UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 4th January 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS2/Governance
Open Data Kit (ODK) Platform
Source: MSN
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) has adopted the Open Data Kit (ODK) platform, a modern digital tool aimed at enhancing transparency and accountability in public spending.
- ODK is a digital platform designed for secure data collection and management.
- The platform enhances transparency in government spending and accountability in various schemes.
- ODK is integrated with the CAG's operating system, OIOS, ensuring efficient data handling.
Additional Details
- End-to-end encryption: ODK provides a secure online portal, protecting the data collected from unauthorized access.
- Multi-language surveys: The platform allows the CAG to conduct surveys in several languages simultaneously, making it accessible to a broader audience.
- Beneficiary Survey: This survey serves as a vital source of information for audit planning and evidence collection.
- The ODK toolkit was successfully implemented to evaluate patient satisfaction during audits of AIIMS facilities in Mangalagiri and Bibinagar.
The implementation of the ODK platform represents a significant step towards improving governmental auditing processes, ensuring that public funds are utilized effectively and responsibly.
GS1/History & Culture
Savitribai Phule: A Pioneer in Women's Education
Source: Business Standard
 Why in News?
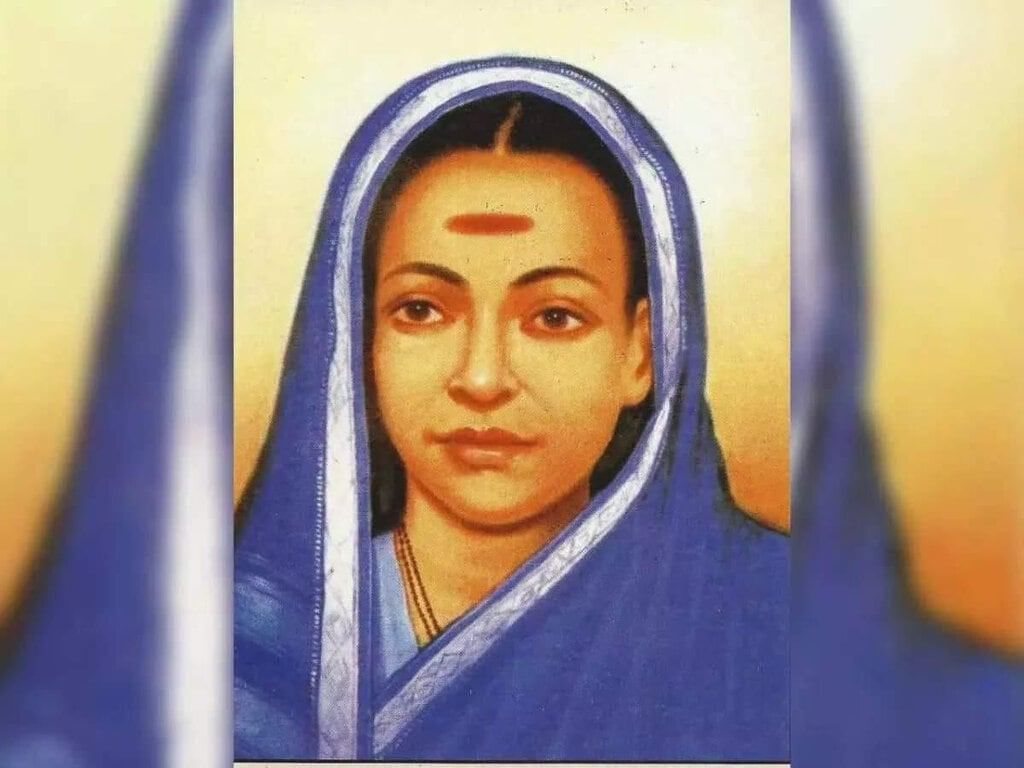
Why in News?On January 3, 2025, Prime Minister Narendra Modi paid tribute to Savitribai Phule on her 194th birth anniversary, recognizing her as India’s first woman teacher and a significant figure in the fight for women's education and social reform.
- Savitribai Phule was born on January 3, 1831, in Naigaon, Maharashtra.
- She, along with her husband Jyotirao Phule, opened the first girls' school in Pune in 1848.
- The couple was instrumental in advocating for women's rights, including inter-caste marriages and the eradication of social evils.
- Savitribai published significant literary works, including her poem collection, Kavya Phule, at the age of 23.
- She actively participated in relief efforts during the 1896 famine and the 1897 Bubonic plague.
Additional Details
- Educational Initiatives: Savitribai and Jyotirao Phule established several schools for girls and marginalized communities, challenging societal norms that restricted education for women and lower castes.
- Satyashodhak Samaj: Founded in 1873, this organization aimed to promote social equality, transcending caste and religious barriers, and included initiatives like the ‘Satyashodhak Marriage’ to oppose traditional Brahmanical practices.
- Advocacy for Social Reforms: Savitribai campaigned against child marriage, sati, and the dowry system, significantly impacting social attitudes towards these practices.
- Savitribai's courage was evident when she defied societal conventions during her husband’s funeral in 1890, symbolizing her commitment to gender equality.
Savitribai Phule's legacy as a champion of education and social reform continues to inspire generations. Her life represents a profound commitment to uplifting the marginalized and advocating for women's rights in India.
GS2/Polity
India, Cross-Border Insolvency and Legal Reform
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The growth of international trade has highlighted the need for effective regulation to tackle the complexities of cross-border insolvency. A reliable insolvency framework is vital for fostering economic stability, attracting foreign investments, and enabling corporate restructuring. However, India's historical and current approaches to insolvency law have faced significant challenges in managing cross-border cases.
- India's insolvency laws have evolved but struggle with cross-border complexities.
- The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) includes provisions for cross-border insolvency but remains largely dormant.
- Judicial challenges and outdated communication methods hinder effective resolution of cross-border insolvency cases.
Additional Details
- Historical Evolution of Insolvency Laws: India's first insolvency law was the Indian Insolvency Act of 1848. Subsequent laws, such as the Presidency-Towns Insolvency Act of 1909 and the Provincial Insolvency Act of 1920, were focused on domestic cases and did not address cross-border situations effectively.
- Introduction of the IBC: Enacted in 2016, the IBC aimed to provide a comprehensive insolvency framework but faced challenges due to dormant sections intended for cross-border insolvency.
- Judicial Challenges: The National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT) lacks powers to enforce foreign insolvency judgments, which restricts its ability to handle cross-border insolvency cases comprehensively.
- Case Study - Jet Airways: The 2019 Jet Airways case illustrated major issues in cross-border insolvency, highlighting the absence of reciprocal agreements and the ineffectiveness of dormant provisions in the IBC.
- Recommendations for Reform: Adopting the UNCITRAL Model Law on Cross-Border Insolvency, modernizing judicial communication, and expanding the NCLT's powers are essential for improving India's cross-border insolvency framework.
In conclusion, India's integration into the global economy necessitates a robust framework for cross-border insolvency. Addressing the limitations of the IBC and implementing recommended reforms is crucial for establishing a more effective insolvency regime.
GS3/Science and Technology
Human Metapneumovirus: Understanding the Emerging Threat
Source: Economic Times
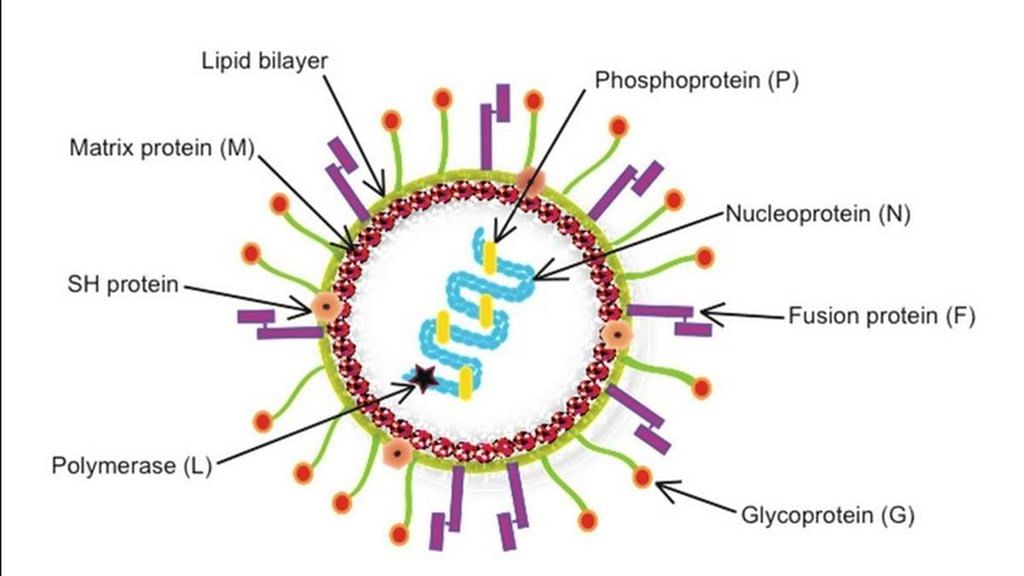 Why in News?
Why in News?China is currently experiencing a rise in respiratory illnesses, with human metapneumovirus (HMPV) becoming a significant concern among health officials and the public.
- HMPV is a respiratory virus that can cause mild infections similar to the common cold.
- First identified in 2001, it belongs to the Pneumoviridae family, which includes other notable viruses such as RSV, measles, and mumps.
- The virus primarily affects children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals.
Additional Details
- Symptoms:HMPV symptoms mimic those of a common cold and include:
- Cough
- Runny or blocked nose
- Sore throat
- Fever
- Wheezing
- Incubation Period: The estimated incubation period for HMPV is between three to six days.
- The illness is usually self-limiting, resolving within a few days with supportive care at home, although some individuals may develop complications like bronchitis or pneumonia, necessitating medical attention.
Transmission
- HMPV spreads through:
- Contact with an infected person
- Touching surfaces contaminated with the virus (e.g., doorknobs, phones, keyboards)
- Secretions from coughs and sneezes
- Close contact, such as shaking hands or hugging
Treatment
- Currently, there is no vaccine or specific antiviral treatment for HMPV.
- Management typically involves over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms like fever and pain, along with decongestants.
- Antibiotics are ineffective against HMPV, as it is a viral infection.
As awareness grows around HMPV, understanding its symptoms, transmission, and management is crucial for public health, especially during peak seasons for respiratory illnesses.
GS3/Economy
Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) 2024
Source: Times of India
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Union Minister of Commerce & Industry recently released the “Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) 2024” report in New Delhi, marking the sixth edition of this important assessment.
- The report was developed based on the Logistics Performance Index of the World Bank, initiated in 2018 by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT).
- It evaluates logistics performance across four key pillars: Logistics Infrastructure, Logistics Services, Operating and Regulatory Environment, and Sustainable Logistics.
- It aims to highlight initiatives undertaken by various States and Union Territories (UTs) and focuses on state-specific opportunities for informed decision-making.
Additional Details
- Coastal Group Achievers: States recognized for their exceptional logistics performance include Gujarat, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Odisha, and Tamil Nadu.
- Fast Movers: Andhra Pradesh and Goa are noted for their rapid improvements in logistics.
- Aspirers: Kerala and West Bengal are identified as states with potential for further growth in logistics.
- Landlocked Group: This includes Haryana, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Bihar, Himachal Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, and Jharkhand.
- North-Eastern Group: States in this category are Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, and Manipur.
- Union Territories: Chandigarh, Delhi, Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, Jammu and Kashmir, Lakshadweep, Puducherry, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, and Ladakh.
The LEADS 2024 report serves as a crucial tool for evaluating and enhancing logistics capabilities across various states and UTs in India, providing insights that can drive strategic improvements in this vital sector.
GS2/Governance
Centralized Pension Payments System (CPPS)
Source: The Hindu
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO) has successfully launched the Centralized Pension Payments System (CPPS) under the Employees’ Pension Scheme 1995, significantly improving the ease of living for millions of pensioners across the country.
- The CPPS allows pensioners to access their pensions from any bank or branch in India.
- It eliminates the need for physical verifications and streamlines the pension payment process.
- Over 7.85 million pensioners will benefit from seamless pension disbursement.
Additional Details
- Implementation: The CPPS is managed by the Employees’ Provident Fund Organisation (EPFO), which is a statutory body under the Employees' Provident Funds and Miscellaneous Act, 1952.
- Features:
- Pensioners can withdraw their pension from any bank without needing to visit the bank for verification at the commencement of their pension.
- Pension amounts are credited immediately upon release, ensuring timely access to funds.
- The system allows for pension disbursement throughout India without requiring the transfer of Pension Payment Orders (PPO) even if the pensioner moves or changes banks.
The CPPS represents a significant transformation from the previous decentralized pension disbursement model, where each EPFO regional office had limited agreements with only a few banks. This advancement promises greater flexibility and accessibility for pensioners nationwide.
GS3/Science and Technology
Methylcobalamin
Source: The Hindu Business Line
 Why in News?
Why in News?Recently, the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India clarified regulations regarding the use of methylcobalamin, a form of vitamin B12.
- Methylcobalamin is a naturally occurring form of vitamin B12.
- It is essential for various bodily functions, including DNA synthesis and red blood cell production.
- Deficiency in vitamin B12 can lead to serious health issues.
- It plays a significant role in neurological health and the production of neurotransmitters.
Additional Details
- Methylcobalamin: This form of vitamin B12 features a methyl group (-CH3) attached to a cobalt atom, distinguishing it from other forms like cyanocobalamin, adenosylcobalamin, and hydroxocobalamin.
- Vitamin B12 is a water-soluble vitamin crucial for cellular functions such as cell growth, blood formation, and protein synthesis.
- It is found in food sources including fish, meat, eggs, and dairy products.
- It is particularly beneficial for individuals with vitamin B12 deficiency and those suffering from diabetes and other neuropathies.
- Regular ingestion of methylcobalamin supports adequate red blood cell production, reducing feelings of fatigue and weakness.
- It is also linked to the prevention and treatment of neurological disorders.
- Furthermore, it is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are vital for regulating mood and mental health.
In conclusion, methylcobalamin is a crucial nutrient that supports various physiological functions and is important for maintaining overall health, particularly in the context of vitamin B12 deficiency.
GS2/Polity
Right to Property
Source: The Hindu
Why in News?
The Supreme Court recently affirmed that the right to property is both a human right and a constitutional right. It ruled that no individual can be deprived of their property without receiving adequate compensation. In exceptional cases of significant delays in compensation disbursement, the court stated that the valuation date for compensation may be adjusted to a more recent date.
- The right to property was downgraded from a Fundamental Right to a constitutional right by the Constitution (Forty-Fourth Amendment) Act, 1978, yet remains a human right within a welfare state.
- According to Article 300-A of the Constitution, no person can be deprived of property except by law. The State must follow legal procedures when dispossessing an individual from their property.
Additional Details
- Case Background: The petitioners acquired residential plots in Gottigere village, Karnataka, between 1995 and 1997. Their lands were acquired in 2003 for the Bengaluru-Mysore Infrastructure Corridor (BMIC) project under the Karnataka Industrial Areas Development Act, 1966.
- Despite the state taking possession of the land, it took over two decades to finalize compensation, prompting repeated legal challenges from landowners.
- The Supreme Court emphasized the principle of eminent domain, clarifying that the State’s ability to acquire land against the owner's wishes necessitates an obligation to provide prompt and fair compensation.
- In light of the prolonged injustice, the Supreme Court exercised its powers under Article 142 of the Constitution to adjust the valuation date to 2019 for calculating compensation.
This ruling highlights the importance of timely compensation in land acquisition cases and reinforces the protection of property rights as integral to individual dignity and welfare.
GS3/Health
What is Blue Baby Syndrome?
Source: ET Health World
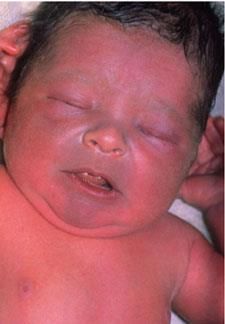 Why in News?
Why in News?High levels of nitrate contamination in groundwater across 440 districts in India pose serious health risks, particularly leading to conditions like blue baby syndrome in infants, making the water unsafe for consumption.
- Blue baby syndrome, also known as cyanosis, causes a bluish or purple tint to a baby's skin.
- It results from poorly oxygenated blood, often due to issues with the heart, lungs, or blood itself.
- The most common cause is exposure to water contaminated with nitrates.
Additional Details
- Symptoms:The primary symptom of blue baby syndrome is a blue discoloration of the skin, especially around the mouth, hands, and feet. Other symptoms may include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Lethargy
- Increased salivation
- Loss of consciousness
- Seizures
- Treatment: Treatment strategies depend on the underlying cause of the condition. If congenital heart defects are present, surgical intervention might be necessary. In severe cases, a medication called methylene blue may be administered via injection.
Blue baby syndrome is a critical health concern that underscores the importance of monitoring environmental factors such as water quality to protect infant health.
GS3/Economy
Project VISTAAR: Enhancing Agricultural Resources Access
Source: Economic Times
 Why in News?
Why in News?The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Madras has recently partnered with the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare to launch Project VISTAAR (Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources), aimed at modernizing the agricultural sector through digitalization.
- Project VISTAAR is a digital platform that integrates information about agricultural start-ups.
- The initiative seeks to improve the agricultural extension system's efficiency and accessibility.
- It features a comprehensive database of over 12,000 start-ups in agriculture and allied sectors.
Additional Details
- Digital Platform: The platform connects farmers with various technological solutions and services, making it easier for them to access innovative resources.
- Significance:The digitalization aims to expand outreach, allowing farmers to receive high-quality advisory services in areas such as:
- Crop production
- Marketing
- Value addition
- Supply chain management
- The advisory services will also provide information on relevant government schemes in agriculture, ensuring farmers can utilize them effectively.
In summary, Project VISTAAR represents a significant advancement in the agricultural extension system, enabling better support and resources for farmers through timely and accurate digital information.
GS3/Economy
Baanknet Portal
Source: Mint
 Why in News?
Why in News?The government has recently launched a revamped e-auction portal named ‘Baanknet’ in Delhi, aimed at streamlining the auction process for properties held by public sector banks.
Key Takeaways
- The Baanknet portal consolidates information on properties put up for e-auction by public sector banks (PSBs).
- It provides a comprehensive platform for buyers and investors, featuring various property types.
- Over 122,500 properties have already been migrated to the platform for auction.
Additional Details
- Features: The portal is equipped with improved functionalities, providing a seamless user experience throughout the pre-auction, auction, and post-auction processes.
- Payment Gateway: It includes an automated and integrated payment gateway along with KYC tools, enhancing security and convenience.
- Architecture: Built on a microservices-based architecture, the portal allows third-party integration via open application programming interface (API).
- Dashboard: Users can access a dashboard featuring ‘Spend Analytics’ and various ‘Management Information System (MIS) Reports’ with just a click.
- A dedicated helpdesk and call center facility are available, including a callback request option for enhanced customer support.
The Baanknet portal simplifies the process of finding and participating in property e-auctions, making it easier for buyers and investors to identify valuable opportunities. Additionally, it significantly aids the recovery process of public sector banks, thereby improving their balance sheets and enhancing credit availability to businesses and individuals.
GS3/Economy
India Secures 14.3% of Global Remittances in 2024: World Bank
Source: The Hindu
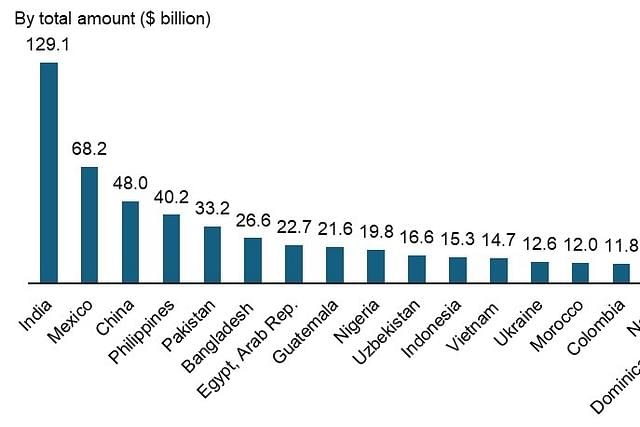 Why in News?
Why in News?In 2024, India achieved a remarkable milestone by receiving a record $129.1 billion in remittances, marking the highest share for any country since 2000, according to the World Bank.
- India accounted for 14.3% of global remittances, the highest share since the beginning of the millennium.
- Remittance growth was approximately 5.8% in 2024, a significant increase from the previous year's growth of 1.2%.
- Mexico and China followed India as the largest recipients, receiving $68 billion and $48 billion respectively.
Additional Details
- Record Inflows: In 2024, India received the highest amount of remittances ever recorded for any country in a single year, totaling $129.1 billion.
- Large Diaspora: India has over 18 million Indians residing abroad, significantly contributing to remittance inflows.
- Shift to High-Income Countries: Many Indian migrants are moving to high-income economies like the United States, United Kingdom, and Australia, where job opportunities are more plentiful.
- Diverse Skill Levels: The Indian migrant population includes both highly skilled professionals, particularly in sectors like IT and healthcare, and semi-skilled or unskilled laborers, enhancing remittance potential.
- Recovery of Job Markets: Post-pandemic recovery in job markets of high-income countries has led to increased employment opportunities, driving remittance flows upward.
The significance of remittances cannot be overstated; they serve as a vital source of income for many households in India, contributing to their welfare and overall economic stability. In 2024, remittances represented approximately 3.3% of India's GDP, indicating their crucial role in supporting the national economy.
Impacts of High Remittances
- Economic Support for Households: Remittances provide essential financial support to families, enabling them to meet daily needs.
- Comparison with Other Financial Flows: Remittances have surpassed other external financial sources like Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) and Official Development Assistance (ODA), highlighting their importance in financing current account deficits and fiscal shortfalls.
- Long-Term Growth Trends: Over the last decade, remittances to low- and middle-income countries have risen by 57%, showcasing their growing significance as a stable income source.
Negative Impacts of Brain Drain
- Loss of Skilled Labor: The phenomenon of brain drain results in a significant depletion of skilled professionals in India, leading to shortages in crucial sectors like healthcare, education, and technology.
- Economic Consequences: The departure of skilled workers decreases tax revenues, limiting public spending on infrastructure and social programs, which can hinder economic growth.
- Impeded National Development: Countries facing brain drain may experience slower overall development due to the loss of human capital, perpetuating a cycle of underdevelopment.
Way Forward
- Enhance Domestic Opportunities: It is essential to strengthen education and healthcare systems and create competitive job opportunities to retain skilled professionals.
- Engage Diaspora Strategically: Leveraging the Indian diaspora for knowledge transfer and investments can create pathways for their contributions to national development, helping maintain connections with local talent.
In conclusion, while remittances play a vital role in supporting the Indian economy, addressing the challenges posed by brain drain is crucial for sustainable development. Strategic engagement with the diaspora and enhancing domestic opportunities will be key to retaining talent and fostering growth.
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|





















