UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 29th December 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
Kamarajar Port: A Major Milestone in India's Maritime Sector
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Minister for Ports, Shipping and Waterways recently highlighted a significant increase in cargo-handling capacity at Indian ports, which has risen by 87 percent over the past nine years. Notably, Kamarajar Port in Tamil Nadu has seen an impressive growth of 154 percent in its cargo handling capabilities.
- Kamarajar Port, formerly known as Ennore Port, is located about 24 km north of Chennai.
- It is the 12th major port in India and holds the distinction of being the first public company port in the country.
- The port was recognized as a major port under the Indian Ports Act, 1908, in March 1999.
- Kamarajar Port operates under a landlord port model, which combines public and private sector operations.
Additional Details
- Landlord Port Model: In this model, the port authority acts as a regulatory body while private companies handle operational aspects like cargo management.
- Main Cargo: The primary cargo handled by Kamarajar Port is coal, alongside LNG, containers, and multipurpose cargo.
- The port is owned by the Chennai Port Trust, which also manages the Port of Chennai.
In summary, Kamarajar Port's growth reflects a broader trend in India's maritime infrastructure, underscoring the importance of public-private partnerships in enhancing cargo-handling efficiency and capacity.
GS3/Environment
Key Facts about Teesta River
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Bengal irrigation department has recently made a strategic decision to supply water to farmlands through pipelines sourced from the Teesta River and its canals. This approach aims to reduce the need for acquiring additional land to construct new canals, sub-canals, and drains.
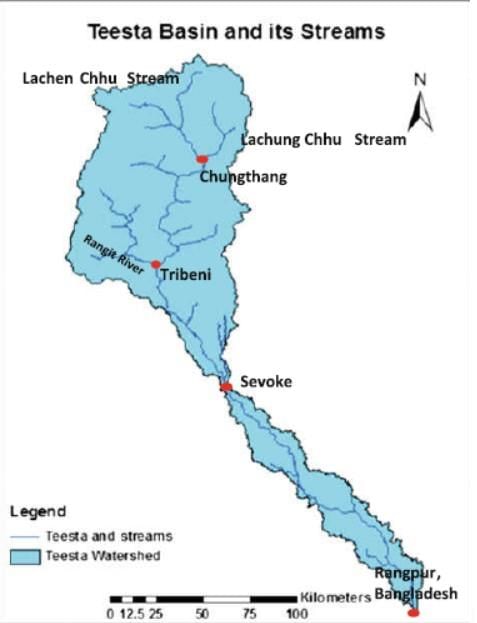
- The Teesta River is a significant Himalayan river flowing through Sikkim and West Bengal in India, and into Rangpur in Bangladesh.
- It serves as a tributary of the Brahmaputra River and forms a natural boundary between Sikkim and West Bengal.
- The river has experienced a change in its course over time, notably around 1787, redirecting its flow to join the Jamuna River in Bangladesh.
Additional Details
- Geographical Course: The Teesta River rises in the Himalayas near Chunthang in Sikkim, flows southward, cutting through the Siwalik Hills east of Darjeeling, and then southeast into the plains of West Bengal.
- Seasonal Variability: The river's flow is greatest during the summer months (June to September) due to the heaviest monsoon rains and significant glacial meltwater contributions.
- Flooding and Navigation Challenges: In its lower reaches, the river is characterized by frequent flooding and violent course changes, which complicate navigation.
- Major Tributaries: The river has several tributaries including:
- Left-bank: Lachung Chhu, Chakung Chhu, Dik Chhu, Rani Khola, Rangpo Chhu.
- Right-bank: Zemu Chhu, Rangyong Chhu, Rangit River.
The decision to utilize the Teesta River for irrigation through pipelines demonstrates an innovative approach in managing water resources effectively while minimizing land acquisition and environmental disruption.
GS1/History & Culture
Lothal: A Global Hub for Maritime Heritage
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?The ancient city of Lothal, part of the Indus Valley Civilization, is set to become a significant center for maritime heritage with the establishment of the National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC) in Gujarat. This initiative, led by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways under the Sagarmala Programme, aims to celebrate India's extensive maritime history while fostering economic and cultural development.
- Lothal, dating back to 2400 BCE, was a crucial hub in the Harappan Civilization known for its advanced dockyard and trade networks.
- The NMHC aims to integrate education, tourism, and cultural preservation, with 65% of construction already completed.
- The project is expected to boost tourism and create jobs, empowering local communities through skill development.
Additional Details
- Historical Significance: Lothal was recognized for its advanced dockyard and thriving trade networks, which connected various regions and facilitated economic activity.
- Key Features of NMHC: The complex will utilize an "edutainment" approach to engage visitors, showcasing maritime history from ancient to modern times.
- Government Initiatives: This flagship project aims to modernize India’s maritime infrastructure, enhancing economic growth through port-led development.
- Community Integration: The development process emphasizes local community involvement to ensure inclusivity and shared benefits.
The National Maritime Heritage Complex in Lothal represents a pivotal step in preserving India's maritime legacy while promoting economic, educational, and cultural advancements. It underscores the historical significance of Lothal and reaffirms India's commitment to maritime excellence on a global scale.
GS2/International Relations
International Day of Epidemic Preparedness
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The International Day of Epidemic Preparedness is commemorated annually on December 27. This day emphasizes the critical importance of prevention, preparedness, and partnership in combating epidemics, urging nations to strengthen their health systems for a safer future.
- The day was first observed on December 27, 2020, following a call from the United Nations General Assembly.
- UN Secretary-General António Guterres has urged nations to invest in resilience and equity to ensure global health and safety.
Additional Details
- Epidemic: An epidemic is defined as a sudden outbreak of disease that affects a large number of individuals within a specific region, community, or population. Examples include yellow fever, smallpox, measles, and polio.
- Not all epidemics are contagious; for instance, West Nile fever and rising obesity rates are also classified as epidemics.
This observance serves as a reminder of the urgent need for global solidarity and investment in health systems capable of preventing, detecting, and responding to infectious disease outbreaks.
GS3/Science and Technology
Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
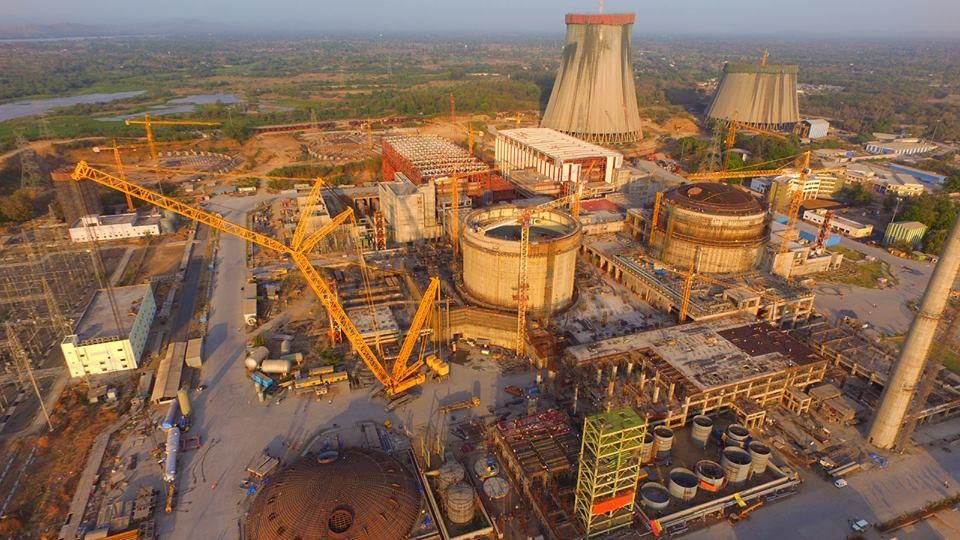
Why in News?An anti-corruption organization in Bangladesh has launched an investigation into the Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant, a significant project with an estimated cost of $12.65 billion that is being constructed with support from Russia.
- The Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant is being built in Iswardi, Pabna District, Rajshahi Division.
- This facility will be Bangladesh's first nuclear power source.
- The plant is owned by the Bangladesh Atomic Energy Commission (BAEC).
- It includes two VVER-1200 reactors developed by the Russian company Rosatom.
- Construction began in November 2017 and aims to generate 2400 megawatts of power.
- Upon completion, it is expected to provide approximately 9% of Bangladesh's total electricity needs.
- The project is primarily financed by a loan from Russia, which will be repaid over a period of 20 years.
Additional Details
- Location: The plant is situated about 160 kilometers northwest of Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh.
- Significance: This project marks a major step towards enhancing Bangladesh's energy security and diversifying its energy sources.
- The investigation into the project underscores the importance of transparency and accountability in large-scale infrastructure initiatives.
The Rooppur Nuclear Power Plant represents a pivotal development in Bangladesh's energy landscape, with its successful completion having the potential to significantly impact the country’s energy supply and economic growth.
GS2/Governance
PM- Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) Scheme
Source: Live Law
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Delhi High Court has recently mandated the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and the Delhi Government to implement the PM- Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM) scheme in the national capital.
- PM-ABHIM is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) with a total outlay of Rs. 64,180 crores for the period from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- The scheme aims to strengthen healthcare infrastructure across India, addressing both urban and rural health needs.
- It focuses on enhancing the capacity of health systems to respond effectively to current and future pandemics and disasters.
Additional Details
- Components under the CSS:
- Establishment of 12 Central Institutions as training and mentorship sites, including 150-bedded Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs).
- Strengthening the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC) with 5 new Regional NCDCs and 20 metropolitan health surveillance units.
- Expansion of the Integrated Health Information Portal to connect all public health labs across States/UTs.
- Operationalization of 17 new Public Health Units and reinforcement of 33 existing units at Points of Entry (32 Airports, 11 Seaports, and 7 land crossings).
- Establishment of 15 Health Emergency Operation Centres and 2 container-based mobile hospitals.
- Creation of a national institution for One Health, 4 new National Institutes for Virology, a Regional Research Platform for the WHO South East Asia Region, and 9 Biosafety Level III laboratories.
- Support for States/UTs:
- Construction of 17,788 rural Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs), targeting areas with populations of 5,000 in plain regions and 3,000 in difficult terrains.
- Support for 11,024 urban Health and Wellness Centres, primarily in slum-like areas, with one Urban HWC for every 15,000-20,000 population.
- Establishment of 3,382 Block Public Health Units (BPHUs) at the block level.
- Integration of Public Health Labs (IPHLs) in 730 districts.
- Creation of Critical Care Hospital Blocks (CCBs) in 602 districts, particularly those with populations exceeding 5 lakhs.
The implementation of the PM-ABHIM scheme is a significant step towards enhancing the health infrastructure in Delhi and across the country, ensuring better preparedness for health emergencies and improving access to healthcare services for all citizens.
GS3/Economy
Migration Trends in India
Source: Business Standard
Why in News?
A recent working paper by the Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM), titled "400 Million Dreams!", provides insights into the changing migration trends in India. This analysis follows a similar study conducted in the Economic Survey of 2016-17 during Arvind Subramanian's tenure as Chief Economic Advisor.
- West Bengal and Rajasthan have emerged as new hotspots for migrant inflows.
- The overall number of migrants has decreased by 11.78% since the 2011 Census.
- Major migration routes include Uttar Pradesh to Delhi and Gujarat to Maharashtra.
Additional Details
- Top States for Migrant Destinations: West Bengal and Rajasthan are now key states, alongside Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, and Madhya Pradesh, which rank among the top five in receiving migrant inflows.
- Decline in Overall Migration: The report indicates that improved economic opportunities in smaller cities have reduced the need for long-distance migration.
- Major Migration Routes: The primary routes in 2023 include Uttar Pradesh to Delhi and Bihar to West Bengal.
- Destination Districts: Key urban centers attracting migrants include Mumbai, Bengaluru, Howrah, and Hyderabad.
The findings from the EAC-PM report are crucial for understanding migration patterns in India, emphasizing the significant changes in destination preferences and the decline in migration trends due to improved local economic opportunities. These insights are essential for policymakers focused on urban planning, infrastructure development, and economic growth.
GS1/Geography
What is Denmark Strait Cataract?
Source: Times of India
 Why in News?
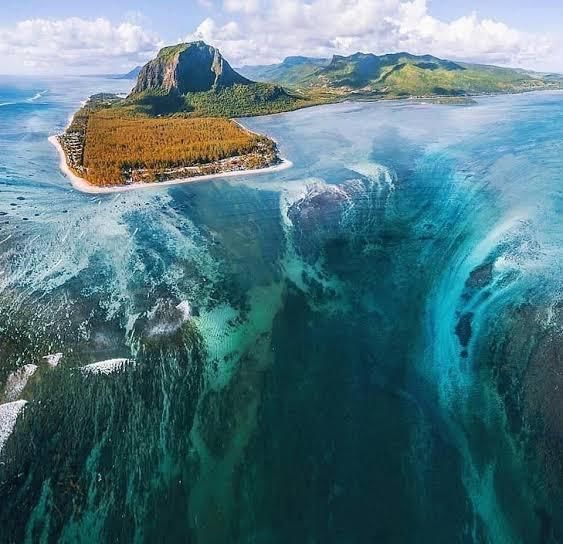
Why in News?The Denmark Strait cataract is an extraordinary underwater phenomenon that significantly impacts global ocean circulation and contributes to the shaping of marine ecosystems, despite being hidden from sight.
- The Denmark Strait cataract is the largest waterfall on Earth.
- It is located in the underwater channel between Iceland and Greenland.
- Its vertical drop measures approximately 2,000 metres, which is over three times the height of Angel Falls.
- The cataract stretches about 480 kilometres across the Denmark Strait.
- This massive waterfall is invisible from the ocean surface.
Additional Details
- Formation: The cataract was formed during the last Ice Age, approximately 17,500 to 11,500 years ago. Glacial activity sculpted the seabed, allowing cold water from the Nordic Seas to flow into the Irminger Sea, a marginal sea of the North Atlantic Ocean.
- This process plays a vital role in the thermohaline circulation, an essential global system of ocean currents that helps regulate climate and marine ecosystems.
The Denmark Strait cataract remains a remarkable yet unnoticed feature of our planet, illustrating the hidden wonders of oceanic geography and their profound effects on the environment.
GS3/Science and Technology
What is GPS Spoofing?
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?Recent reports from OPSGROUP indicate a notable increase in GPS interference incidents, particularly involving 'spoofing' with false signals, occurring in conflict zones around the world, including areas near India's borders with Pakistan.
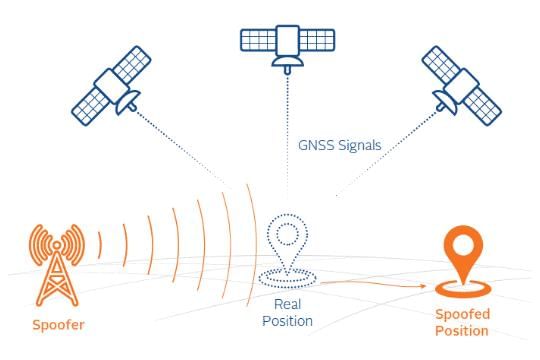
- GPS spoofing involves the manipulation of GPS signals, misleading receivers about their actual location.
- This practice poses significant risks to various applications that rely on accurate GPS data, including navigation and time synchronization.
Additional Details
- GPS Spoofing: This technique, also referred to as simulation, involves broadcasting counterfeit GPS signals to deceive a GPS receiver. By presenting false information, it causes the receiver to report an incorrect location.
- How GPS Works: The Global Positioning System (GPS) operates by transmitting signals from satellites to receivers on Earth, which calculate their position based on the time it takes for these signals to arrive.
- Exploitation of Vulnerabilities: The weak signal strength of GPS satellites makes them susceptible to interference. Attackers can overpower real signals with fake ones, leading to erroneous location data.
- Typically, a GPS spoofer first learns about the target's GPS setup, including signal types and processing methods, before sending stronger counterfeit signals that the receiver mistakenly identifies as legitimate.
The rise in GPS spoofing incidents highlights the critical need for enhanced security measures in GPS technology to protect against such cyberattacks, which can have far-reaching implications in various sectors.
GS3/Economy
Formation of the FREE-AI Committee by the Reserve Bank of India
Source: Economic Times
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has established a committee named FREE-AI, aimed at developing a framework for the responsible and ethical implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) within the financial sector.
- The FREE-AI committee consists of eight members.
- It will be chaired by Pushpak Bhattacharyya, a professor at IIT Bombay.
- The committee includes representatives from various organizations including NITI Aayog, HDFC Bank, and Microsoft India.
- A report is expected within six months from the committee's first meeting.
Additional Details
- Committee Composition: The panel comprises members from significant institutions such as IIT Madras, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, and the law firm Trilegal, ensuring a diverse range of expertise and perspectives.
- Mandate of the Committee: The committee's responsibilities include studying the current level of AI adoption in financial services, reviewing global regulatory approaches, and recommending governance frameworks for the ethical use of AI.
- The committee will also focus on identifying potential risks associated with AI and suggest a framework for evaluating, mitigating, and monitoring these risks for regulated entities.
This initiative by the RBI highlights the growing importance of establishing ethical guidelines and governance for AI in the financial sector, reflecting a proactive approach to ensure that technological advancements are aligned with regulatory standards and public trust.
GS3/Economy
Why Inflation Will Be a Key Concern in 2025
Source: Economic Times
Why in News?
2024 has been a mixed year for India's economy, with remarkable growth in the first half, surprising many, including government officials. However, challenges emerged in the latter half, characterized by slowing growth, persistent inflation, and ongoing disagreements between the RBI and the Finance Ministry regarding policy responses.
- Clamour for a rate cut has intensified among top government officials.
- India's economic performance in 2023-24 was initially strong but showed signs of slowing down.
- Inflation remains a concern, impacting hopes for interest rate cuts.
Additional Details
- Rate Cut Advocacy: Since November, government officials have pushed for an RBI rate cut to prioritize growth and investments, especially as Q2 GDP growth slowed to a 7-quarter low of 5.4% due to weak urban demand.
- Economic Performance Overview: Last year, India enjoyed record stock market highs and a GDP growth of 7.7% in the first half of 2023-24. The Finance Ministry anticipated a growth rate exceeding 6.5% for the full year.
- The government's focus on employment and consumption in the 2024-25 Union Budget included a significant capex plan of ₹11.11 lakh crore to support growth.
- Despite high consumer inflation spiking in September due to food prices, the RBI opted not to lower interest rates, complicating the economic outlook.
The ongoing tension between the RBI and Finance Ministry regarding the management of growth and inflation is crucial for shaping economic policy in 2025. As inflationary pressures persist alongside slowing growth, balancing these factors remains a significant challenge for the government.
GS2/International Relations
Navigating India's Complex Foreign Policy Challenges
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?In June 2024, following Prime Minister Modi's third term, India is experiencing heightened diplomatic activity amidst global instability and regional upheavals, particularly concerning Bangladesh. As 2025 approaches, India's foreign policy must remain flexible and responsive to these evolving challenges.
- Intense diplomatic engagements following Prime Minister Modi's re-election.
- Key challenges faced by South Block in 2024.
- India's navigation through global conflicts and its diplomatic agenda for 2025.
Additional Details
- India-China Relations: The most significant negotiation involved the disengagement at the Line of Actual Control. The first meeting between Modi and Xi Jinping in five years occurred at the BRICS summit in Kazan, aimed at rebuilding trust after multiple PLA transgressions since 2020.
- Strengthening Ties with France: French President Emmanuel Macron's attendance at India’s Republic Day celebrations solidified cooperation in defense, energy, and maritime sectors, showcasing bilateral reliability.
- Trade Agreements: The completion of the India-European Free Trade Association agreement in early 2024 served as a template for future agreements, although no significant progress was made with Australia, the U.K., or the EU by year-end.
- Diplomatic Engagements: Prime Minister Modi hosted leaders from neighboring countries during his swearing-in, excluding Pakistan, with successful exchanges with Bhutan, Sri Lanka, and Maldives.
- Relations with Bangladesh: The ousting of Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina in August 2024 strained India-Bangladesh relations, marked by rising attacks on Hindu minorities.
- Worsening Ties with Canada: Allegations of Indian involvement in the Nijjar killing led to a breakdown in relations, with India freezing diplomatic ties with Canada.
- Legal Challenges with the U.S.: Escalating tensions arose due to indictments involving the Adani group and a link to an alleged assassination plot, although the new pro-India U.S. administration offers potential for improved relations.
- Regional Rivalries: The U.S.'s increasing involvement in South Asia and China’s growing influence in Nepal pose ongoing challenges for India.
- Global Conflicts: India maintained a neutral position during the Russia-Ukraine conflict and the Gaza situation, advocating for peace while refraining from assigning blame to Israel.
- Focus on West Asia: India shifted towards bilateral engagements with West Asian nations amidst challenges faced by initiatives like IMEC and I2U2.
- Strengthening U.S.-India Relations: External Affairs Minister Jaishankar's discussions with the Trump transition team indicate a strong focus on U.S. relations for 2025, with high-profile visits anticipated.
- Engagement with Iran: India is set to host a ministerial visit from Iran and has planned discussions on critical technology with U.S. NSA Jake Sullivan.
In conclusion, India's foreign policy landscape for 2025 is marked by both challenges and opportunities, necessitating a strategic approach to maintain regional stability and foster international relations amidst shifting dynamics.
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|





















