UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 4th February 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Governance
Gyan Bharatam Mission
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The Union Budget for 2025-26 has introduced the Gyan Bharatam Mission, a significant initiative aimed at the conservation and documentation of India's manuscript heritage.
- The Gyan Bharatam Mission aims to conserve and document over one crore manuscripts.
- This mission focuses on the survey, documentation, and preservation of manuscripts held in academic institutions, museums, libraries, and by private collectors.
- A key component is the establishment of a national digital repository for the Indian knowledge system, facilitating knowledge sharing.
- The digitization efforts will centralize traditional knowledge, making it accessible to researchers, students, and institutions globally.
Additional Details
- What is a Manuscript? A manuscript is defined as a handwritten document on materials such as paper, bark, cloth, metal, or palm leaf, dating back at least 75 years and possessing significant scientific, historical, or aesthetic value. Notably, lithographs and printed volumes do not qualify as manuscripts.
- Manuscripts exist in numerous languages and scripts, often with variations of the same language represented in different scripts, such as Sanskrit written in Oriya, Grantha, and Devanagari scripts.
- Unlike historical records, such as epigraphs or revenue records that provide direct accounts of events, manuscripts primarily contain knowledge content.
The Gyan Bharatam Mission represents a vital step towards safeguarding India's rich manuscript heritage and ensuring its availability for future generations and scholarly research.
GS3/Science and Technology
Launch of GARBH-INi Data Repository and Ferret Research Facility
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India has made significant advancements in biomedical research and innovation with the inauguration of the country's first Ferret Research Facility, the establishment of the GARBH-INi data repository, and the signing of a crucial technology transfer agreement.
- The GARBH-INi Data Repository is a comprehensive data dashboard that includes one of South Asia's largest pregnancy cohort datasets.
- It has been developed under the GARBH-INi program and provides access to extensive clinical data, images, and biospecimens from over 12,000 pregnant women, newborns, and postpartum mothers.
- This platform is designed to facilitate global research aimed at enhancing maternal and neonatal health outcomes.
Additional Details
- GARBH-INi Program: This initiative promotes maternal and child health and focuses on developing predictive tools for preterm birth. It operates under the Department of Biotechnology of the Union Ministry of Science and Technology as an interdisciplinary collaboration.
- The program is led by the Translational Health Science and Technology Institute (THSTI) located in the NCR Biotech cluster, Faridabad, and is part of the Atal Jai Anusandhan Biotech Mission, which is dedicated to Nationally Relevant Technology Innovation (UNaTI).
The GARBH-INi data repository serves as a gateway for researchers to delve into the extensive data available, promoting collaboration and impactful discoveries in the field of maternal and neonatal health.
GS3/Economy
MAKHANA
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
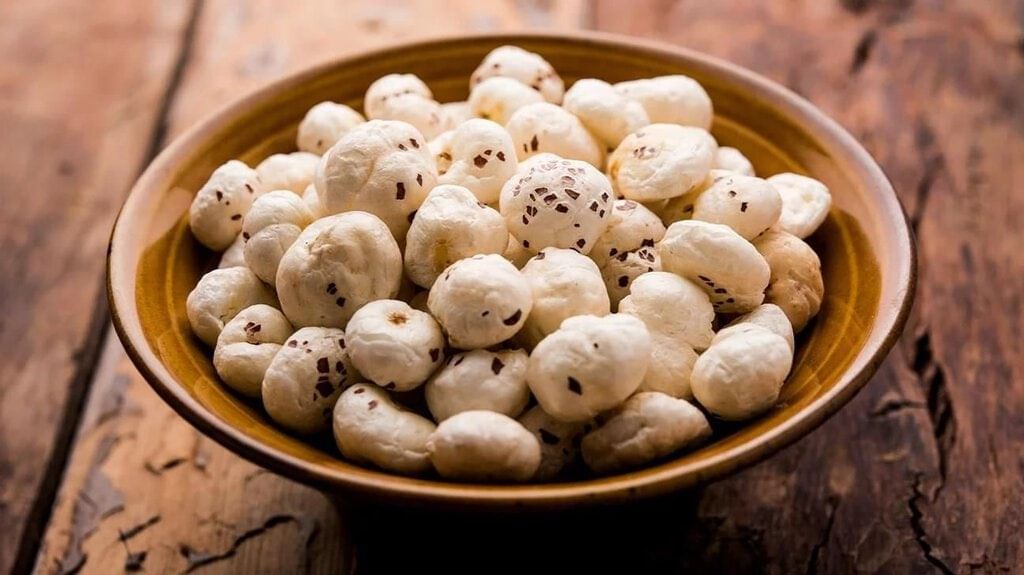
The Union Finance Minister announced the establishment of a “Makhana Board” in Bihar during the presentation of the Union Budget. This initiative aims to enhance the cultivation and marketing of fox nuts in the region.
- Bihar produces about 90% of India’s Makhana, particularly in its northern and eastern regions.
- Makhana, also known as the fox nut, is the dried edible seed of the gorgon plant (Euryale ferox), found in freshwater ponds across South and East Asia.
- The plant features distinctive violet and white flowers along with large, prickly leaves that can exceed one meter in diameter.
- The edible seeds have an outer layer that varies from black to brown, leading to its nickname, the ‘Black Diamond.’
- Processed seeds are popularly consumed as popped snacks called ‘lava.’
- Makhana is nutritious, offering a rich source of carbohydrates, protein, and minerals, and can be utilized in various forms for medicinal and nutritional purposes.
- In 2022, ‘Mithila Makhana’ received a Geographical Indication tag.
- Besides Bihar, Makhana is also cultivated in smaller amounts in states like Assam, Manipur, West Bengal, Tripura, and Odisha, as well as in countries such as Nepal, Bangladesh, China, Japan, and Korea.
Additional Details
- Climatic Conditions for Cultivation: Makhana is primarily grown in tropical and subtropical regions, thriving in stagnant water bodies such as ponds, lakes, ditches, or wetlands with shallow depths of 4-6 feet.
- The optimal conditions for Makhana cultivation require temperatures between 20-35°C, relative humidity of 50-90%, and annual rainfall ranging from 100-250 cm.
The establishment of the Makhana Board is expected to significantly boost the cultivation and marketing efforts, ultimately benefiting the local economy and promoting the unique agricultural heritage of Bihar.
GS1/Geography
Araku Valley
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
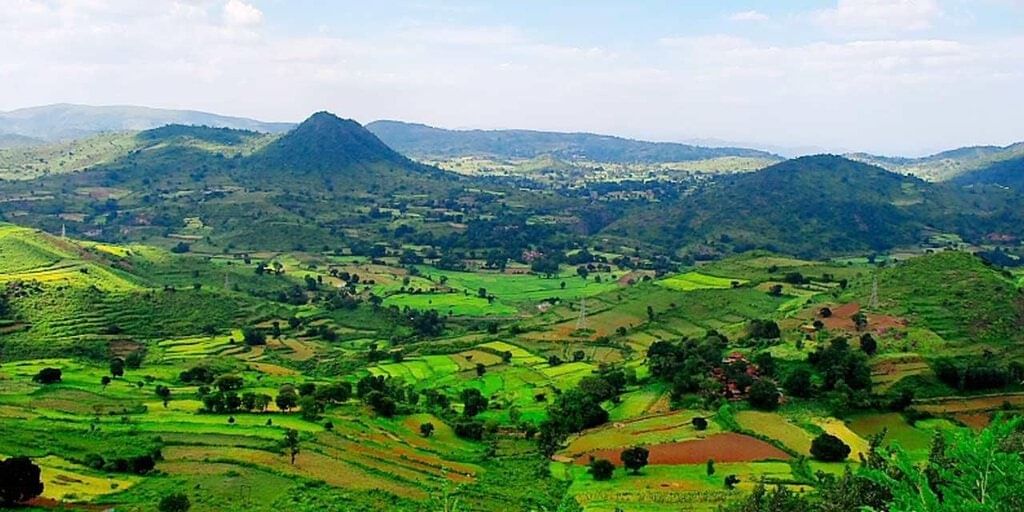
The recent Araku Utsav, titled ‘Chali’, was a vibrant three-day festival held in the Araku Valley, located in the Alluri Sitharama Raju (ASR) district of Andhra Pradesh. The event showcased a rich tapestry of performances by Adivasis from various states, highlighting the cultural diversity of the region.
- Araku Valley is known for its scenic beauty and cultural significance.
- The region is home to diverse flora and fauna, being part of the Eastern Ghats’ biodiversity hotspot.
- Economic activities include organic coffee cultivation, which has gained a Geographical Indication (GI) tag.
Additional Details
- Location: Araku Valley is situated in the Alluri Sitharama Raju district of Andhra Pradesh.
- Elevation: The valley stands at approximately 1,200 meters above sea level.
- Climate:
- Receives significant rainfall during the monsoon season (June–September).
- Experiences pleasant winters from December to February, with temperatures ranging from 5–10°C.
- Flora & Fauna: The region boasts dense tropical forests with species such as teak, bamboo, and various medicinal plants.
- The Anantagiri and Sunkarimetta Reserved Forests, part of Araku Valley, are rich in biodiversity and are known for bauxite mining.
- Wildlife includes species such as the Indian bison (gaur), leopards, and peacocks.
- Economic Importance:
- Araku Valley is renowned for its organic coffee plantations, which have received a GI tag.
- Tourism attractions include:
- Borra Caves, famous for limestone formations.
- Katiki Waterfalls, known for their natural beauty.
- Padmapuram Gardens, a lush botanical garden.
- Dumbriguda Chaparai, a natural rock formation with waterfalls.
In summary, Araku Valley is not only a picturesque hill station but also a vital center for cultural heritage and economic activities, particularly in organic coffee cultivation and tourism.
GS3/Science and Technology
Asteroid 2024 YR4: Potential Impact on Earth
Source: BBC
Why in News?
A newly identified asteroid, designated as 2024 YR4, has been reported by NASA to have a slight chance of colliding with Earth in 2032. This discovery raises concerns due to the asteroid's size and its potential to cause significant localized damage if it were to impact a populated area.
- 2024 YR4 has a little over 1% chance of crashing into Earth.
- The asteroid is comparable in size to a football field.
- It was initially discovered in December of the previous year from a telescope in Chile.
- The asteroid passed closest to Earth on Christmas Day, at a distance of approximately 800,000 kilometers.
Additional Details
- Destruction Potential: The Torino Scale rates 2024 YR4 at 3 on a scale of 0 to 10, indicating a moderate risk of damage.
- The asteroid could release energy equivalent to 8 to 10 megatons of TNT upon impact, significantly more than the energy released by the Chelyabinsk asteroid, which was smaller.
- Frequency of Impacts: Thousands of asteroids enter Earth's atmosphere daily, but most are small and burn up. Large asteroids capable of global disasters are much rarer.
- Efforts are underway by space agencies, including NASA's Double Asteroid Redirection Test (DART), to develop planetary defense strategies against potential asteroid collisions.
In summary, while the chances of asteroid 2024 YR4 colliding with Earth are low, its size and potential energy release warrant close monitoring by astronomers. Continued advancements in planetary defense mechanisms are essential to mitigate risks from such celestial threats.
GS3/Economy
Some Wind Behind the Sails of India’s Shipping Industry
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Indian government has made significant strides in developing the maritime sector, which had been largely neglected by previous administrations. Despite these efforts contributing to economic growth and improved infrastructure, the Indian shipping industry faces stagnation due to several ongoing structural challenges.
- Significant investment in maritime infrastructure under the Sagarmala Programme.
- Persistent challenges such as financial constraints and regulatory hurdles hinder the shipping industry's growth.
- Decline in market share of Indian shipping companies against foreign counterparts.
Additional Details
- Sagarmala Programme: Launched to enhance India’s maritime infrastructure, with 839 projects requiring an investment of ₹5.8 lakh crore outlined as of September 2024. Key focuses include port modernization, port connectivity, and port-led industrialization.
- Economic Growth: India's GDP rose from ₹153 trillion in 2016-17 to ₹272 trillion in 2022-23, and EXIM trade increased from $66 billion to $116 billion in the same period.
- Challenges: High borrowing costs, unfavorable tax policies, and inadequate shipbuilding infrastructure continue to limit the competitiveness of Indian shipping companies.
- Government Initiatives: Recent measures include the Maritime Development Fund (MDF) of ₹25,000 crore and customs duty exemptions on shipbuilding spares, but clarity on fund mobilization is needed.
- Need for Reforms: Long-term financing at competitive rates, expansion of shipbuilding infrastructure, and tax reforms are essential for improving the shipping sector's viability.
Overall, while India's maritime infrastructure has seen significant improvements, the shipping industry itself has not experienced proportional growth. Addressing the critical challenges faced by the industry is essential for fully leveraging India's maritime potential and enhancing its position in international trade.
GS3/Environment
Green Cardamom
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
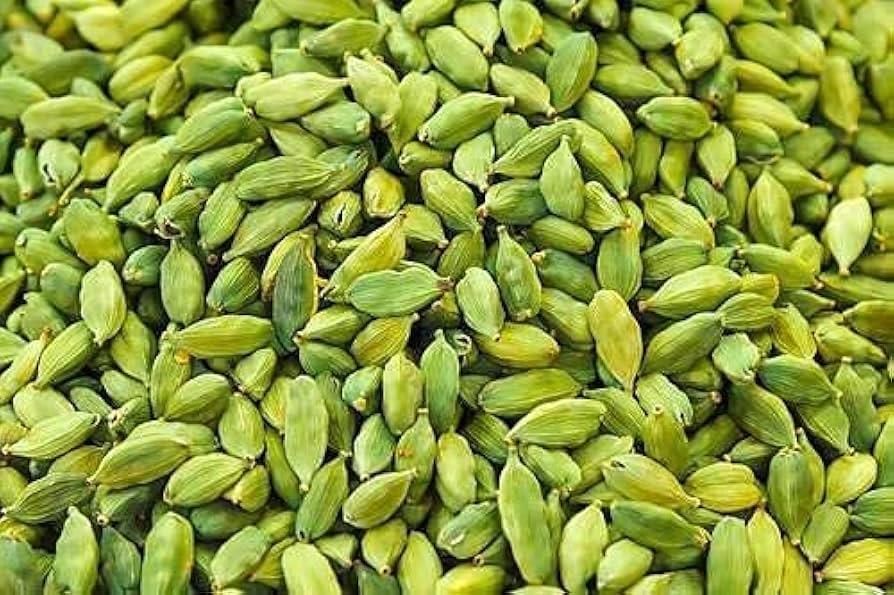
An international research team has identified six new species closely related to Elettaria cardamomum, commonly known as green cardamom, enhancing our understanding of this important spice.
- Green cardamom is often referred to as the Queen of Spices.
- It is primarily cultivated in the Southern Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu.
- The plant thrives in specific climatic and soil conditions.
- Newly identified species expand the genus Elettaria to include seven species.
Additional Details
- Family: Green cardamom belongs to the Zingiberaceae family.
- Native Habitat: It is originally found in the evergreen rain forests of the Western Ghats.
- Soil Requirements: Cardamom is cultivated in forest loamy soils that are acidic, with a pH range from 5.0 to 6.5.
- Altitude: The crop can be grown at elevations between 600 to 1500 meters.
- Temperature: It requires a temperature range of 10 to 35 degrees Celsius.
- Rainfall: Ideal rainfall is between 1500 to 4000 mm.
- The growth of cardamom is improved when planted in humus-rich soils with low to medium phosphorus and medium to high potassium.
- Green cardamom is widely used as a flavoring agent and in traditional medicine.
The genus Elettaria now includes two newly described species: E. facifera, identified in Kerala's Periyar Tiger Reserve, and E. tulipifera, found in the Agasthyamalai hills. The seed capsules of E. cardamomum are the source of the commercially valuable green cardamom.
GS3/Environment
Black Kite Nesting Activity in Chennai
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recent observations have highlighted that black kites have started nesting in a tower structure located in Chennai, indicating a unique adaptation of these birds to urban environments.
- Black kites are medium-sized birds of prey belonging to the family Accipitridae.
- They are known for their opportunistic hunting behavior and soaring flight patterns.
- These birds inhabit a wide range of environments, showcasing great adaptability.
Additional Details
- Appearance: Black kites are characterized by their medium size, predominantly brown dorsal coloration that darkens at the wing and tail tips, small bead-like dark brown eyes, and a large black, hook-shaped beak designed for tearing flesh.
- Habitat: They thrive in diverse habitats including wetlands, riverbanks, coastal areas, grasslands, open savannas, shrublands, and woodlands.
- Distribution: Their presence spans tropical regions across Australasia, Eurasia, and Africa.
- Diet: Black kites are versatile feeders, consuming carrion, live prey such as birds, mammals, fish, lizards, amphibians, invertebrates, and even plant matter like palm oil fruits.
- Conservation Status: According to the IUCN, they are classified as Least Concern, and under the Wild Life Protection Act of 1972, they are listed in Schedule-II.
This nesting behavior in urban structures like towers highlights the adaptability of black kites and emphasizes the need for ongoing studies to understand their ecological impact and conservation status in urban settings.
GS3/Economy
ELS Cotton: A Five-Year Mission for Improvement
Source: Indian Express
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Union Finance Minister recently announced a five-year initiative aimed at enhancing the productivity and sustainability of cotton farming in India. This mission particularly emphasizes the promotion of extra-long staple (ELS) cotton varieties to improve India’s cotton yields, which are currently lagging behind those of other countries.
- India’s cotton yields are significantly lower than Brazil and China, which average 20 and 15 quintals per acre, respectively.
- Improvements in seed quality, timely agronomic advice, and technology adoption are essential for boosting ELS cotton production.
Additional Details
- What is Extra-long Staple Cotton? Cotton is categorized based on fiber length into long, medium, and short staple. ELS cotton, characterized by fiber lengths of 30 mm and above, primarily derives from the species Gossypium barbadense, known as Egyptian or Pima cotton. In India, ELS cotton is cultivated in certain regions of Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
- Current Yield Comparisons: The average yield of medium staple cotton in India ranges from 10 to 12 quintals per acre, whereas ELS cotton yields only 7-8 quintals per acre, making it less appealing to farmers.
- Despite the Minimum Support Price (MSP) of Rs 7,521 for long staple cotton compared to Rs 7,121 for medium staple cotton, farmers remain hesitant to switch to ELS cotton due to lower yields and challenges in marketing their high-quality produce.
In conclusion, while ELS cotton offers the potential for premium fabric production, various challenges, including lower yields and market access, hinder its widespread adoption in India. The government's initiative aims to address these issues and enhance the cotton farming landscape.
GS3/Economy
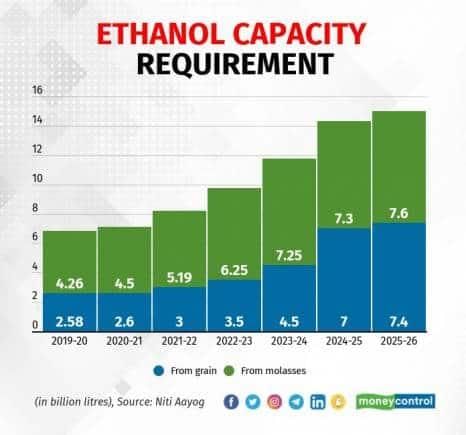
India's Ethanol Blending Targets
Source: PIB
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Government of India is poised to achieve a significant milestone by reaching a 20% ethanol blending in petrol within the next two months, a target that was initially set for 2026. This initiative is expected to enhance energy security, reduce dependence on oil imports, and provide substantial benefits to farmers.
- India aims for 20% ethanol blending in petrol ahead of the original target.
- Annual production of fuel ethanol is projected to reach 1,100 crore litres.
- Various feedstocks, including sugar, rice, and maize, are being utilized to increase ethanol production.
Additional Details
- Ethanol Production Sources:The government is expanding ethanol production through multiple sources:
- Sugar and Molasses are expected to contribute around 400 crore litres.
- Food Corporation of India (FCI) Rice will provide an additional 110 crore litres of ethanol.
- Maize and broken rice are estimated to supply a significant portion, supported by improved distillery capacities.
- Role of Maize:Maize has become crucial in ethanol production, with a notable increase in cultivation and imports.
- In 2024, India imported maize worth ₹100 crore and saw a 10% increase in maize cultivation.
- Major maize-producing states include Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Government Initiatives:Key policy reforms and incentives have been introduced, such as:
- Reduction of FCI Rice Price from ₹28/kg to ₹22.5/kg to promote cost-effective ethanol production.
- Modification of sugar mills into dual-feed distilleries for ethanol production from both sugar and maize.
- Financial incentives for producers, including subsidized loans and long-term contracts.
In conclusion, India's push towards ethanol blending marks a pivotal step for sustainable energy, aiming to reduce oil imports and support the agricultural sector. With continuous investment and advancements in technology, India has the potential to become a global leader in biofuel production while balancing food security and energy needs.
GS1/Geography
North Sea and Its Geological Significance
Source: Frontiers
Why in News?
Recent research has unveiled substantial landforms located deep beneath the North Sea, indicating that this region was once covered by a massive ice sheet during the middle of the last ice age.
- The North Sea is a relatively shallow and enclosed sea in Northwestern Europe.
- It serves as a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, connecting to it through the Norwegian Sea and the English Channel.
- It links to the Baltic Sea via the Kattegat and Skagerrak straits.
- Key bordering countries include the United Kingdom, Norway, Denmark, Germany, the Netherlands, Belgium, and France.
- The North Sea covers approximately 570,000 square kilometers.
- Major rivers flowing into the North Sea include the Forth, Elbe, Weser, Ems, Rhine, Meuse, Scheldt, Thames, and Humber.
- It hosts two of the world's largest ports: Hamburg and Rotterdam.
- The North Sea is recognized as one of the most vital fishing grounds globally.
Additional Details
- Geological Features: The newly discovered landforms suggest significant geological activity and changes over thousands of years, providing insights into the Earth's climatic history.
- This region is also critical for maritime trade and ecological diversity due to its various marine environments.
In conclusion, the North Sea not only plays a crucial role in regional geography and ecology but also offers valuable data regarding past ice age conditions, which can enhance our understanding of climate change and its impacts on sea levels and landforms.
|
59 videos|5398 docs|1143 tests
|





















