UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 5th October 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS1/Geography
Key Facts about Negro River
Source: BBC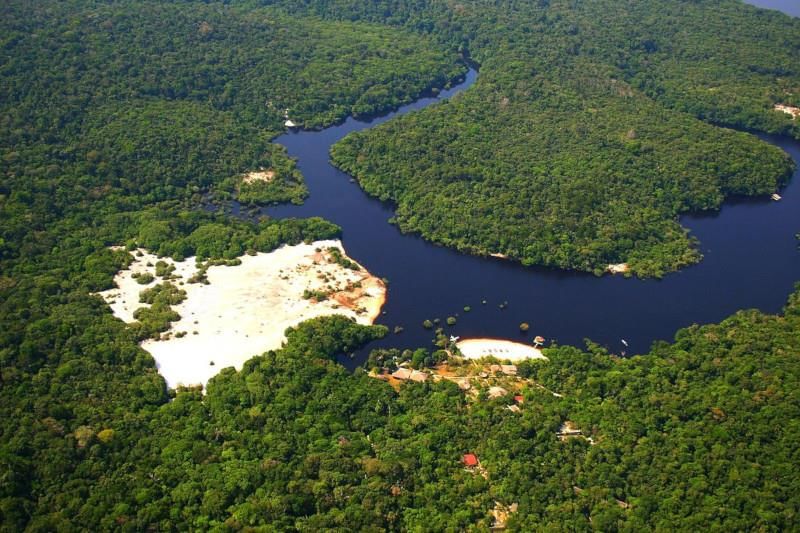
Why in News?
One of the Amazon River’s significant tributaries, the Negro River, has recently been reported to have reached its lowest level in 122 years, according to Brazil’s geological service.
About Negro River:
- The Rio Negro ranks as one of the largest tributaries of the Amazon River.
- It is among the world's largest rivers regarding water discharge.
Course:
- Origin: The river originates from multiple headstreams, including the Vaupés (Mapés) and Guainía, which rise in the rainforests of eastern Colombia.
- It flows along the borders of Colombia and Venezuela before entering Brazil, where it is officially known as the Rio Negro.
- The river generally meanders in an east-southeast direction, collecting water from tributaries such as the Branco River.
- Its journey leads to Manaus, Brazil, the largest city in the Amazon Rainforest.
- At Manaus, it merges with the Solimões River to form the Amazon River.
Name Origin:
- The name "Negro," meaning "black" in Portuguese, is derived from the river's dark water.
- This dark coloration is due to the decomposition of organic matter and the presence of tannins leached from surrounding vegetation.
Water Characteristics:
- The Rio Negro is recognized as the largest blackwater river globally.
- Despite its dark appearance, the water has low sediment levels and is considered one of the cleanest rivers on Earth.
Environmental Significance:
- Protected reserves and national parks along the Rio Negro contribute to a vast protected area known as the Central Amazon Ecological Corridor.
- This corridor is the largest section of protected Amazon rainforest, covering an area of 52 million hectares, making it one of the largest protected areas in the world.
GS3/Environment
What is Pseumenes siangensis?
Source: Deccan Herald

Why in News?
Entomologists have recently identified a new species of potter wasp from Arunachal Pradesh, named Pseumenes siangensis.
About Pseumenes siangensis:
- This is a newly discovered species of wasp belonging to the genus Pseumenes.
- It is part of the subfamily Eumeninae, commonly referred to as potter wasps.
- Pseumenes siangensis is mainly found in the Oriental region.
- These solitary wasps are known for their unique behavior of constructing small, pot-like mud nests for their larvae.
- Globally, there are around 3,795 species of potter wasps categorized across 205 genera.
- Prior to this discovery, only one species of the genus Pseumenes was reported in India, making Pseumenes siangensis a significant addition to the country's wasp diversity.
- This species was found in the Upper Siang District, located in the Eastern Himalayas.
- The name 'siangensis' is derived from the Siang Valley, which is the location of its discovery.
- Measuring approximately 30.2 mm in length, this new species is distinguished from others by its unique morphological characteristics and color patterns.
- Pseumenes siangensis plays an important role in pest control, as its larvae primarily consume caterpillars and other insects.
GS3/Economy
National Agriculture Code
Source: Indian Express

Why in news?
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) has initiated the development of a National Agriculture Code (NAC), similar to the existing National Building Code and National Electrical Code.
About
- The National Agriculture Code aims to encompass the entire agricultural cycle and will include a guidance note for future standardization.
- The NAC will be divided into two main sections:
- The first section will outline general principles applicable to all crops.
- The second section will specify standards tailored to particular crops, such as paddy, wheat, oilseeds, and pulses.
- This code will serve as a reference for farmers, agricultural universities, and officials engaged in agriculture.
- It will address all agricultural processes and post-harvest activities, including:
- Crop selection
- Land preparation
- Sowing or transplanting
- Irrigation and drainage
- Soil health management
- Plant health management
- Harvesting and threshing
- Primary processing
- Post-harvest management
- Sustainability practices
- Record maintenance
- The NAC will set standards for managing agricultural inputs, including:
- Use of chemical fertilizers
- Pesticides
- Weedicides
- It will also provide guidelines for crop storage and traceability.
- The code will cover innovative and emerging areas such as:
- Natural farming
- Organic farming
- Application of Internet of Things (IoT) in agriculture
Objectives:
- To establish a practical national code that encompasses agricultural practices, considering:
- Agro-climatic zones
- Crop varieties
- Socio-economic diversity
- All aspects of the agrifood value chain
- To promote a culture of quality within Indian agriculture by providing necessary references to policymakers, agriculture departments, and regulators to integrate NAC provisions into their programs and regulations.
- To create a comprehensive manual for farmers to facilitate informed decision-making in agricultural practices.
- To align relevant Indian Standards with recommended agricultural practices.
- To address broader agricultural aspects including:
- SMART farming
- Sustainability
- Traceability
- Documentation processes
- To support capacity-building initiatives organized by agricultural extension services and civil society organizations.
GS3/Science and Technology
What is Motor Neuron Disease (MND)?
Source: Deccan Herald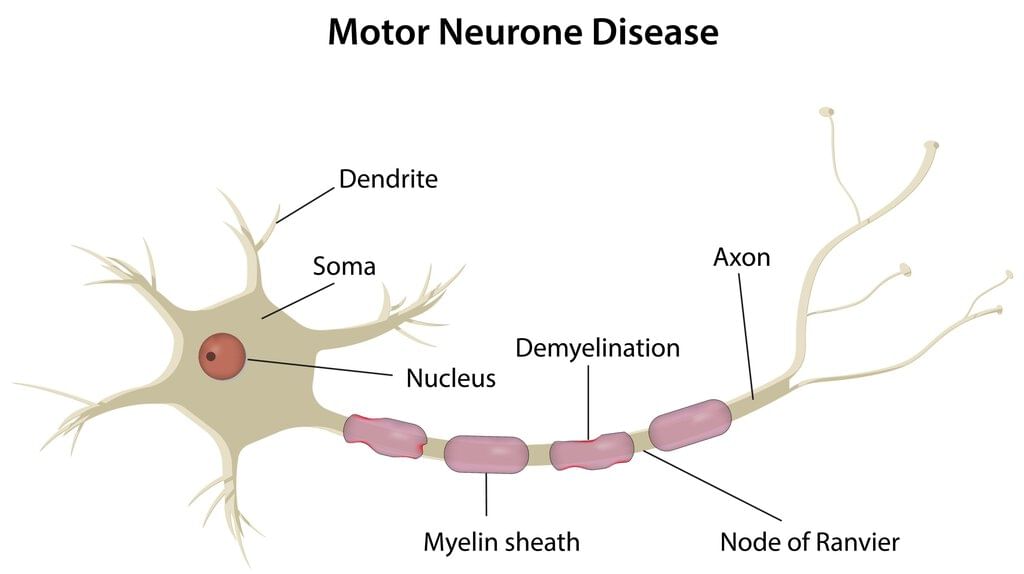
Why in News?
Researchers recently developed DNA molecules which contain "invisibility cloak" sequences which can selectively target diseased cells in motor neuron disease.
About Motor Neuron Disease (MND):
- MND is a rare condition that leads to the progressive deterioration of specific parts of the nervous system.
- This condition results in muscle weakness and often visible muscle wasting.
- MND is also known as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) and Lou Gehrig's disease.
Cause
- MND occurs when motor neurons, which are specialized nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, cease to function properly and die prematurely, a process known as neurodegeneration.
- Motor neurons transmit signals from the brain to muscles, enabling movement. They are crucial for both voluntary actions (like walking) and involuntary actions (like breathing).
- As the disease worsens, individuals may find it increasingly challenging to perform these activities.
- It is generally accepted that MND results from a mix of environmental, lifestyle, and genetic factors.
- About 20% of MND cases are associated with genetic factors, with half of these genetic cases occurring in individuals who have a family history of the disease.
- MND primarily affects older adults, particularly those in their 60s and 70s, though it can also impact younger adults.
Symptoms:
- Symptoms of MND typically emerge gradually over weeks to months.
- Initial symptoms often manifest on one side of the body and progressively worsen over time.
- The disease frequently begins with muscle weakness in the hands, feet, or voice, but it can initiate in various parts of the body and advance at different rates.
- As MND progresses, individuals may experience increasing levels of disability.
- The average life expectancy following an MND diagnosis ranges from one to five years, although approximately 10% of patients may live for ten years or longer.
Treatment
- Currently, there is no cure for MND; however, various treatments can help alleviate the symptoms and improve quality of life.
GS3/Science and Technology
Why you should care about Mapping of the Fruit Fly’s Brain?
Source: Indian Express

Why in News?
Research has recently made headlines as scientists have successfully mapped the entire brain of an adult fruit fly, marking a significant achievement in neuroscience. This is the first time such a comprehensive mapping of an adult animal's brain has been accomplished.
How Was the Fruit Fly Brain Mapped?
- The mapping process of the fruit fly's brain (Drosophila melanogaster) initiated in 2013.
- Researchers immersed the brain of an adult fruit fly in a chemical solution, which solidified it into a rigid block for further analysis.
- This meticulous process involved creating 7,050 sections of the brain and resulted in the generation of 21 million images to detail the entire brain structure.
- The first high-resolution image of the brain was produced over a decade into the research project.
Key Findings
- The research identified over 50 million synaptic connections among 139,000 neurons (the nerve cells of the brain).
- Scientists classified these neurons into 8,453 distinct types, establishing the largest catalog of cell types found in any brain to date.
- The study provided insights into the functionality of different cell types and the mechanisms by which the fruit fly's eyes interpret motion and color.
- A novel group of neurons, termed "hub neurons," was discovered, which may facilitate faster information processing.
Significance of the Work
- While the human brain exhibits greater complexity, the fundamental communication patterns among neurons show remarkable similarity between fruit flies and humans.
- Fruit flies serve as an essential model organism in neuroscience, effectively addressing many cognitive challenges that human brains encounter.
- This research could advance our understanding of various mental health disorders, including Parkinson's disease and depression.
- The success in mapping the fruit fly's brain raises optimism that a complete mapping of the human brain may eventually be achievable.
GS3/Science and Technology
What is Ceres?
Source: Earth Sky

Why in News?
Researchers have recently revealed that Ceres is a highly icy celestial body that may have once been a world covered by a muddy ocean.
About Ceres:
- Ceres is classified as a dwarf planet and is the largest object found in the asteroid belt situated between Mars and Jupiter.
- It holds the distinction of being the only dwarf planet located within the inner solar system.
- Discovered in 1801 by Giuseppe Piazzi, Ceres was the first object identified in the asteroid belt.
- The name "Ceres" is derived from the Roman goddess of agriculture and harvests, and it is also the origin of the term "cereal."
- Initially categorized as an asteroid, Ceres was reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006 due to its size and distinct characteristics.
- NASA's Dawn spacecraft made history in 2015 by becoming the first mission to explore a dwarf planet.
Features:
- Ceres has a radius of approximately 296 miles (476 kilometers), which is about 1/13 the radius of Earth.
- It is located 8 Astronomical Units (AU) from the Sun, where one AU represents the average distance from the Earth to the Sun.
- One complete orbit around the Sun takes Ceres around 1,682 Earth days.
- Ceres has a rapid rotation period, completing one full turn every 9 hours, resulting in one of the shortest days in the solar system.
- Formed alongside the solar system roughly 4.5 billion years ago, Ceres originated from the gravitational collapse of swirling gas and dust.
- While it shares more characteristics with terrestrial planets like Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, Ceres is notably less dense.
- It is believed to have a solid core with a mantle comprising mainly of water ice, while its crust consists of rocky and dusty materials interspersed with significant salt deposits.
What is a Dwarf Planet?
- A dwarf planet is defined as a celestial body that orbits the Sun and is not classified as a natural satellite (moon).
- For practical purposes, a dwarf planet is smaller than Mercury but large enough for its own gravity to give it a rounded shape.
- The term was officially recognized by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) in August 2006, which designated Pluto, Eris, and other similar objects as the first members of this classification.
- Unlike major planets, dwarf planets lack the mass to clear their orbital path of smaller bodies due to insufficient gravitational force.
- In June 2008, the IAU introduced a subcategory known as "plutoids," which refers to dwarf planets located farther from the Sun than Neptune.
- Except for Ceres, all recognized dwarf planets fall into the category of plutoids.
GS3/Environment
EnviStats India 2024
Source: New Indian Express
Why in News?
The Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation (MoSPI) has released the seventh consecutive edition of the publication titled "EnviStats India 2024: Environment Accounts."
This publication is structured according to the System of Environmental-Economic Accounting (SEAA) framework and covers various aspects such as Energy Accounts, Ocean Accounts, Soil Nutrient Index, and Biodiversity.
Highlights EnviStats India 2024
- From 2000 to 2023, there has been a notable 72% increase in the number of Total Protected Areas, alongside a 16% increase in the area covered by these protected zones.
- The coverage of Mangroves, a vital sub-ecosystem within the ocean ecosystem, has seen an approximate 8% increase from 2013 to 2021.
- The report encompasses details on India's taxonomic faunal and floral diversity, including the status of species such as the Leopard and Snow Leopard.
- It includes insights on Genetic Conservation, utilizing data from various stakeholder ministries and agencies.
- The report compiles Species Richness data of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, categorized by taxonomic groups, using spatial datasets from IUCN.
What is System of Environmental-Economic Accounting?
- The System of Environmental-Economic Accounting (SEEA) serves as an internationally recognized statistical standard that illustrates the interactions between the economy and the environment.
- It aims to provide a comprehensive body of information regarding the stocks and changes in environmental assets.
- The SEEA consists of two main components: SEEA-Central Framework (SEEA-CF) and SEEA-Ecosystem Accounting (SEEA-EA).
SEEA-Central Framework
SEEA-Central Framework
- This framework concentrates on the individual components of the environment that supply material and space necessary for economic activities.
SEEA-Ecosystem Accounting
- This is a complementary framework to the SEEA-CF, designed to offer an integrated and comprehensive statistical structure for organizing data related to habitats and landscapes.
- It measures ecosystem services, tracks changes in ecosystem assets, and connects this information with economic activities and other human endeavors.
GS1/Indian Society
How circular migration can help meet global skill shortages and lift Indians out of poverty?
Source: Indian Express

Why in news?
Maharashtra's 997 youth, earning Rs 1.37 lakh in Israel, engage in circular migration, boosting skills through labour mobility agreements.
What is Circular Migration?
- Circular migration refers to the movement of people between their home country and another country for work, with the intention of returning home after a specified period.
Triple Win Scenario
- Migrants: They benefit by securing high-paying jobs, enhancing their skills, and receiving social security benefits while abroad.
- Home Country (e.g., India): Gains as returning workers bring back new skills and experiences, which can enhance local industries.
- Host Country (e.g., Israel, Germany): Benefits by acquiring the skilled workforce needed to fill labor shortages without long-term immigration issues.
Contribution to Skill Development and Poverty Alleviation
- Skill Development: Indian workers gain exposure to international work environments, advanced technologies, and management practices, thereby improving their skills and employability.
- Poverty Alleviation: Higher wages in developed countries enable migrants to remit money back home, enhancing the economic conditions of their families and aiding in poverty reduction.
Mitigating Brain Drain
- Temporary Nature: Since these workers return after a predetermined period (e.g., five years), they help prevent the permanent loss of talent to foreign nations.
- Knowledge Transfer: Returning migrants apply the skills and technologies learned abroad to their home country's industries, benefiting the local economy.
Policy Implications for Effective Circular Migration
- Skill Matching and Training: Governments need to ensure that migrant workers' skills align with the requirements of destination countries, and provide necessary refresher training.
- Government-to-Government Agreements: Strong bilateral agreements are vital to protect workers' rights, ensure fair compensation, and provide adequate support in destination countries.
- Streamlined Procedures: Policies should simplify legal processes, expedite passport issuance, and eliminate barriers such as language skills through language training in relevant languages like Japanese, German, or French.
Conclusion
- Circular migration presents a "triple win" situation by benefiting migrants, their home countries, and host nations. It enhances skills, increases incomes, mitigates brain drain, and fosters knowledge transfer, provided there is appropriate policy support, skill matching, and streamlined processes.
GS3/Environment
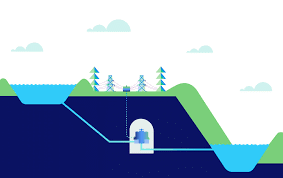
What are Pumped Hydropower Projects?
Source: Business Standard
Why in News?
The Union Environment Ministry’s expert panel has decided that it will not grant final clearances to pumped hydropower projects proposed in the Western Ghats region without site visits. With the fragile ecology of the Western Ghats in mind, this will ascertain the impact of such projects on the environment.
About:
- Pumped hydropower projects, commonly referred to as pumped storage hydropower (PSH) projects, serve as large-scale energy storage systems that harness water to both generate and store electricity.
- These projects represent the most prevalent form of energy storage utilized in today's electric grid.
Working:
- The system consists of two water reservoirs located at different elevations, allowing power generation through the flow of water from the upper to the lower reservoir (discharge), which passes through a turbine.
- It also requires energy to pump water back into the upper reservoir (recharge).
- PSH functions similarly to a massive battery, storing energy and releasing it when demand arises.
Types:
- Open-loop: These PSH systems link a reservoir to a naturally flowing water source through a tunnel, utilizing a turbine/pump and generator/motor for water movement and electricity generation.
- Closed-loop: These systems interconnect two reservoirs without any flowing water features, again employing a turbine/pump and generator/motor for operation.
Benefits:
- Grid stability: PSH projects contribute to maintaining grid balance during peak demand or low supply periods.
- Renewable energy integration: They facilitate the incorporation of renewable energy sources into the electricity grid.
Challenges:
- Significant initial investment costs.
- Requires thorough design and planning.
- Environmental and regulatory constraints must be navigated.
PSH Projects in India:
- The central government is advocating for an increase in pumped storage project (PSP) capacities to address the variability in solar and wind energy within the electricity grid.
- The Central Electricity Authority of India (CEA) has assessed India’s on-river pumped storage hydro potential to be approximately 103 GW.
- The Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) has recently approved environment-related permissions for pumped storage hydropower projects with a total capacity of 11.98 gigawatts (GW).
- The Expert Appraisal Committee (EAC) on River Valley and Hydroelectric Projects has endorsed Greenko Energy’s project of 3.66 GW in Sonbhadra district, Uttar Pradesh, marking it as the largest project to receive an environmental clearance recommendation.
- Additionally, two projects of 1.2 GW each from Sterlite Grid and Gandhwani Energy in Chhattisgarh have received recommendations.
- Other projects include a 2.22 GW project by Oju Subansiri Hydro Power Corporation in Arunachal Pradesh and a 1.5 GW project by JSW Energy in Maharashtra, which have also been approved.
- This approval represents the most substantial batch of new technology energy storage projects sanctioned in a single action in the country.
Concerns Regarding PSPs in Western Ghats:
- The EAC noted that the MoEFCC had issued terms of reference (ToR) or initial permissions for 15 PSPs in the Western Ghats region.
- These preliminary permissions outline the necessary scope for environmental impact assessment studies, which are required prior to public consultations before final environmental clearance can be granted.
- Several of these PSPs are located in villages designated as eco-sensitive areas according to the government’s draft notification aimed at protecting the Western Ghats.
- Due to potential adverse effects on biodiversity and forests in this fragile region, the EAC has mandated site visits to ensure comprehensive evaluation.
GS3/Economy
New GI Tagged Products
Source: Indian Express
Why in News?
Recently, the Geographical Indications Registry in Chennai granted the GI tag to eight products from the Assam region, including traditional food items and several unique varieties of rice beer.
About
New GI Tagged Products:
- Unique varieties of rice beer
- Bodo Jou Gwran: This variety has the highest alcohol content, reaching approximately 16.11%, compared to other rice beers made by the Bodo community.
- Maibra Jou Bidwi: Known locally as ‘Maibra Jwu Bidwi’ or ‘Maibra Zwu Bidwi’, this beer is cherished and often served as a welcoming drink by many Bodo tribes. It is made by fermenting half-cooked rice (mairong) with minimal water and adding a small amount of ‘amao’, which acts as a yeast source.
- Bodo Jou Gishi: Another traditional rice-based alcoholic beverage that undergoes fermentation.
- Traditional Food Products
- Bodo Napham: A popular dish made from fermented fish that is prepared anaerobically in a sealed container, requiring a fermentation period of about two to three months.
- Bodo Ondla: A curry made from rice powder that is flavored with garlic, ginger, salt, and alkali.
- Bodo Gwkha: Also known as ‘Gwka Gwkhi’; this dish is traditionally prepared during the Bwisagu festival.
- Bodo Narzi: A semi-fermented food made with jute leaves (Corchorus capsularis), which is rich in Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and essential minerals including calcium and magnesium.
- Bodo Aronai: A small, intricately designed cloth measuring between 1.5 to 2.5 meters long and 0.5 meters wide.
|
44 videos|5271 docs|1113 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 5th October 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the main characteristics of the Negro River? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of Pseumenes siangensis? |  |
| 3. What does the National Agriculture Code entail? |  |
| 4. What are the symptoms and causes of Motor Neuron Disease (MND)? |  |
| 5. Why is mapping the fruit fly's brain important for scientific research? |  |
















