Gomera, La Palma, and El Hierro.
- Climate and Oceanic Conditions: The islands have a subtropical climate with warm temperatures and minimal seasonal variation, influenced by the Canary Current, which creates hazardous sea conditions.
- Gateway to Europe: The Canary Islands are increasingly becoming a stepping stone for migrants seeking entry into continental Europe, facing numerous risks such as:
- Strong ocean currents.
- Overcrowded and poorly equipped boats.
- Adverse weather conditions.
- Atlantic Migration Route: The route from West Africa to the Canary Islands is recognized as one of the most dangerous migration paths globally, with the majority of migrant fatalities occurring on this journey.
This alarming trend highlights the urgent need for international cooperation and effective policies to ensure the safety and humane treatment of migrants.
GS3/Environment
Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The Wildlife Institute of India in Dehradun is launching India’s inaugural Fishing Cat Collaring Project at Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary, which is known to be a thriving habitat for this endangered species.
- Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary is located at the confluence ohef the Godavari River and the Bay of Bengal in Andhra Pradesh.
- The sanctuary features extensive mangrove forests, representing the second-largest mangrove ecosystem in India.
- It is home to various endangered species including the Fishing Cat, Smooth Indian Otter, and Olive Ridley Turtles.
Additional Details
- Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary:
Situated in the Kakinada district of Andhra Pradesh, the sanctuary encompasses a unique convergence of ecosystems. Approximately 40% of its area consists of sea backwaters, while the rest includes intermingled creeks affected by tidal waters.
- Vegetation and Flora:
The sanctuary boasts extensive mangrove and dry deciduous tropical forests, with notable species such as Rhizophora spp, Avicennia spp, and Sonnertia spp.
- Fauna:
The diverse wildlife includes endangered mammals like the Smooth Indian Otter and the Fishing Cat, along with a variety of birds such as the Black-capped Kingfisher and the Brahminy Kite.
- Fishing Cat:
The Fishing Cat (Prionailurus viverrinus) is a medium-sized, nocturnal predator primarily found in wetland habitats across Southeast Asia. They are exceptional swimmers, adept at pursuing fish.
- Conservation Status:
The Fishing Cat is classified as Vulnerable by the IUCN and is listed in CITES Appendix II and Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972.
This initiative aims to enhance the conservation efforts for the Fishing Cat and ensure the protection of its habitat within the increasingly vital ecosystem of the Coringa Wildlife Sanctuary.
GS3/Economy
Household Consumption Expenditure Survey 2023-24
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?The average household consumption spending per capita in India has increased by approximately 3.5% in real terms from August 2023 to July 2024 compared to the previous year, according to the latest findings from the Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES).
- The HCES is crucial for understanding household consumption patterns and economic well-being.
- The survey shows a notable increase in Monthly Per Capita Consumption Expenditure (MPCE), particularly in rural areas.
- Consumption inequality has decreased across both rural and urban populations.
Additional Details
- Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES): A survey designed to gather information on the consumption and expenditure of households on goods and services. It plays a key role in assessing economic well-being and is used to update the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- The survey is conducted by the National Sample Survey Office (NSSO) under the Ministry of Statistics & Programme Implementation (MoSPI).
- The MPCE serves as the primary indicator for analyzing household consumption trends.
- In 2023-24, the average MPCE (without imputation) increased by about 9% in rural areas and 8% in urban areas compared to 2022-23, highlighting a decrease in the urban-rural gap.
- Non-food items remain the largest contributors to household expenditure, with beverages, processed foods, and transportation being significant categories.
- The Gini coefficient, which measures consumption inequality, has decreased from 0.266 to 0.237 in rural areas and from 0.314 to 0.284 in urban areas, indicating a reduction in inequality.
Overall, the findings from the HCES 2023-24 reflect sustained growth in household consumption, particularly in rural regions, and provide valuable insights into changing economic dynamics in India.
GS3/Environment
High Arsenic Levels in Staple Foods
Source: DTE
Why in News?
Recent studies have revealed alarming levels of arsenic contamination in staple foods such as rice, wheat, and potatoes in Bihar, posing significant health risks to many, particularly in rural areas.
- Arsenic has been detected in staple foods in 11 districts of Bihar, raising urgent public health concerns.
- Long-term exposure to arsenic can lead to serious health issues, including cancer.
- Arsenic contamination is primarily linked to groundwater sources, particularly in the Ganga-Brahmaputra-Meghna basin.
Additional Details
- Health Impacts: Prolonged exposure to arsenic-contaminated water can cause conditions such as arsenicosis, which includes skin lesions and various cancers (skin, bladder, kidney, lung). It is classified as a Group 1 carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC).
- Non-Carcinogenic Risks: Long-term exposure can also lead to non-carcinogenic effects like skin pigmentation changes and the development of hard patches on palms and soles.
- Sources of Contamination: The primary source of arsenic in Indian groundwater is geological. Alluvial aquifers in the Ganga-Brahmaputra basin are particularly vulnerable due to human activities like excessive groundwater extraction.
Addressing arsenic contamination in food and water sources is crucial for public health, especially in regions severely affected by this issue. Urgent measures are needed to monitor and mitigate arsenic levels in both drinking water and agricultural produce.
GS3/Economy
Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER)
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has recently highlighted significant changes in the Real Effective Exchange Rate (REER) of the Indian rupee, indicating its impact on the economy and trade.
- The REER of the Indian rupee reached a record high of 114 in November 2024.
- Higher REER values indicate overvaluation of the rupee, affecting export competitiveness.
- NEER and REER indices now include a broader basket of 36 currencies.
Additional Details
- NEER (Nominal Effective Exchange Rate): This is the weighted average of a currency’s bilateral exchange rates with multiple trading partners. It reflects the nominal strength of a currency but does not account for inflation or price level differences.
- REER (Real Effective Exchange Rate): An improvement over NEER, it adjusts for relative price levels between domestic and foreign economies, calculated as NEER multiplied by the ratio of the Domestic Price Index to the Foreign Price Index.
- Currency Basket: The indices used to calculate NEER and REER have expanded from six to a broader set of 36 currencies, reflecting India's diverse trade relations.
- Factors Influencing NEER and REER:
- Productivity Differences
- Terms of Trade
- Inflation
- Fiscal Spending
The recent rise in REER signifies overvaluation, which can lead to reduced export competitiveness while making imports cheaper. This situation requires careful monitoring to maintain a balanced trade environment.
GS3/Environment
How Sea Otters Are Saving Coastal Ecosystems
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
The significant recovery of sea otter populations in California, particularly in the Elkhorn Slough National Estuarine Research Reserve, has played a crucial role in controlling the proliferation of invasive green crabs.
- Sea otters are essential for maintaining the health of coastal ecosystems.
- They consume a substantial number of green crabs each year, aiding in the control of this invasive species.
- Sea otters have unique adaptations that enable them to thrive in cold ocean environments.
Additional Details
- About Sea Otters: These marine mammals belong to the weasel family and inhabit the Pacific coasts of North America and Asia. They primarily live in water but occasionally come ashore to rest.
- Historical Context: Sea otters were heavily hunted for their luxurious fur in the 18th and 19th centuries but have since bounced back after being designated as a threatened species and receiving federal protection in 1977.
- Feeding Habits: Sea otters consume between 50,000 to 120,000 green crabs annually, effectively mitigating the invasive species problem along the West Coast.
- Unique Characteristics: Unlike many marine mammals that use blubber for warmth, sea otters have a high metabolism and consume about 25% of their body weight daily. They are equipped with webbed feet and water-repellent fur to keep warm and dry.
Green Crab (Portunus Sanguinolentus)
- Habitat: Originally from the Atlantic Ocean and the Baltic Sea, the green crab has spread to various regions, including Australia, South America, and South Africa.
- Physical Features: Adult green crabs typically have a carapace width of about 90 mm. Their coloration can range from green to brown, grey, or red, with the latter often resulting from delayed moulting.
- Diet: They primarily feed on small crustaceans, mollusks, and worms.
- Impact on Ecosystems:The invasive nature of green crabs poses threats to coastal ecosystems by:
- Damaging critical seagrass beds that serve as habitats for various marine species.
- Overhunting prey species that are vital for the survival of native species.
- Outcompeting native species for essential resources like food and habitat.
The resurgence of sea otters is not only a success story of conservation but also a vital aspect of restoring balance to coastal ecosystems affected by invasive species like the green crab.
GS3/Economy
Manmohanomics, In His Own Words
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
Dr. Manmohan Singh, a distinguished economist and former Prime Minister of India, has had a profound influence on the nation's economic policies and reforms, particularly during the critical period of economic liberalization in the early 1990s.
Key Takeaways
- Significant contributions to India's shift from a centrally-planned economy to a liberalized market economy.
- Advocated for market-driven growth while addressing issues of inequality and the need for state intervention.
- His tenure as Prime Minister witnessed both rapid economic growth and challenges related to governance and corruption.
Additional Details
- Economic Liberalization: Initiated in 1991, these reforms included reducing trade barriers, emphasizing fiscal discipline, and attracting foreign investments.
- Key Economic Principles: Emphasized the importance of planning in conjunction with market forces, highlighted the risks of inequality, and advocated for open trade policies.
- Public Sector Reforms: Stressed the need for autonomy and accountability in PSUs, criticizing political interference and inefficiencies.
- Focus on Education and Health: Advocated for universal primary education and healthcare as essential for enhancing productivity and societal well-being.
Manmohan Singh's economic vision, characterized by pragmatism and foresight, has significantly reshaped India's economic landscape. His leadership during the liberalization period and his commitment to reforms across various sectors remain crucial to understanding India's economic transformation. Despite facing challenges and criticisms during his later years, his legacy endures, highlighting the effectiveness of informed and thoughtful policymaking.
GS2/Governance
PRADHAN MANTRI RASHTRIYA BAL PURASKAR
Source: The Hindu Why in News?
Why in News?
The President of India, Smt Droupadi Murmu, recently honored 17 children with the Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar at a ceremony held at the Rashtrapati Bhavan Cultural Centre. This award recognizes exceptional achievements by children in various fields.
- The Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar is India's highest civilian award for children.
- A total of 17 children were awarded across seven different categories.
- The ceremony also marked the observance of 'Veer Bal Diwas' in memory of the sons of Guru Gobind Singh.
Additional Details
- Eligibility: A child must be an Indian citizen and resident of India, aged between 5 and 18 years. Achievements must have occurred within two years prior to the application deadline.
- Categories of Awards:The awards are presented in seven categories:
- Bravery
- Art & Culture
- Environment
- Innovation
- Science & Technology
- Social Service
- Sports
- Award Process: Nominations for the awards are invited from various sources such as state governments, school boards, and ministries. The initial scrutiny is performed by a Screening Committee, followed by final selection by the National Selection Committee.
The Pradhan Mantri Rashtriya Bal Puraskar not only celebrates the extraordinary talents of children but also emphasizes the importance of recognizing and encouraging young achievers in society.
GS2/Governance
PM CARES Fund Collects ₹912 Crore in Post-Pandemic Year
Source: Financial Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?The PM CARES Fund has garnered ₹912 crore in contributions during the financial year 2022-23, which includes ₹909.64 crore in voluntary donations and ₹2.57 crore in foreign contributions. This indicates sustained support for the Fund even in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic.
- The PM CARES Fund was established on March 27, 2020, as a Public Charitable Trust to manage emergencies like the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Donations to the Fund enjoy 100% tax exemption under Section 80G of the Income Tax Act and qualify as CSR expenditure under the Companies Act, 2013.
- The Fund operates under the Foreign Contribution Regulation Act (FCRA) and has a designated account for foreign donations.
Additional Details
- Objective: The Fund aims to provide relief and support during public health emergencies or other crises, including enhancing healthcare infrastructure and funding relevant research.
- The management consists of the Prime Minister as the ex-officio Chairperson along with the Defence Minister, Home Minister, and Finance Minister as trustees.
- Since its inception, the Fund has collected a total of ₹13,605 crore, with ₹9,912 crore collected in the last financial year alone.
- In 2022-23, ₹439 crore was disbursed, primarily for initiatives such as support for children affected by the pandemic and procurement of oxygen concentrators.
Despite its contributions, the PM CARES Fund faces criticism regarding transparency and accountability. Critics argue it is not audited by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) and does not fall under the Right to Information (RTI) Act, raising concerns about public trust. Addressing these issues could enhance the Fund's credibility and effectiveness in future emergencies.
GS2/International Relations
UNGA Adopts Milestone Cybercrime Treaty
Source: UN News
 Why in News?
Why in News?The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA) has successfully adopted a legally binding treaty aimed at combating cybercrime, culminating a significant five-year negotiation process among Member States. This treaty marks the first international criminal justice agreement established in over two decades.
- The treaty was adopted unanimously by all 193 UN member states.
- A signing ceremony is planned for 2025 in Hanoi, Vietnam.
Additional Details
- Objective: The treaty seeks to prevent and combat cybercrime, enhance international cooperation, and protect human rights in cyberspace.
- Key Provisions:
- Addressing Cybercrime: Targets various crimes including terrorism, human trafficking, financial fraud, drug smuggling, and data theft through ICT platforms.
- Victim-Centric Approach: Focuses on protecting vulnerable groups and ensuring justice for victims.
- International Cooperation: Promotes evidence-sharing, joint investigations, and capacity-building among nations.
- Safeguarding Human Rights: Balances cybersecurity needs with protection of freedom of expression, privacy, and access to information.
- Adaptability: Allows for the introduction of additional protocols to address emerging cyber threats.
- Capacity-Building: Supports the development of cybercrime legislation and enhances law enforcement capabilities.
- Public Awareness: Encourages global education campaigns and proactive measures to prevent cyber offenses.
- Significance:
- Landmark in International Law: Represents a global commitment to cybersecurity.
- Strengthening Cybersecurity: Provides tools to mitigate ICT-enabled threats.
- Protecting Vulnerable Groups: Ensures justice and protection for marginalized communities affected by cybercrime.
- Economic and Social Benefits: Safeguards global economies and promotes investment in cybersecurity infrastructure.
- Flexibility for Future Threats: Provisions for adapting to challenges posed by AI-driven cyber threats.
This treaty represents a significant milestone in the fight against cybercrime, emphasizing the importance of international cooperation and human rights protection in the digital age.
GS2/International Relations
China Approves Dam Over Brahmaputra
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
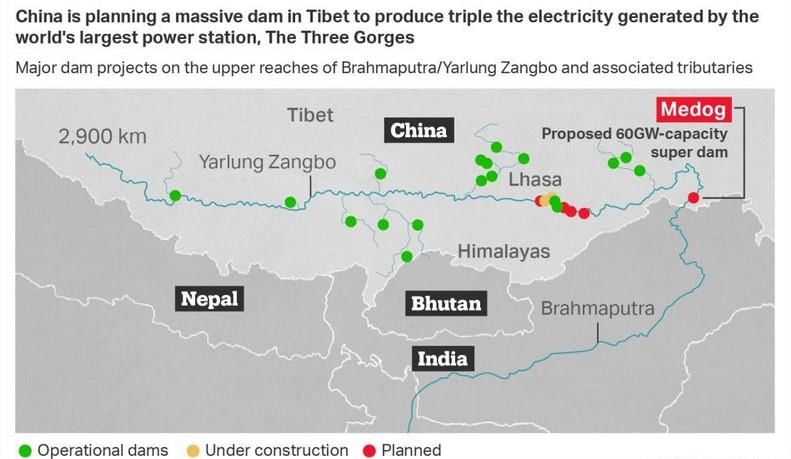
Why in News?China has recently announced the construction of the world’s largest dam on the Brahmaputra River, known as the Yarlung Zangbo in Tibet. This development has raised significant concerns for India and Bangladesh, the lower riparian states that rely on the river's waters.
- The dam is part of China’s 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) and its long-term strategy up to 2035.
- It will be constructed in the lower reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River in Tibet, close to the Indian border.
- The project involves an investment exceeding $137 billion, surpassing any previous infrastructure projects, including the Three Gorges Dam.
Additional Details
- Geopolitical Control: The dam gives China the ability to regulate the flow of water, raising fears of potential disruption during conflicts.
- Environmental Impact: There are risks to biodiversity, sediment flow, and the health of ecosystems downstream in the sensitive Himalayan region.
- Seismic Hazards: The dam's location near a tectonic plate boundary heightens the risk of earthquakes, posing additional safety concerns.
- Livelihood Disruption: Local communities that depend on the river for agriculture and fishing may face significant challenges due to altered water flow.
- Transparency Issues: The lack of data sharing and unilateral decisions by China can increase distrust among neighboring riparian states.
This ambitious infrastructure project is poised to have far-reaching implications for regional water politics, environmental stability, and the livelihoods of millions who depend on the Brahmaputra River.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|





















