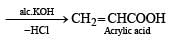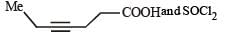All Exams >
JEE >
Chemistry 35 Year Past year Papers JEE Main & Advanced >
All Questions
All questions of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids for JEE Exam
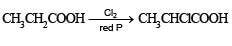
Among the following acids which has the lowest pKa value?- a)CH3CH2COOH
- b)(CH3)2 CH - COOH
- c)HCOOH
- d)CH3COOH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following acids which has the lowest pKa value?
a)
CH3CH2COOH
b)
(CH3)2 CH - COOH
c)
HCOOH
d)
CH3COOH

|
Anshika Rane answered |
pKa = –log Ka; HCOOH is the strongest acid and hence it has the highest Ka or lowest pKa value.
When CH2 = CH — COOH is reduced with LiAlH4, the compound obtained will be- a)CH2 = CH — CH2OH
- b)CH3 — CH2 — CH2OH
- c)CH3 — CH2 — CHO
- d)CH3 — CH2 — COOH
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
When CH2 = CH — COOH is reduced with LiAlH4, the compound obtained will be
a)
CH2 = CH — CH2OH
b)
CH3 — CH2 — CH2OH
c)
CH3 — CH2 — CHO
d)
CH3 — CH2 — COOH
|
|
Prasad Mehra answered |
Explanation:
Reduction of CH2 = CH — COOH with LiAlH4:
- When CH2 = CH — COOH is reduced with LiAlH4, the carbonyl group (COOH) is reduced to an alcohol group (CH2OH).
- LiAlH4 is a strong reducing agent that can reduce carbonyl groups to alcohols.
Obtained Compound:
- The compound obtained after reduction will be CH2 = CH — CH2OH.
- The double bond remains intact while the carbonyl group is reduced to an alcohol group.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - CH2 = CH — CH2OH.
Reduction of CH2 = CH — COOH with LiAlH4:
- When CH2 = CH — COOH is reduced with LiAlH4, the carbonyl group (COOH) is reduced to an alcohol group (CH2OH).
- LiAlH4 is a strong reducing agent that can reduce carbonyl groups to alcohols.
Obtained Compound:
- The compound obtained after reduction will be CH2 = CH — CH2OH.
- The double bond remains intact while the carbonyl group is reduced to an alcohol group.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'A' - CH2 = CH — CH2OH.
Which of the following compounds will react with ethanolic KCN?- a)ethyl chloride
- b)acetyl chloride
- c)chlorobenzene
- d)benzaldehyde
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds will react with ethanolic KCN?
a)
ethyl chloride
b)
acetyl chloride
c)
chlorobenzene
d)
benzaldehyde

|
Poulomi Datta answered |
The given reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction.
With ethanolic KCN, allyl bromide and ethyl bromide reacts to form nitrile compound. Chlorobenzene and vinyl bromide does not react as they have = bond and the bond is shorter and stronger cann't be replaced by CN group.

The enolic form of acetone contains- a)9 sigma bonds, 1 pi-bond and 2 lone pairs
- b)8 sigma bonds, 2 pi-bonds and 2 lone pairs
- c)10 sigma bonds, 1 pi-bond and 1 lone pair
- d)9 sigma bonds, 2 pi-bonds and 1 lone pair
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The enolic form of acetone contains
a)
9 sigma bonds, 1 pi-bond and 2 lone pairs
b)
8 sigma bonds, 2 pi-bonds and 2 lone pairs
c)
10 sigma bonds, 1 pi-bond and 1 lone pair
d)
9 sigma bonds, 2 pi-bonds and 1 lone pair
|
|
Ameya Mishra answered |
The enolic form of acetone refers to the structure of acetone when it exists in its enol tautomeric form. In this form, one of the carbonyl oxygen atoms in acetone is protonated, resulting in the formation of an enol group (-C=C-OH). Let's break down the structure and analyze the number of sigma bonds, pi-bonds, and lone pairs in the enolic form of acetone.
Structure of the enolic form of acetone:
CH3-C(=C(OH))-CH3
The structure can be divided into three parts: the methyl group (-CH3), the double bond (C=C), and the hydroxyl group (-OH).
Counting sigma bonds:
- The methyl group has three sigma bonds: one C-C bond and two C-H bonds.
- The double bond has one sigma bond between the carbon atoms (C=C).
- The hydroxyl group has three sigma bonds: one C-O bond and two O-H bonds.
Therefore, the total number of sigma bonds in the enolic form of acetone is 3 + 1 + 3 = 7.
Counting pi-bonds:
- The double bond (C=C) consists of one pi bond.
Therefore, the enolic form of acetone has 1 pi-bond.
Counting lone pairs:
- The oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group has two lone pairs.
Therefore, the enolic form of acetone has 2 lone pairs.
Summarizing the results:
- The enolic form of acetone has a total of 7 sigma bonds (3 from the methyl group, 1 from the double bond, and 3 from the hydroxyl group).
- It also has 1 pi-bond (from the double bond) and 2 lone pairs (from the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group).
Hence, option A is the correct answer, as it correctly states that the enolic form of acetone contains 9 sigma bonds (7 from the atoms and 2 from the methyl groups), 1 pi-bond (from the double bond), and 2 lone pairs (from the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group).
Structure of the enolic form of acetone:
CH3-C(=C(OH))-CH3
The structure can be divided into three parts: the methyl group (-CH3), the double bond (C=C), and the hydroxyl group (-OH).
Counting sigma bonds:
- The methyl group has three sigma bonds: one C-C bond and two C-H bonds.
- The double bond has one sigma bond between the carbon atoms (C=C).
- The hydroxyl group has three sigma bonds: one C-O bond and two O-H bonds.
Therefore, the total number of sigma bonds in the enolic form of acetone is 3 + 1 + 3 = 7.
Counting pi-bonds:
- The double bond (C=C) consists of one pi bond.
Therefore, the enolic form of acetone has 1 pi-bond.
Counting lone pairs:
- The oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group has two lone pairs.
Therefore, the enolic form of acetone has 2 lone pairs.
Summarizing the results:
- The enolic form of acetone has a total of 7 sigma bonds (3 from the methyl group, 1 from the double bond, and 3 from the hydroxyl group).
- It also has 1 pi-bond (from the double bond) and 2 lone pairs (from the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group).
Hence, option A is the correct answer, as it correctly states that the enolic form of acetone contains 9 sigma bonds (7 from the atoms and 2 from the methyl groups), 1 pi-bond (from the double bond), and 2 lone pairs (from the oxygen atom in the hydroxyl group).
The compound that does NOT liberate CO2, on treatment with aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution, is- a)Benzoic acid
- b)Benzenesulphonic acid
- c)Salicylic acid
- d)Carbolic acid (Phenol)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound that does NOT liberate CO2, on treatment with aqueous sodium bicarbonate solution, is
a)
Benzoic acid
b)
Benzenesulphonic acid
c)
Salicylic acid
d)
Carbolic acid (Phenol)

|
Siddharth Chaudhary answered |
Carbolic acid (Phenol) is weaker acid than carbonic acid and hence does not liberate CO2 on treatment with aq. NaHCO3 solution.
Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?- a)Acetamide
- b)Acetic acid
- c)Ethyl acetate
- d)Butan-2-one
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following is reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon?
a)
Acetamide
b)
Acetic acid
c)
Ethyl acetate
d)
Butan-2-one
|
|
Siddharth Basak answered |
To determine which compound can be reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon, we need to understand the process of reduction and the properties of the given compounds.
Reduction with Zinc and Hydrochloric Acid:
The reduction of a compound with zinc and hydrochloric acid involves the transfer of hydrogen atoms from the reducing agents (zinc and hydrochloric acid) to the compound, resulting in the formation of a hydrocarbon.
Given Compounds:
a) Acetamide
b) Acetic acid
c) Ethyl acetate
d) Butan-2-one
To identify the compound that can be reduced, we need to consider the presence of functional groups and the reactivity of these functional groups towards reduction.
Acetamide:
Acetamide contains an amide functional group (RCONH2). Amides are not easily reduced by zinc and hydrochloric acid. They require stronger reducing agents or harsher conditions. Therefore, acetamide is not likely to be reduced to a hydrocarbon by zinc and hydrochloric acid.
Acetic Acid:
Acetic acid contains a carboxylic acid functional group (RCOOH). Carboxylic acids can be reduced to aldehydes or alcohols, but they are not directly converted to hydrocarbons by zinc and hydrochloric acid. Therefore, acetic acid is not likely to be reduced to a hydrocarbon in this reaction.
Ethyl Acetate:
Ethyl acetate contains an ester functional group (RCOOR'). Esters can be reduced to alcohols, but they are not directly converted to hydrocarbons by zinc and hydrochloric acid. Therefore, ethyl acetate is not likely to be reduced to a hydrocarbon in this reaction.
Butan-2-one:
Butan-2-one contains a ketone functional group (RCOCH3). Ketones can be reduced to secondary alcohols or further reduced to hydrocarbons by zinc and hydrochloric acid. Therefore, butan-2-one can be reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D) Butan-2-one.
Reduction with Zinc and Hydrochloric Acid:
The reduction of a compound with zinc and hydrochloric acid involves the transfer of hydrogen atoms from the reducing agents (zinc and hydrochloric acid) to the compound, resulting in the formation of a hydrocarbon.
Given Compounds:
a) Acetamide
b) Acetic acid
c) Ethyl acetate
d) Butan-2-one
To identify the compound that can be reduced, we need to consider the presence of functional groups and the reactivity of these functional groups towards reduction.
Acetamide:
Acetamide contains an amide functional group (RCONH2). Amides are not easily reduced by zinc and hydrochloric acid. They require stronger reducing agents or harsher conditions. Therefore, acetamide is not likely to be reduced to a hydrocarbon by zinc and hydrochloric acid.
Acetic Acid:
Acetic acid contains a carboxylic acid functional group (RCOOH). Carboxylic acids can be reduced to aldehydes or alcohols, but they are not directly converted to hydrocarbons by zinc and hydrochloric acid. Therefore, acetic acid is not likely to be reduced to a hydrocarbon in this reaction.
Ethyl Acetate:
Ethyl acetate contains an ester functional group (RCOOR'). Esters can be reduced to alcohols, but they are not directly converted to hydrocarbons by zinc and hydrochloric acid. Therefore, ethyl acetate is not likely to be reduced to a hydrocarbon in this reaction.
Butan-2-one:
Butan-2-one contains a ketone functional group (RCOCH3). Ketones can be reduced to secondary alcohols or further reduced to hydrocarbons by zinc and hydrochloric acid. Therefore, butan-2-one can be reduced with zinc and hydrochloric acid to give the corresponding hydrocarbon.
Therefore, the correct answer is option D) Butan-2-one.
Silver Mirror test is given by which one of the following compounds?- a)Acetaldehyde
- b)Acetone
- c)Formaldehyde
- d)Benzophenone
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Silver Mirror test is given by which one of the following compounds?
a)
Acetaldehyde
b)
Acetone
c)
Formaldehyde
d)
Benzophenone

|
Ipsita Sen answered |
Both for maldeh yde an d a cetaldeh yde give silver mirror with Tollen’s reagent.
Which of the following reagents may be used to distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid?- a)Aqueous NaOH
- b)Tollen’s reagent
- c)Molisch reagent
- d)Neutral FeCl3
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following reagents may be used to distinguish between phenol and benzoic acid?
a)
Aqueous NaOH
b)
Tollen’s reagent
c)
Molisch reagent
d)
Neutral FeCl3

|
Anshika Rane answered |
Phenol gives a violet colour with neutral ferric chloride solution whereas benzoic acid does not give this test.
Statement-1 : Dimethyl sulphide is commonly used for the reduction of an ozonide of an alkene to get the carbonyl compounds.Statement-2 : It reduces the ozonide giving water soluble dimethyl sulphoxide and excess of it evaporates.- a)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 isTrue; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1
- b)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1
- c)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False
- d)Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement-1 : Dimethyl sulphide is commonly used for the reduction of an ozonide of an alkene to get the carbonyl compounds.
Statement-2 : It reduces the ozonide giving water soluble dimethyl sulphoxide and excess of it evaporates.
a)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 isTrue; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1
b)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1
c)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False
d)
Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True.

|
Aryan Sen answered |
TIPS/Formulae : Ozonide can be reduced by (CH3)2S to give carbonyl compounds and dimethyl sulphoxide.
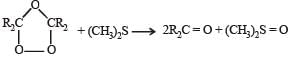
Each of this question contains STATEMENT-1 (Assertion/ Statement ) and STATEMENT-2 (Reason/Explanation) and has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.Q. Statement-1 : Acetate ion is more basic than the methoxide ion.Statement-2 : The acetate ion is resonance stabilized- a)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 isTrue; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1
- b)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1
- c)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False
- d)Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Each of this question contains STATEMENT-1 (Assertion/ Statement ) and STATEMENT-2 (Reason/Explanation) and has 4 choices (a), (b), (c) and (d) out of which ONLY ONE is correct.
Q.
Statement-1 : Acetate ion is more basic than the methoxide ion.
Statement-2 : The acetate ion is resonance stabilized
a)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 isTrue; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1
b)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1
c)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False
d)
Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True.

|
Sanchita Iyer answered |
TIPS/Formulae :
Acetate ion is reasonance stabilized while methoxide ion is not.
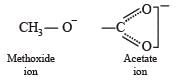
Hence, acetate ion is less basic than methoxide ion.
The increasing order of the rate of HCN addition to compound A – D is(A) HCHO
(B) CH3COCH3
(C) PhCOCH3
(D) PhCOPh- a)D < C < B < A
- b)C < D < B < A
- c)A < B < C < D
- d)D < B < C < A
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The increasing order of the rate of HCN addition to compound A – D is
(A) HCHO
(B) CH3COCH3
(C) PhCOCH3
(D) PhCOPh
(B) CH3COCH3
(C) PhCOCH3
(D) PhCOPh
a)
D < C < B < A
b)
C < D < B < A
c)
A < B < C < D
d)
D < B < C < A

|
Sahana Ahuja answered |
NOTE : Addition of HCN to carbonyl compounds is nucleophilic addition reaction. The order of reactivity of carbonyl compounds is Aldehydes (smaller to higher) Ketones (smaller to higher), Then
HCHO > CH3COCH3 > Ph.COCH3 > PhCOPh
NOTE : The lower reactivity of Ketones is due to presence of two alkyl group which shows +I effect.
The reactivity of Ketones decreases as the size of alkyl group increases.
The reactivity of Ketones decreases as the size of alkyl group increases.
The most suitable reagent for the conversion of R - CH2 - OH → R- CHO is:- a)KMnO4
- b)K2Cr2O7
- c)CrO3
- d)PCC (Pyridinium Chlorochromate)
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The most suitable reagent for the conversion of R - CH2 - OH → R- CHO is:
a)
KMnO4
b)
K2Cr2O7
c)
CrO3
d)
PCC (Pyridinium Chlorochromate)

|
Anshika Rane answered |
An excellent reagent for oxidation of 1° alcohols to aldehydes is PCC.
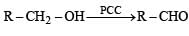
Which one of the following will most readily be dehydrated in acidic condition ?- a)
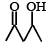
- b)
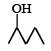
- c)
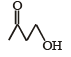
- d)
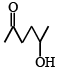
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following will most readily be dehydrated in acidic condition ?
a)
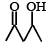
b)
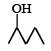
c)

d)
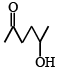
|
|
Baby Ghosh answered |
Yeah..It will be option A...That compund will undergoes readily in acidic medium..because that compound is more stable than other compounds.
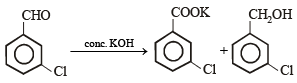
m-Chlorobenzaldehyde on reaction with conc. KOH at room temperature gives- a)potassium m-chlorobenzoate and m-hydroxybenzaldehyde
- b)m-hydroxybenzaldehyde and m-chlorobenzyl alcohol
- c)m-chlorobenzyl alcohol and m-hydroxybenzyl alcohol
- d)potassium m-chlorobenzoate and m-chlorobenzyl alcohol.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
m-Chlorobenzaldehyde on reaction with conc. KOH at room temperature gives
a)
potassium m-chlorobenzoate and m-hydroxybenzaldehyde
b)
m-hydroxybenzaldehyde and m-chlorobenzyl alcohol
c)
m-chlorobenzyl alcohol and m-hydroxybenzyl alcohol
d)
potassium m-chlorobenzoate and m-chlorobenzyl alcohol.

|
Jatin Dasgupta answered |
NOTE : m-Chlobenzaldehyde does not contains α-H atom. It is an example of Cannizzaro reaction
Trichloroacetaldehyde was subjected to Cannizzar o’s reaction by using NaOH. The mixture of the products contains sodium trichloroacetate and another compound. The other compound is :- a)2, 2, 2-Trichloroethanol
- b)Trichloromethanol
- c)2, 2, 2-Trichloropropanol
- d)Chloroform
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Trichloroacetaldehyde was subjected to Cannizzar o’s reaction by using NaOH. The mixture of the products contains sodium trichloroacetate and another compound.
The other compound is :
a)
2, 2, 2-Trichloroethanol
b)
Trichloromethanol
c)
2, 2, 2-Trichloropropanol
d)
Chloroform
|
|
Debanshi Singh answered |
Xidation to give trichloroacetic acid and chloroform.
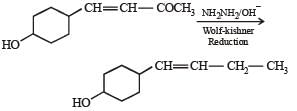
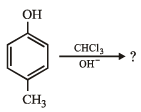
In the given transformation, which of the following is the most appropriate reagent ?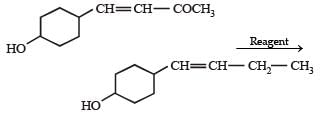
- a)
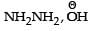
- b)Zn – Hg/ HCl
- c)Na, Liq NH3
- d)NaBH4
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In the given transformation, which of the following is the most appropriate reagent ?

a)
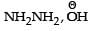
b)
Zn – Hg/ HCl
c)
Na, Liq NH3
d)
NaBH4

|
Ruchi Yadav answered |
Aldehydes and ketones canbereduced to hydrocarbons by the action (i) of amalgamated zinc and concentrated hydrochloric acid (Clemmensen reduction), or (b) of hydrazine (NH2NH2) and a strong base like NaOH, KOH or potassium tert-butoxide in a high-boiling alcohol like ethylene glycol or triethylene glycol (Wolf-Kishner reduction)
Statement-1 : p-Hydroxybenzoic acid has a lower boiling point than o-hydroxybenzoic acid.Statement-2 : o-Hydroxybenzoic acid has intramolecular hydrogen bonding.- a)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 isTrue; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1
- b)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1
- c)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False
- d)Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement-1 : p-Hydroxybenzoic acid has a lower boiling point than o-hydroxybenzoic acid.
Statement-2 : o-Hydroxybenzoic acid has intramolecular hydrogen bonding.
a)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 isTrue; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1
b)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1
c)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False
d)
Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True.

|
Nandita Basak answered |
p-Hydroxybenzoic acid has higher boiling point than o-hydroxybenzoic acid due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding. Thus, statement-1 is false. o-Hydroxybezoic acid shows intramolecular H-bonding thus, statement2 is true.
A mixture of benzaldehyde and formaldehyde on heating with aqueous NaOH solution gives- a)benzyl alcohol and sodium formate
- b)sodium benzoate and methyl alcohol
- c)sodium benzoate and sodium formate
- d)benzyl alcohol and methyl alcohol
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A mixture of benzaldehyde and formaldehyde on heating with aqueous NaOH solution gives
a)
benzyl alcohol and sodium formate
b)
sodium benzoate and methyl alcohol
c)
sodium benzoate and sodium formate
d)
benzyl alcohol and methyl alcohol

|
Jatin Dasgupta answered |
TIPS/Formulae : Both compounds do not contain a-hydrogen hence undergo Crossed Cannizzaro reaction.
Initially OH- attacks at the carbonyl carbon of HCHO than that of PhCHO because carbonyl carbon of HCHO is
(i) more el ectrophilic
(ii) less sterically hindered to give hydroxyalkoxide which acts as hydride donor in next step to give sodium formate.
Initially OH- attacks at the carbonyl carbon of HCHO than that of PhCHO because carbonyl carbon of HCHO is
(i) more el ectrophilic
(ii) less sterically hindered to give hydroxyalkoxide which acts as hydride donor in next step to give sodium formate.
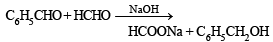
Which of the following compounds will give a yellow precipitate with iodine and alkali?- a)2-Hydroxypropane
- b)acetophenone
- c)methyl acetate
- d)acetamide
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following compounds will give a yellow precipitate with iodine and alkali?
a)
2-Hydroxypropane
b)
acetophenone
c)
methyl acetate
d)
acetamide
|
|
Kajal Iyer answered |
Answer:
Introduction:
In this question, we are asked to determine which of the given compounds will give a yellow precipitate with iodine and alkali. The reaction of iodine with alkali forms a complex, which is typically yellow in color. Let's analyze each compound and determine if it will give a yellow precipitate.
Analysis:
a) 2-Hydroxypropane:
2-Hydroxypropane is an alcohol, which contains a hydroxyl group (-OH). When this compound reacts with iodine and alkali, the hydroxyl group can oxidize to form a carbonyl compound. The carbonyl compound can further react with iodine to form a yellow precipitate. Therefore, 2-Hydroxypropane is expected to give a yellow precipitate.
b) Acetophenone:
Acetophenone is a ketone, which contains a carbonyl group (>C=O). Ketones do not react with iodine and alkali to form a yellow precipitate. Therefore, Acetophenone is not expected to give a yellow precipitate.
c) Methyl acetate:
Methyl acetate is an ester, which contains an ester functional group (-COO-). Esters do not react with iodine and alkali to form a yellow precipitate. Therefore, Methyl acetate is not expected to give a yellow precipitate.
d) Acetamide:
Acetamide is an amide, which contains an amide functional group (-CONH2). Amides do not react with iodine and alkali to form a yellow precipitate. Therefore, Acetamide is not expected to give a yellow precipitate.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, the compounds that are expected to give a yellow precipitate with iodine and alkali are 2-Hydroxypropane and Acetophenone. Therefore, the correct answer is option A and B.
Introduction:
In this question, we are asked to determine which of the given compounds will give a yellow precipitate with iodine and alkali. The reaction of iodine with alkali forms a complex, which is typically yellow in color. Let's analyze each compound and determine if it will give a yellow precipitate.
Analysis:
a) 2-Hydroxypropane:
2-Hydroxypropane is an alcohol, which contains a hydroxyl group (-OH). When this compound reacts with iodine and alkali, the hydroxyl group can oxidize to form a carbonyl compound. The carbonyl compound can further react with iodine to form a yellow precipitate. Therefore, 2-Hydroxypropane is expected to give a yellow precipitate.
b) Acetophenone:
Acetophenone is a ketone, which contains a carbonyl group (>C=O). Ketones do not react with iodine and alkali to form a yellow precipitate. Therefore, Acetophenone is not expected to give a yellow precipitate.
c) Methyl acetate:
Methyl acetate is an ester, which contains an ester functional group (-COO-). Esters do not react with iodine and alkali to form a yellow precipitate. Therefore, Methyl acetate is not expected to give a yellow precipitate.
d) Acetamide:
Acetamide is an amide, which contains an amide functional group (-CONH2). Amides do not react with iodine and alkali to form a yellow precipitate. Therefore, Acetamide is not expected to give a yellow precipitate.
Conclusion:
Based on the analysis, the compounds that are expected to give a yellow precipitate with iodine and alkali are 2-Hydroxypropane and Acetophenone. Therefore, the correct answer is option A and B.
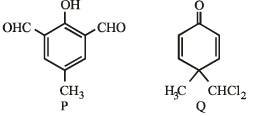
PASSAGE-3Two aliphatic aldehydes P and Q react in the presence of aqueous K2CO3 to give compound R, which upon treatment with HCN provides compound S. On acidification and heating, S gives the product shown below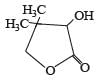 Q. The compounds P and Q respectively are :
Q. The compounds P and Q respectively are :- a)
- b)
- c)
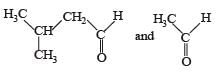
- d)
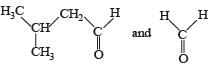
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
PASSAGE-3
Two aliphatic aldehydes P and Q react in the presence of aqueous K2CO3 to give compound R, which upon treatment with HCN provides compound S. On acidification and heating, S gives the product shown below

Q. The compounds P and Q respectively are :
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Sahana Joshi answered |
Let us summarize the given facts of the problem.
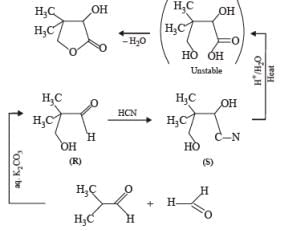
(P & Q)
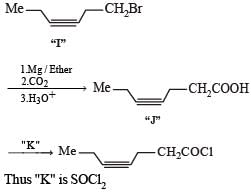
PASSAGE -1In the following reaction sequence, product I, J and L are formed.K represents a reagent.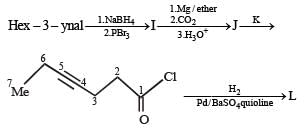 Q.The structure of the product I is –
Q.The structure of the product I is –- a)
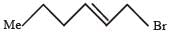
- b)
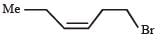
- c)
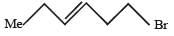
- d)
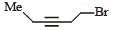
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
PASSAGE -1
In the following reaction sequence, product I, J and L are formed.
K represents a reagent.

Q.The structure of the product I is –
a)

b)
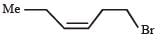
c)

d)
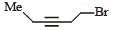

|
Ishita Reddy answered |
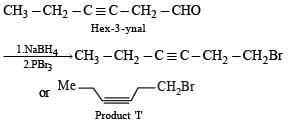
Sodium borohydride reduces –CHO Selectively into –CH2O
PASSAGE-4In the following reaction sequence, the compound J is an intermediate.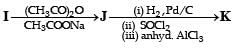 J (C9H8O2) gives effervescence on treatment with NaHCO3 and a positive Baeyer’s test.Q. The compound I is
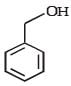
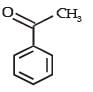
J (C9H8O2) gives effervescence on treatment with NaHCO3 and a positive Baeyer’s test.Q. The compound I is- a)
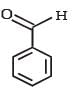
- b)
- c)
- d)
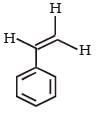
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
PASSAGE-4
In the following reaction sequence, the compound J is an intermediate.
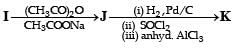
J (C9H8O2) gives effervescence on treatment with NaHCO3 and a positive Baeyer’s test.
Q. The compound I is
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Ishita Reddy answered |
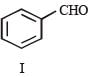
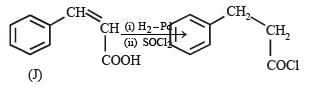
Reactions of compound J (C9H8O2) indicates that it has C = C linkage and – COOH group. Thus, J can be written as C6H5CH = CH COOH. Since, J is unsaturated carboxylic acid and it is formed by the reactions of compound I with (CH3CO)2O and CH3COONa, compound I should be an aldehyde (recall Perkin reaction). Thus the whole series of reactions can be written as below.
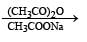
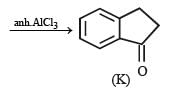
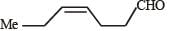
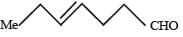
In the following reaction sequence, product I, J and L are formed.K represents a reagent. Q. The structure of product L is
Q. The structure of product L is- a)
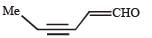
- b)

- c)
- d)
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In the following reaction sequence, product I, J and L are formed.
K represents a reagent.

Q. The structure of product L is
a)
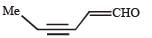
b)

c)

d)


|
Sahana Joshi answered |
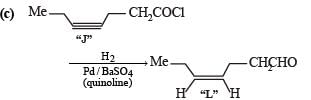
It is Rosemmund reaction. Simultaneously the reagent H2-Pd also reduces carbon-carbon triple bond to double bond (syn -addition) giving cis product.
In Cannizzaro reaction given below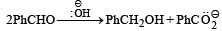 the slowest step is :
the slowest step is :- a)the transfer of hydride to the carbonyl group
- b)the abstraction of proton from the carboxylic group
- c)the deprotonation of Ph CH2OH
- d)the attack of :
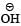 at the carboxyl group
at the carboxyl group
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In Cannizzaro reaction given below
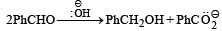
the slowest step is :
a)
the transfer of hydride to the carbonyl group
b)
the abstraction of proton from the carboxylic group
c)
the deprotonation of Ph CH2OH
d)
the attack of : 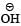 at the carboxyl group
at the carboxyl group
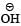 at the carboxyl group
at the carboxyl group

|
Ruchi Yadav answered |
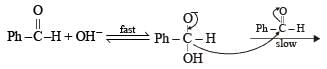

4-Methylbenzenesulphonic acid reacts with sodium acetate to give- a)
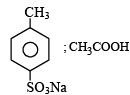
- b)
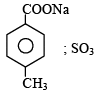
- c)
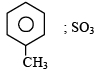
- d)
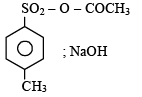
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
4-Methylbenzenesulphonic acid reacts with sodium acetate to give
a)

b)

c)

d)
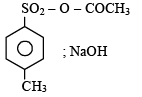

|
Rithika Mishra answered |
This is simply an acid-base reaction.
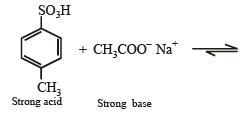
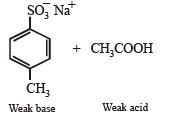
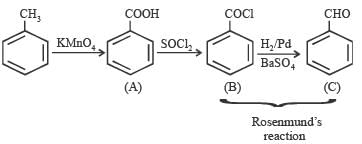
Benzoyl chloride is prepared from benzoic acid by- a)Cl2, hν
- b)SO2Cl2
- c)SOCl2
- d)Cl2, H2O
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Benzoyl chloride is prepared from benzoic acid by
a)
Cl2, hν
b)
SO2Cl2
c)
SOCl2
d)
Cl2, H2O

|
Nilesh Goyal answered |
C6H5 COOH + SOCl2 → C6H5COCl + SO2 + HCl
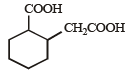
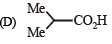
The compound that undergoes decarboxylation most readily under mild condition is- a)
- b)
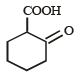
- c)
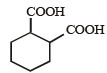
- d)
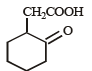
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The compound that undergoes decarboxylation most readily under mild condition is
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Milan Roy answered |
β-Ketoacids undergo decarboxylation easily.
Ethyl ester  The product P will be
The product P will be- a)
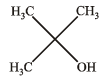
- b)
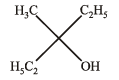
- c)
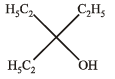
- d)
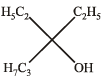
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Ethyl ester  The product P will be
The product P will be
 The product P will be
The product P will bea)
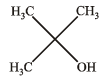
b)
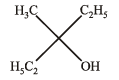
c)

d)


|
Pranav Pillai answered |
Recall that, esters react with excess of Grignard reagents to form 3º alcohols having at least two identical alkyl groups corresponding to Grignard reagent.
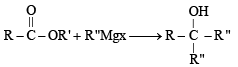
Which of the following will undergo aldol condensation?- a)acetaldehyde
- b)propanaldehyde
- c)benzaldehyde
- d)trideuteroacetaldehyde
Correct answer is option 'A,B,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following will undergo aldol condensation?
a)
acetaldehyde
b)
propanaldehyde
c)
benzaldehyde
d)
trideuteroacetaldehyde

|
Nandini Nair answered |
TIPS/Formulae :
Carbonyl compounds having α – H or α - D undergo aldol condensation.
Carbonyl compounds having α – H or α - D undergo aldol condensation.
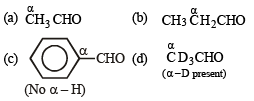
Which of the following are examples of aldol condensation?- a)
- b)
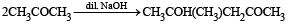
- c)
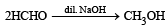
- d)
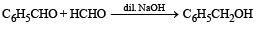
Correct answer is option 'A,B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following are examples of aldol condensation?
a)
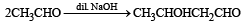
b)
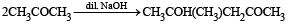
c)
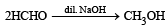
d)
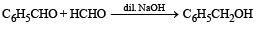

|
Amrita Sarkar answered |
NOTE : Aldehydes and ketones containing a-Hydrogen atom undergo aldol condensation.
An enantiomerically pure acid is treated with a racemic mixture of an alcohol having one chiral carbon. The ester formed will be- a)Optically active mixture
- b)Pure enantiomer
- c)Meso compound
- d)Racemic mixture
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An enantiomerically pure acid is treated with a racemic mixture of an alcohol having one chiral carbon. The ester formed will be
a)
Optically active mixture
b)
Pure enantiomer
c)
Meso compound
d)
Racemic mixture

|
Atharva Pillai answered |
The optically active acid will react with d and l forms of alcohol present in the racemic mixture at different rates to form two diastereomers in unequal amounts leading to optical activity of the product.
Polarisation of electrons in acrolein may be written as- a)
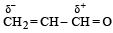
- b)
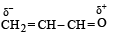
- c)
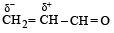
- d)
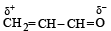
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Polarisation of electrons in acrolein may be written as
a)
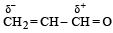
b)
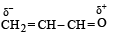
c)
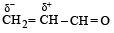
d)
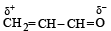

|
Krish Ghoshal answered |
NOTE : –CHO produces –R effect i.e. it withdraws electrons from the double bond or from a conjugated system towards itself.
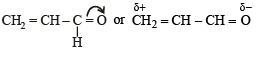
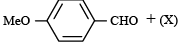
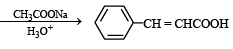 The compound (X) is
The compound (X) is- a)CH3COOH
- b)BrCH2 - COOH
- c)(CH3CO)2O
- d)CHO - COOH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?


The compound (X) is
a)
CH3COOH
b)
BrCH2 - COOH
c)
(CH3CO)2O
d)
CHO - COOH

|
Siddharth Chaudhary answered |
TIPS/Formulae : This reaction is an example of “Perkin reaction”.
The compound X should be (CH3CO)2O.
In this step the carbanion is obtained by removal of an α–H atom from a molecule of an acid anhydride, the anion of the corresponding acid acting as a necessary base.
The compound X should be (CH3CO)2O.
In this step the carbanion is obtained by removal of an α–H atom from a molecule of an acid anhydride, the anion of the corresponding acid acting as a necessary base.
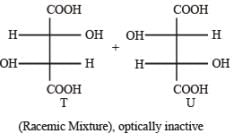
With reference to the scheme given below, which of the given statement(s) about T, U, V and W is (are) correct ?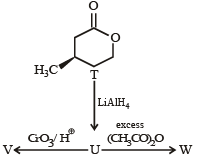
- a)T is soluble in hot aqueous NaOH
- b)U is optically active
- c)Molecular formula of W is C10H18O4
- d)V gives effer vescen ce on treatment with aqueous NaHCO3.
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
With reference to the scheme given below, which of the given statement(s) about T, U, V and W is (are) correct ?

a)
T is soluble in hot aqueous NaOH
b)
U is optically active
c)
Molecular formula of W is C10H18O4
d)
V gives effer vescen ce on treatment with aqueous NaHCO3.

|
Nikhil Sen answered |
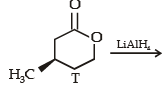
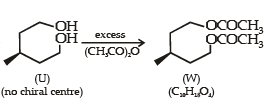
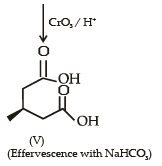
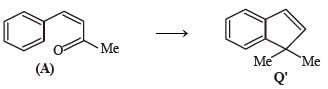
PASSAGE-2A carbonyl compound P, which gives positive iodoform test, undergoes reaction with MeMgBr followed by dehydration to give an olefin Q. Ozonolysis of Q leads to a dicarbonyl compound R, which undergoes intramolecular aldol reaction to give predominantly S.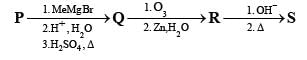 Q. The structures of the products Q and R, respectively, are
Q. The structures of the products Q and R, respectively, are- a)
- b)
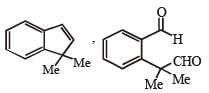
- c)
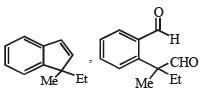
- d)
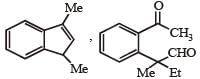
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
PASSAGE-2
A carbonyl compound P, which gives positive iodoform test, undergoes reaction with MeMgBr followed by dehydration to give an olefin Q. Ozonolysis of Q leads to a dicarbonyl compound R, which undergoes intramolecular aldol reaction to give predominantly S.
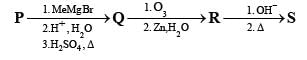
Q. The structures of the products Q and R, respectively, are
a)

b)

c)

d)


|
Aryan Sen answered |
Iodoform test of compound P points out that P has – COCH3 group which shows that it may be either option (a) or (b) of Q. 16. Further since the dicarbonyl compound R has at least one a-H atom w.r.t to one of the carbonyl groups which is possible when R is produced from (b) of Q. 18; (a) option of Q. 16 will give dicarbonyl compound having two –CHO, none of which has a-H atom.
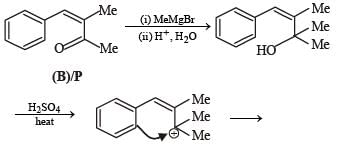
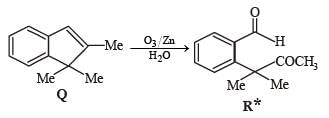
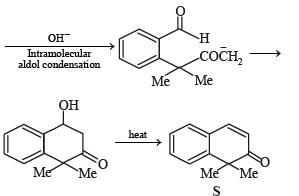
* Structure of R would be R' when P is (A)
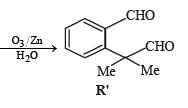
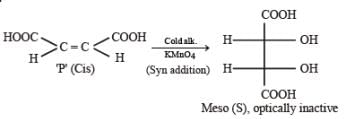
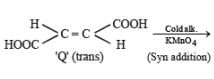
PASSAGE-5P and Q are isomers of dicarboxylic acid C4H4O4. Both decolorize Br2/H2O. On heating, P forms the cyclic anhydride. Upon treatment with dilute alkaline KMnO4, P as well as Q could produce one or more than one from S, T and U.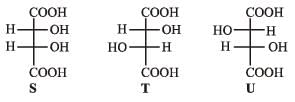
- a)Optically active S an d optically active pair (T, U)
- b)Optically in active S and optically in active pair (T, U)
- c)Optically active pair (T, U) and optically active S
- d)Optically inactive pair (T, U)) and optically inactive S
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
PASSAGE-5
P and Q are isomers of dicarboxylic acid C4H4O4. Both decolorize Br2/H2O. On heating, P forms the cyclic anhydride. Upon treatment with dilute alkaline KMnO4, P as well as Q could produce one or more than one from S, T and U.

a)
Optically active S an d optically active pair (T, U)
b)
Optically in active S and optically in active pair (T, U)
c)
Optically active pair (T, U) and optically active S
d)
Optically inactive pair (T, U)) and optically inactive S

|
Roshni Chavan answered |
Th e correct order of increasing acid stren ght of the compounds(A) CH3CO2H
(B) MeOCH2CO2H
(C) CF3CO2H
 is
is- a)D < A < B < C
- b)A < D < B < C
- c)B < D < A < C
- d)D < A < C < B
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Th e correct order of increasing acid stren ght of the compounds
(A) CH3CO2H
(B) MeOCH2CO2H
(C) CF3CO2H

(B) MeOCH2CO2H
(C) CF3CO2H

is
a)
D < A < B < C
b)
A < D < B < C
c)
B < D < A < C
d)
D < A < C < B

|
Gauri Chauhan answered |
The correct order of increasing acid strength
CF3 . COOH > MeOCH2COOH > CH3COOH > (Me)2CH.COOH
[NOTE : Electron withdrawing groups increase the acid strength and electron donating groups decrease the acid strength.]
Chapter doubts & questions for Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Chemistry 35 Year Past year Papers JEE Main & Advanced 2025 is part of JEE exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids - Chemistry 35 Year Past year Papers JEE Main & Advanced in English & Hindi are available as part of JEE exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup
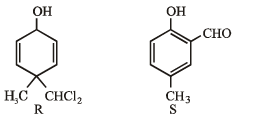
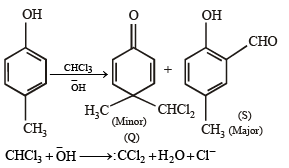
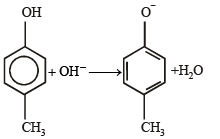
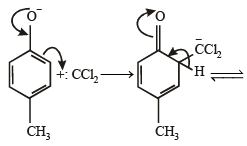
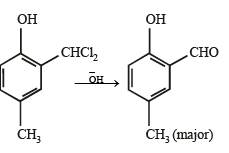
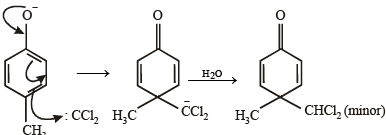

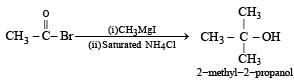
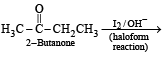
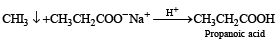
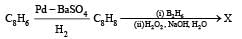
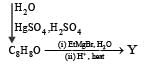
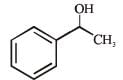
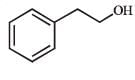
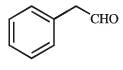

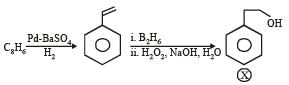
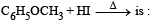
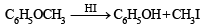
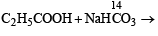
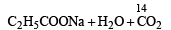
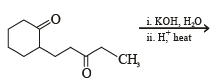
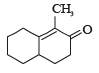
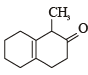
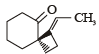
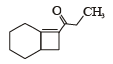
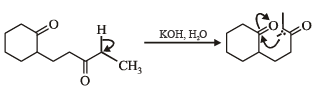
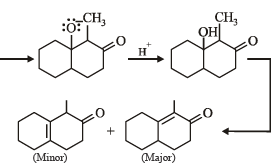
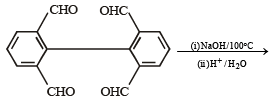
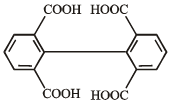
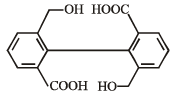
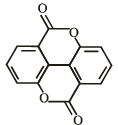
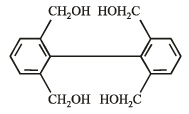
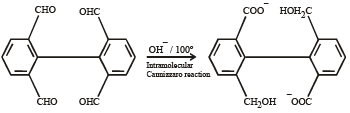
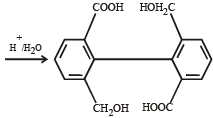
















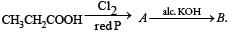 What is B?
What is B?