All questions of Curved Mirrors for Grade 9 Exam
A 10 mm long awl pin is placed vertically in front of a concave mirror. A 5 mm long image of the awl pin is formed at 30 cm in front of the mirror. The focal length of this mirror is- a)- 30 cm
- b)- 20 cm
- c)- 40 cm
- d)- 60 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A 10 mm long awl pin is placed vertically in front of a concave mirror. A 5 mm long image of the awl pin is formed at 30 cm in front of the mirror. The focal length of this mirror is
a)
- 30 cm
b)
- 20 cm
c)
- 40 cm
d)
- 60 cm
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
Given h0 = +10 mm - + 0.1 cm
h2 = - 5 mm = -0 .5 cm
for real image, v = - 30 cm
h2 = - 5 mm = -0 .5 cm
for real image, v = - 30 cm
Now magnification,
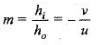
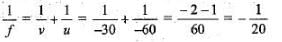
∴ f = -20 cm
A linear object is placed at a distance equal to focal length of a convex mirror. Its image is formed
- a)at infinite distance
- b)at the principal focus of mirror
- c)behind the mirror at a distance f/2
- d)in front of mirror at a distance f/2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A linear object is placed at a distance equal to focal length of a convex mirror. Its image is formed
a)
at infinite distance
b)
at the principal focus of mirror
c)
behind the mirror at a distance f/2
d)
in front of mirror at a distance f/2
|
|
Karthik murthy answered |
When a linear object is placed at a distance equal to focal length of a convex mirror then its virtual image is form ed behind the mirror at a distance f/2
As per sign convention u = - f and focal length o f convex mirror is + ve, hence from mirror formula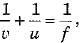 we have
we have
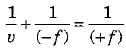 or
or 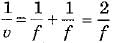 or
or 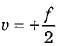
As per sign convention u = - f and focal length o f convex mirror is + ve, hence from mirror formula
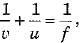 we have
we have 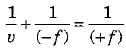 or
or 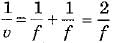 or
or 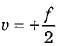
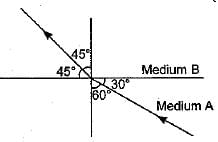
Figure shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B. Refractive index of the medium B relative to medium A is
- a)
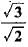
- b)
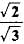
- c)
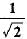
- d)√2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Figure shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B. Refractive index of the medium B relative to medium A is


a)
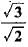
b)
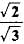
c)
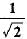
d)
√2

|
Sun Ray Institute answered |
Here, ∠i = 60°, ∠r = 45°
Using Snell’s law of refraction, refractive index of medium B with respect to medium A.
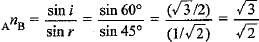
Using Snell’s law of refraction, refractive index of medium B with respect to medium A.
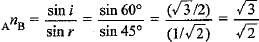
Transparent medium is one :
- a)Which allows light to pass through
- b)Which absorbs most of the light
- c)Which do not allows light to pass through
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Transparent medium is one :
a)
Which allows light to pass through
b)
Which absorbs most of the light
c)
Which do not allows light to pass through
d)
None of these

|
Imk Pathshala answered |
A transparent medium is a material that partially allows light to pass through.
When light encounters a transparent medium, it can penetrate the material and transmit through it.
Examples of transparent mediums include glass, water, and air.
Transparent mediums are essential for various applications such as optics, windows, and lenses.
Can you explain the answer of this question below:A concave lens of 20 cm focal length forms an image 15 cm from the lens. What is the object distance?
- A:
60 cm
- B:
30 cm
- C:
-60 cm
- D:
-30 cm
The answer is c.
A concave lens of 20 cm focal length forms an image 15 cm from the lens. What is the object distance?
60 cm
30 cm
-60 cm
-30 cm
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
Focal length= -20(as it is concave lens)
v= -15 (as concave lens always forms virtual and erect image on left of lens)
Putting these values in lens formula,
1/ -20 - 1/u = 1/ -15
-1/ u= 1/-15 + 1/20
-1/u = -4+3/60
-1/u = -1/60
-u = -60
[u =60]
v= -15 (as concave lens always forms virtual and erect image on left of lens)
Putting these values in lens formula,
1/ -20 - 1/u = 1/ -15
-1/ u= 1/-15 + 1/20
-1/u = -4+3/60
-1/u = -1/60
-u = -60
[u =60]
An object 2 cm high is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror which produces an inverted image 4 cm high. Find the position of the image.
- a)-30 cm
- b)30 cm
- c)40 cm
- d)-40 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An object 2 cm high is placed at a distance of 15 cm from a concave mirror which produces an inverted image 4 cm high. Find the position of the image.
a)
-30 cm
b)
30 cm
c)
40 cm
d)
-40 cm
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The magnification produced by a concave mirror is given by the formula:
m = -v/u
where, m = magnification v = image distance u = object distance
From the problem, we have: u = -15 cm (since the object is placed in front of the mirror, the distance is negative) m = -4/2 = -2 (since the image is inverted and 4 cm high whereas the object is 2 cm high)
Substituting these values in the magnification formula, we get:
-2 = -v/(-15)
Simplifying, we get:
v = 30 cm
Therefore, the position of the image is 30 cm from the concave mirror.
The lens which is used to correct myopia (shortsightedness) is- a)Both convex and concave
- b)Concave lens
- c)Converging lens
- d)Convex Lens
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The lens which is used to correct myopia (shortsightedness) is
a)
Both convex and concave
b)
Concave lens
c)
Converging lens
d)
Convex Lens
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Shortsightedness is corrected using a concave (curved inwards) lens which is placed in front of a myopic eye, moving the image back to the retina and making it clearer.
A magnified real image is formed by a convex lens when the obiect is at:
- a)F
- b)Infinity
- c)2F
- d)Between F and 2F
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A magnified real image is formed by a convex lens when the obiect is at:
a)
F
b)
Infinity
c)
2F
d)
Between F and 2F
|
|
Radha Iyer answered |
To get the real and magnified image for a convex lens, the object is placed in between F and 2F.
A virtual, erect and magnified image of an object is to be produced with a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm. Object may be placed at a distance of- a)10 cm from the mirror
- b)15 cm from the mirror
- c)24 cm from the mirror
- d)48 cm from the mirror
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A virtual, erect and magnified image of an object is to be produced with a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm. Object may be placed at a distance of
a)
10 cm from the mirror
b)
15 cm from the mirror
c)
24 cm from the mirror
d)
48 cm from the mirror
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
A concave mirror forms a virtual, erect and magnified image when an object is placed between pole and focus point of the mirror. As focal length of given concave mirror, hence object must be placed at a distance less than 12 cm i.e., u < 12 cm. Thus, the object may be placed at a distance of 10 cm from the mirror.
A ray of light AM is incident on a concave mirror as shown below. Then which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the reflected ray ?
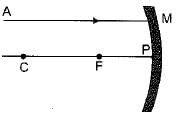
- a)
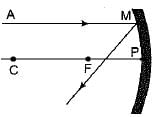
- b)
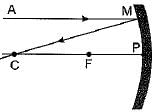
- c)
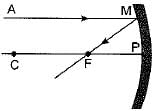
- d)
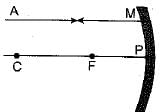
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A ray of light AM is incident on a concave mirror as shown below. Then which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the reflected ray ?


a)

b)

c)

d)

|
|
Naman pandey answered |
As the incident light ray is coming parallel to the principal axis of given concave mirror, the reflected ray must pass through the principal focus of mirror.
A lens has a power of +0.5 D. It is - a)a concave lens of focal length 5 m
- b)a convex lens of focal length 5 cm
- c)a convex lens of focal length 2 m
- d)a concave lens of focal length 2 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A lens has a power of +0.5 D. It is
a)
a concave lens of focal length 5 m
b)
a convex lens of focal length 5 cm
c)
a convex lens of focal length 2 m
d)
a concave lens of focal length 2 m
|
|
Sanya jain answered |
Given, power of the lens = 0.5 D.
We know that the power of the lens is given by the formula:
Power (P) = 1/f, where f is the focal length of the lens.
Therefore, we can write:
0.5 D = 1/f
Solving for f, we get:
f = 1/0.5 D
f = 2 m
Hence, the focal length of the lens is 2 m.
Therefore, the correct option is (c) a convex lens of focal length 2 m.
Explanation:
A convex lens has a positive power and can converge the light rays to a point. The focal length of a convex lens is positive. When the power of the lens is given, we can find the focal length of the lens using the formula P = 1/f. Here, the power is given as 0.5 D. On substituting the values, we get the focal length as 2 m. Hence, the lens is a convex lens of focal length 2 m.
We know that the power of the lens is given by the formula:
Power (P) = 1/f, where f is the focal length of the lens.
Therefore, we can write:
0.5 D = 1/f
Solving for f, we get:
f = 1/0.5 D
f = 2 m
Hence, the focal length of the lens is 2 m.
Therefore, the correct option is (c) a convex lens of focal length 2 m.
Explanation:
A convex lens has a positive power and can converge the light rays to a point. The focal length of a convex lens is positive. When the power of the lens is given, we can find the focal length of the lens using the formula P = 1/f. Here, the power is given as 0.5 D. On substituting the values, we get the focal length as 2 m. Hence, the lens is a convex lens of focal length 2 m.
Which lens always forms diminished and erect image ?
- a)Convex lens
- b)Concave lens
- c)Converging lens
- d)Both convex and concave
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which lens always forms diminished and erect image ?
a)
Convex lens
b)
Concave lens
c)
Converging lens
d)
Both convex and concave

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
A concave lens (also known as a diverging lens) is thinner in the center and thicker at the edges. When light rays pass through a concave lens, they diverge (spread out), causing the rays to appear to come from a single point on the same side of the lens as the object. This results in the formation of a virtual image.
Key characteristics of the image formed by a concave lens:
- Diminished: The image is smaller than the actual object.
- Erect: The image is upright, meaning it has the same orientation as the object.
- Virtual: The image cannot be projected on a screen because the light rays do not actually meet but only appear to do so when extended backward.
Because of these properties, a concave lens always forms a diminished, erect, and virtual image, no matter where the object is placed in front of the lens.
On the other hand, a convex lens (also known as a converging lens) can form different types of images (real and inverted or virtual and erect) depending on the position of the object relative to the lens. But it does not always form a diminished and erect image, unlike the concave lens.
The unit of linear magnification is- a)Dioptre
- b)Metre
- c)Metre per second
- d)It is unitless
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The unit of linear magnification is
a)
Dioptre
b)
Metre
c)
Metre per second
d)
It is unitless
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Magnification is thr ratio of size of image to size of object and since it is a ratio of tel similar quantities hence it is unitless.
In a convex lens, where is the image formed, when an object is placed at 2F ?- a)Between F and 2F
- b)At focus (F)
- c)At 2F on the other side
- d)At 2F on the same side
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In a convex lens, where is the image formed, when an object is placed at 2F ?
a)
Between F and 2F
b)
At focus (F)
c)
At 2F on the other side
d)
At 2F on the same side
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
At the 2F point, the object distance equals the image distance and the object height equals the image height. As the object distance approaches one focal length, the image distance and image height approaches infinity.
If the magnification has a negative sign, the image formed by the concave mirror must be- a)Real and inverted
- b)Virtual and inverted
- c)Virtual and erect
- d)Real and erect
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
If the magnification has a negative sign, the image formed by the concave mirror must be
a)
Real and inverted
b)
Virtual and inverted
c)
Virtual and erect
d)
Real and erect
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
We know that, if the magnification value is negative sign in the concave mirror, then the image will be real and inverted. Especially, when you come to concave mirror, the images are formed at the left of the mirror. So, it forms real and inverted.
No matter how far or close you stand from a mirror, your image is always virtual and erect. The mirror is- a)convex mirror
- b)plane mirror
- c)concave mirror
- d)either a convex or a plane mirror
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
No matter how far or close you stand from a mirror, your image is always virtual and erect. The mirror is
a)
convex mirror
b)
plane mirror
c)
concave mirror
d)
either a convex or a plane mirror
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
Irrespective of the position of an object both convex mirror and plane mirror form virtual and erect images. Of course image formed by a plane mirror is of same size as the object but image formed by convex mirror is always diminished one.
The muscles of the iris control the- a)focal length of the eye-lens
- b)opening of the pupil
- c)shape of the crystalline lens
- d)optic nerve
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The muscles of the iris control the
a)
focal length of the eye-lens
b)
opening of the pupil
c)
shape of the crystalline lens
d)
optic nerve

|
Nk Classes answered |
The Laws of Reflection for Mirrors
- The laws of reflection apply to all mirrors, regardless of their shape.
- These laws state that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- This means that the light rays that strike the mirror are reflected at the same angle.
- Whether the mirror is concave, convex, or plane, these laws will always hold true.
- Therefore, option B is correct as it includes all mirrors, not just a specific type.
- The laws of reflection apply to all mirrors, regardless of their shape.
- These laws state that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
- This means that the light rays that strike the mirror are reflected at the same angle.
- Whether the mirror is concave, convex, or plane, these laws will always hold true.
- Therefore, option B is correct as it includes all mirrors, not just a specific type.
An object of size 2.0 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror. The distanceof the object from the mirror equals the radius of curvature. The size of the image will be - a)0.5 cm
- b)1.5 cm
- c)1.0cm
- d)2.0 cm
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
An object of size 2.0 cm is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a concave mirror. The distance
of the object from the mirror equals the radius of curvature. The size of the image will be
a)
0.5 cm
b)
1.5 cm
c)
1.0cm
d)
2.0 cm
|
|
Ishan Choudhury answered |
The size of the image will be 2.0 cm.
V=U(given)
m=-v/u
m= - 1
m=h`/h
-1=h`/2
h`=-2
h=2cm
V=U(given)
m=-v/u
m= - 1
m=h`/h
-1=h`/2
h`=-2
h=2cm
A convex lens of focal length 12 cm produces a magnification of -1. The object should be placed at;- a)-12 cm
- b)-24 cm
- c)-48 cm
- d)-96 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
A convex lens of focal length 12 cm produces a magnification of -1. The object should be placed at;
a)
-12 cm
b)
-24 cm
c)
-48 cm
d)
-96 cm
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
1/v - 1/u
1/f =-1/u - 1/u
1/f = - 2/u
u=-2f
u=-24 cm
1/f =-1/u - 1/u
1/f = - 2/u
u=-2f
u=-24 cm
The angle of incidence of any light ray passing through the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is- a)0°
- b)45°
- c)90°
- d)60°
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle of incidence of any light ray passing through the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is
a)
0°
b)
45°
c)
90°
d)
60°
|
|
Chirag raman answered |
The angle of incidence of any light ray passing through the centre of curvature of a spherical mirror is 0°, because a line joining centre of curvature to any point on the mirror is a normal drawn at that point of the mirror.
Rays from sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of the image is exactly equal to the size of the object ?- a)30 cm in front of mirror
- b)15 cm in front of mirror
- c)Between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of mirror
- d)Less than 15 cm in front of mirror
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Rays from sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of the image is exactly equal to the size of the object ?
a)
30 cm in front of mirror
b)
15 cm in front of mirror
c)
Between 15 cm and 30 cm in front of mirror
d)
Less than 15 cm in front of mirror
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
As light rays from sun (u = ∞) converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror, hence focal length of concave mirror f = - 15 cm.
To form an image of exactly same size as that of an object, the object should be placed at the centre of curvature (u = R = 2f) of mirror. Hence, the object should be placed at 30 cm in front of mirror.
To form an image of exactly same size as that of an object, the object should be placed at the centre of curvature (u = R = 2f) of mirror. Hence, the object should be placed at 30 cm in front of mirror.
The angle of incidence is the angle between- a)the incident ray and the surface of the mirror
- b)the reflected ray and the surface of the mirror
- c)the normal to the surface and the incident ray
- d)the normal to the surface and the reflected ray
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle of incidence is the angle between
a)
the incident ray and the surface of the mirror
b)
the reflected ray and the surface of the mirror
c)
the normal to the surface and the incident ray
d)
the normal to the surface and the reflected ray
|
|
Hitakshi 💞💞 answered |
The angle between the incident ray and the normal is called as angle of incidence and it is generally denoted by i. The angle between the normal and the reflected ray is called as angle of reflection and it is generally denoted by r.
A ray of light is reflected by the pole of a concave mirror at an angle of 80o. The angle of incidence will be
- a)80º
- b)180º
- c)0º
- d)50º
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A ray of light is reflected by the pole of a concave mirror at an angle of 80o. The angle of incidence will be
a)
80º
b)
180º
c)
0º
d)
50º
|
|
Ashiii answered |
Angle of Reflection = Angle of Incidence
Angle of Reflection = 80॰
⁂ Angle of Incidence = 80॰
..v@.**
An object is placed before a concave lens. The image formed- a)is always erect
- b)may be erect or inverted
- c)is always inverted
- d)is always real
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An object is placed before a concave lens. The image formed
a)
is always erect
b)
may be erect or inverted
c)
is always inverted
d)
is always real

|
Headway Institute answered |
Because concave lens always produce an
Image which is always erect, diminished and virtual.
Image which is always erect, diminished and virtual.
In case of a real and inverted image the magnification of a mirror is- a)positive and large
- b)negative
- c)positive and small
- d)negative and large
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In case of a real and inverted image the magnification of a mirror is
a)
positive and large
b)
negative
c)
positive and small
d)
negative and large
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
Magnification is negative for a real and inverted image formed by a mirror.
In which of the following, the image of an object placed at infinity will be highly diminished and point sized ?- a)Concave mirror only
- b)Convex mirror only
- c)Convex lens only
- d)All types of mirrors and lenses
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following, the image of an object placed at infinity will be highly diminished and point sized ?
a)
Concave mirror only
b)
Convex mirror only
c)
Convex lens only
d)
All types of mirrors and lenses

|
Flembe Academy answered |
- When an object is placed at infinity, a parallel beam of light is incident on the mirror/lens.
- For all types of mirrors and lenses the beam will get focussed at the principal focus of mirror/lens and a highly diminished, point size image is formed there.
The minimum distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is (f = focal length of the lens) - a)2.5 f
- b)2 f
- c)4 f
- d)f
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The minimum distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is (f = focal length of the lens)
a)
2.5 f
b)
2 f
c)
4 f
d)
f
|
|
Arun Sharma answered |
Let the distance between the object and its real image formed by convex lens be d1.
Let the distance of the object from lens be x,so,the image distance from the lens is (d-x)
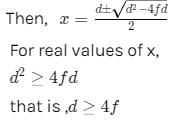
Let the distance of the object from lens be x,so,the image distance from the lens is (d-x)
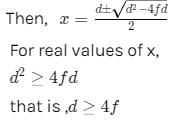
The minimum distance between an object and its real image in a convex lens is 4f.
hence,option C is correct.
.
hence,option C is correct.
.
Refractive index of glass w.r.t. air is 3/2. What is the refractie index of air w.r.t glass ?- a)2/3
- b)1
- c)Zero
- d)(3/2)2
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Refractive index of glass w.r.t. air is 3/2. What is the refractie index of air w.r.t glass ?
a)
2/3
b)
1
c)
Zero
d)
(3/2)2
|
|
Zara Khan answered |
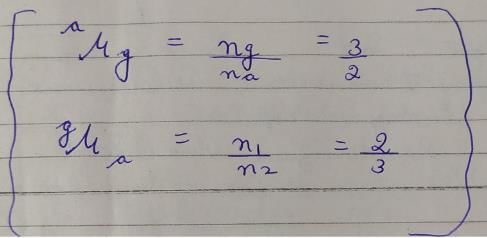
If refractive index of glass w.r.t air is 3/2 , then refractive index of air w. r. t glass will be it's reciprocal ie. ⅔ ..
An object is placed before a convex lens. The image formed- a)is always real
- b)may be real or virtual
- c)is always virtual
- d)is always erect
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
An object is placed before a convex lens. The image formed
a)
is always real
b)
may be real or virtual
c)
is always virtual
d)
is always erect

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
Convex Lens: A convex lens is thicker at the center and thinner at the edges. When light rays pass through a convex lens, they converge at a point called the focal point.
Image Formation: When an object is placed before a convex lens, the light rays from the object refract through the lens and form an image on the other side. The image formation by a convex lens depends on the distance of the object from the lens.
Real or Virtual Image: The image formed by a convex lens can be real or virtual, depending on the position of the object relative to the lens.
Real Image: A real image is formed when the light rays actually converge at a point after passing through the lens. This real image can be projected onto a screen and is always inverted.
- Virtual Image: A virtual image is formed when the light rays appear to converge at a point on the same side of the lens as the object. This virtual image cannot be projected onto a screen and is always upright.
- Conclusion: Therefore, when an object is placed before a convex lens, the image formed may be real or virtual, depending on the position of the object relative to the lens.
An object 4 cm tall is placed in front of a convex lens. It produces an image 3 cm tall. What is the magnification of the lens ?
- a)1.33
- b)12
- c)0.75
- d)11
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An object 4 cm tall is placed in front of a convex lens. It produces an image 3 cm tall. What is the magnification of the lens ?
a)
1.33
b)
12
c)
0.75
d)
11
|
|
Rohit Sharma answered |
We know, height of the object is 4 cm h1, height of the image is 3 cm, h2.
So we have, m = h2/h1
=> m = 3/4
=> m = 0.75
Therefore, magnification of the lens is 0.75
So we have, m = h2/h1
=> m = 3/4
=> m = 0.75
Therefore, magnification of the lens is 0.75
If a lens has a focal length, F = +12 cm, then it is a- a)Can be convex or concave
- b)Convex lens
- c)Diverging lens
- d)Concave lens
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a lens has a focal length, F = +12 cm, then it is a
a)
Can be convex or concave
b)
Convex lens
c)
Diverging lens
d)
Concave lens
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The focal length of convex lens is always positive. Image obtained can be either real or virtual.
A concave mirror is used to form an image of the sun on a white screen. If the lower half of the mirror is covered with a black paper, the effect on the image formed on the screen would be- a)to make the image less bright than before
- b)to make the lower half of the image disappear
- c)to prevent the image from being focussed
- d)to make the image smaller in size
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A concave mirror is used to form an image of the sun on a white screen. If the lower half of the mirror is covered with a black paper, the effect on the image formed on the screen would be
a)
to make the image less bright than before
b)
to make the lower half of the image disappear
c)
to prevent the image from being focussed
d)
to make the image smaller in size
|
|
Gourav khanna answered |
If lower half (or a part) of a mirror is covered with a black paper then complete image of the object will be formed as before. However, the image will be less bright now.
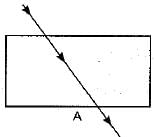
The path of a ray of light coming from air passing through a rectangular glass slab traced by four students are shown as A, B, C and D in figure. Which one of them is correct?
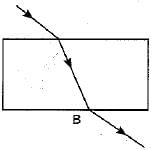
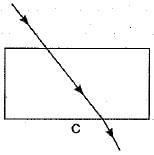
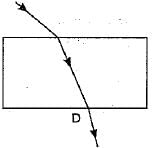
- a)A
- b)B
- c)C
- d)D
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The path of a ray of light coming from air passing through a rectangular glass slab traced by four students are shown as A, B, C and D in figure. Which one of them is correct?








a)
A
b)
B
c)
C
d)
D
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
When a light ray is incident oblikely on one face of rectangular glass slab, the emergent ray will be parallel to the incident ray and shifted sideward slightly.
A point object is placed on the principal axis of a spherical mirror. The object-distance u is - a)definitely negative
- b)definitely positive
- c)positive if the object is to the left of the centre of curvature
- d)positive if the object is to the right of the centre of curvature
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A point object is placed on the principal axis of a spherical mirror. The object-distance u is
a)
definitely negative
b)
definitely positive
c)
positive if the object is to the left of the centre of curvature
d)
positive if the object is to the right of the centre of curvature
|
|
Ritu Saxena answered |
Option ( a) is the correct answer. As the object is always placed on the left side of the mirror and according to the sign convention, it has negative value for 'so axis.
Therefore, spherical mirrors have only one reflecting surface and it will be negative only.
As per the cartesian sign convention followed for mirrors and lenses- a)focal length of concave mirror and concave lens is negative
- b)focal length of concave mirror and convex lens is negative
- c)focal length of convex mirror and convex lens is negative
- d)focal length of convex mirror and concave lens is negative
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
As per the cartesian sign convention followed for mirrors and lenses
a)
focal length of concave mirror and concave lens is negative
b)
focal length of concave mirror and convex lens is negative
c)
focal length of convex mirror and convex lens is negative
d)
focal length of convex mirror and concave lens is negative
|
|
Kiran Mehta answered |
As per the new Cartesian sign convention followed focal length of a concave mirror as well as of a concave lens is taken with negative sign.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object ?- a)At infinity
- b)At twice the focal length
- c)Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus.
- d)At the principal focus of the lens
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object ?
a)
At infinity
b)
At twice the focal length
c)
Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus.
d)
At the principal focus of the lens
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
At twice the focal length the image formed by convex lens is real and of the same size as object.
An object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. The distance between its imageand the pole is - a)equal to f
- b)between f and 2f
- c)equal to 2f
- d)greater than 2f
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
An object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror. The distance between its image
and the pole is
a)
equal to f
b)
between f and 2f
c)
equal to 2f
d)
greater than 2f
|
|
Ishaani mehta answered |
Explanation:
The given situation can be represented as follows:

Here, C is the centre of curvature of the concave mirror, F is the focus, and P is the pole.
Now, let us consider the path of light rays from the object to the mirror and then to its image.
- The light rays from the object are parallel to the principal axis and fall on the mirror.
- At the point of incidence, the light rays are reflected and converge towards the focus F.
- However, since the object is placed at the centre of curvature C, the reflected rays pass through F and become parallel to the principal axis.
- These parallel rays then converge at the position of the image I.
Therefore, we can see that the image is formed at a distance equal to twice the focal length from the mirror.
- From the mirror formula:
1/f = 1/v + 1/u
where f is the focal length, v is the image distance, and u is the object distance.
- In this case, since the object is placed at C, u = -2f (negative sign indicates that it is on the opposite side of the mirror).
- We want to find v, the distance between the image and the pole.
- Substituting the given values, we get:
1/f = 1/v - 1/2f
Multiplying both sides by vf2, we get:
2f = v + f
Therefore, v = 2f - f = f.
Hence, the distance between the image and the pole is equal to the focal length of the mirror, which is option C.
The given situation can be represented as follows:

Here, C is the centre of curvature of the concave mirror, F is the focus, and P is the pole.
Now, let us consider the path of light rays from the object to the mirror and then to its image.
- The light rays from the object are parallel to the principal axis and fall on the mirror.
- At the point of incidence, the light rays are reflected and converge towards the focus F.
- However, since the object is placed at the centre of curvature C, the reflected rays pass through F and become parallel to the principal axis.
- These parallel rays then converge at the position of the image I.
Therefore, we can see that the image is formed at a distance equal to twice the focal length from the mirror.
- From the mirror formula:
1/f = 1/v + 1/u
where f is the focal length, v is the image distance, and u is the object distance.
- In this case, since the object is placed at C, u = -2f (negative sign indicates that it is on the opposite side of the mirror).
- We want to find v, the distance between the image and the pole.
- Substituting the given values, we get:
1/f = 1/v - 1/2f
Multiplying both sides by vf2, we get:
2f = v + f
Therefore, v = 2f - f = f.
Hence, the distance between the image and the pole is equal to the focal length of the mirror, which is option C.
A ray of light is incident on a concave mirror. If it is parallel to the principal axis, the reflected ray will- a)pass through the focus
- b)pass through the centre of curvature
- c)pass through the pole
- d)retrace its path
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A ray of light is incident on a concave mirror. If it is parallel to the principal axis, the reflected ray will
a)
pass through the focus
b)
pass through the centre of curvature
c)
pass through the pole
d)
retrace its path
|
|
Diana Nair answered |
A ray of light which is parallel to the principle axis after reflection will pass through the focus of a concave mirror.
In which of the following, the image of an object placed at infinity will be highly diminished and point sized ?- a)Concave mirror only
- b)Convex mirror only
- c)Convex lens only
- d)Concave mirror, convex mirror, concave lens and convex lens
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In which of the following, the image of an object placed at infinity will be highly diminished and point sized ?
a)
Concave mirror only
b)
Convex mirror only
c)
Convex lens only
d)
Concave mirror, convex mirror, concave lens and convex lens
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The incident ray coming from the object placed at infinity will be parallel to the principal axis. When the parallel beam of light incident on a mirror or lens, irrespective of their nature, after reflection/refraction, will pass or appear to pass through their principal focus. Hence highly diminished and point size image will be formed at their focus.
In a convex mirror for any position of the object in front of mirror, the image formed is- a)situated between pole and principal focus of mirror
- b)virtual and erect
- c)diminished in size
- d)all of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
In a convex mirror for any position of the object in front of mirror, the image formed is
a)
situated between pole and principal focus of mirror
b)
virtual and erect
c)
diminished in size
d)
all of these
|
|
Shobha singhania answered |
For a convex mirror irrespective of the position of object the image formed is virtual, erect and diminished one. Moreover, the image is always situated between pole and principal focus of the mirror.
The distance at which an object should be placed from a thin convex lens of focal length 10 cm to obtain a virtual image of double of its size is- a)15 cm
- b)– 5 cm
- c)-10cm
- d)5.5 cm
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The distance at which an object should be placed from a thin convex lens of focal length 10 cm to obtain a virtual image of double of its size is
a)
15 cm
b)
– 5 cm
c)
-10cm
d)
5.5 cm
|
|
Neha Patel answered |
given : f = 10 cm , m = 2
v / u = 2
v = 2u
v = 2u -------(1)
according to lens formula ,
1/v - 1/u = 1/f
1/v - 1/u = 1/10 --------(2)
substitute (1) in (2)
1/2u - 1/u = 1/10
1 - 2 / 2u = 1/10
-1 / 2u = 1/10
-10 = 2u
u = -10/2
u = -5 cm
therfore object should be placed 5 cm away from the lens
A ray of light, which is parallel to the principal axis of the concave mirror, after reflection passes through the- a)Centre of curvature
- b)Focal length
- c)Pole of the mirror
- d)Principal focus of the mirror
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A ray of light, which is parallel to the principal axis of the concave mirror, after reflection passes through the
a)
Centre of curvature
b)
Focal length
c)
Pole of the mirror
d)
Principal focus of the mirror
|
|
Vikas Kumar answered |
An incident ray which passes through the focus of the mirror is reflected parallel to the principal axis. An incident ray which passes through the centre of curvature of the mirror is reflected back along its own path (since it is normally incident on the mirror).
Indicate the only correct statement.- a)The image formed by a convex mirror can be taken on the screen.
- b)A convex mirror can produce a parallel beam of light from a point source.
- c)The image of'an object placed at the focus of a convex mirror will be formed at infinity.
- d)A concave mirror can never form a diminished virtual image.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Indicate the only correct statement.
a)
The image formed by a convex mirror can be taken on the screen.
b)
A convex mirror can produce a parallel beam of light from a point source.
c)
The image of'an object placed at the focus of a convex mirror will be formed at infinity.
d)
A concave mirror can never form a diminished virtual image.

|
EduRev Class 10 answered |
Option D: "A concave mirror can never form a diminished virtual image."
Correct. A concave mirror can form a diminished real image but never a diminished virtual image. Virtual images formed by concave mirrors are always enlarged.
A convergent beam of light passes through a diverging lens of focal length 0.2 m and comes to focus 0.3 m behind the lens. Find the position of the point at which the beam would converge in the absence of lens.- a)0.1 m
- b)0.22 m
- c)0.2 m
- d)0.12 m
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A convergent beam of light passes through a diverging lens of focal length 0.2 m and comes to focus 0.3 m behind the lens. Find the position of the point at which the beam would converge in the absence of lens.
a)
0.1 m
b)
0.22 m
c)
0.2 m
d)
0.12 m
|
|
Neha Patel answered |
The image is 0.3 m to the right of the lens. This is 0.5 m TO THE RIGHT OF the left hand (image) focal point.
As explained above, concave lenses have their focal points on the opposite side of the lens to a convex lens.
So in the formula so* si = f^2 si = 0.5
f^2 = 0.2 ^2= 0.04
Therefore so = 0.04/ 0.5 = 0.08 m
This means that the object must have been 0.08 m to the left of its focal point.
which places it at 0.12m from the lens
This would be the point at which the rays of light would have converged if the lens had not been present.
It is actually a VIRTUAL OBJECT because the light never actually reaches this point.
The final point the light reaches is a REAL IMAGE because the light actually does focus at this point as can be seen by putting a paper screen there.
The angle of reflection is the angle between - a)the incident ray and the surface of the mirror
- b)the reflected ray and the surface of the mirror
- c)the normal to the surface and the incident ray
- d)the normal to the surface and the reflected ray
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The angle of reflection is the angle between
a)
the incident ray and the surface of the mirror
b)
the reflected ray and the surface of the mirror
c)
the normal to the surface and the incident ray
d)
the normal to the surface and the reflected ray
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Angle of reflection is the angle between a reflected ray and the normal drawn at the point of incidence to a reflecting surface.
Drop of water behaves likes a- a)Diverging lens
- b)Concave lens
- c)Convex lens
- d)Both convex and concave
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Drop of water behaves likes a
a)
Diverging lens
b)
Concave lens
c)
Convex lens
d)
Both convex and concave
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
The surface of a water drop curves outward to make a dome. This outward, or convex, curvature bends light rays inward. will act as a concave lens that bends the light rays outward. As a result, letters seen through the layer of water in a cup appear smaller than they are.
A magnifying glass is a- a)Both convex and concave
- b)Concave lens
- c)Diverging lens
- d)Convex Lens
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A magnifying glass is a
a)
Both convex and concave
b)
Concave lens
c)
Diverging lens
d)
Convex Lens
|
|
Ꭰꮰ Ꮥꮑꭿꮶꭼ answered |
A magnifying glass is a convex lens used to make an object appear much larger than it actually is. This works when the object is placed at a distance less than the focal length from the lens.
Which lens always forms a virtual image ?- a)Concave lens
- b)Convex lens
- c)Converging lens
- d)Both convex and concave
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which lens always forms a virtual image ?
a)
Concave lens
b)
Convex lens
c)
Converging lens
d)
Both convex and concave
|
|
Nandini nair answered |
Explanation:
A virtual image is an image that cannot be projected onto a screen. It is always located on the opposite side of the lens from the object and is always upright. Virtual images are formed when light rays appear to come from a point behind the lens, rather than actually converging at that point.
Concave Lens:
- A concave lens is thinner at the center and thicker at the edges.
- When light rays pass through a concave lens, they diverge or spread out.
- As a result, a concave lens always forms a virtual image that is upright, smaller in size, and located between the lens and the object.
Convex Lens:
- A convex lens is thicker at the center and thinner at the edges.
- When light rays pass through a convex lens, they converge or come together.
- Depending on the placement of the object, a convex lens can form either a real or virtual image.
Converging Lens:
- A converging lens is another name for a convex lens.
- As discussed above, a converging lens can form both real and virtual images.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanation, it can be concluded that a concave lens always forms a virtual image.
A virtual image is an image that cannot be projected onto a screen. It is always located on the opposite side of the lens from the object and is always upright. Virtual images are formed when light rays appear to come from a point behind the lens, rather than actually converging at that point.
Concave Lens:
- A concave lens is thinner at the center and thicker at the edges.
- When light rays pass through a concave lens, they diverge or spread out.
- As a result, a concave lens always forms a virtual image that is upright, smaller in size, and located between the lens and the object.
Convex Lens:
- A convex lens is thicker at the center and thinner at the edges.
- When light rays pass through a convex lens, they converge or come together.
- Depending on the placement of the object, a convex lens can form either a real or virtual image.
Converging Lens:
- A converging lens is another name for a convex lens.
- As discussed above, a converging lens can form both real and virtual images.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanation, it can be concluded that a concave lens always forms a virtual image.
Which of the following can be used to form a virtual image of an object?
I. convex lens
II. concave lens
III. concave mirror- a)II only
- b)II and III only
- c)I and III only
- d)I, II and III
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following can be used to form a virtual image of an object?
I. convex lens
II. concave lens
III. concave mirror
I. convex lens
II. concave lens
III. concave mirror
a)
II only
b)
II and III only
c)
I and III only
d)
I, II and III

|
Adidev Nair answered |
A concave lens forms
real and inverted image
. When the
object
is placed very close to the
lens
, the
image
formed is
virtual
, erect and magnified.
A
concave lens
always
forms
erect,
virtual
and smaller
image
than the
object
.
Concave
mirrors
can produce
both real and
virtual images
; they
can
be upright (if
virtual
) or inverted (if real); they
can
be behind the
mirror
(if
virtual
) or in front of the
mirror
(if real); they
can
also be enlarged, reduced, or the same size as
object
.
Chapter doubts & questions for Curved Mirrors - Physics 2025 is part of Grade 9 exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Grade 9 exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Grade 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Curved Mirrors - Physics in English & Hindi are available as part of Grade 9 exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Grade 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Physics
307 videos|482 docs|202 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily











