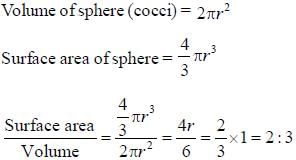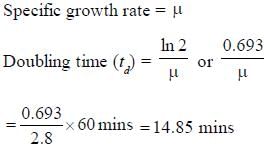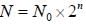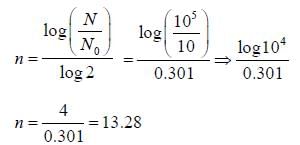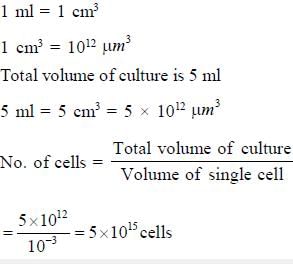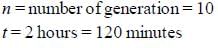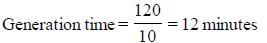All Exams >
Biotechnology Engineering (BT) >
Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026 >
All Questions
All questions of Microbiology for Biotechnology Engineering (BT) Exam
HIV replicates its genome using unique mechanisms. Which of the following statements regarding the same are correct?- a)HIV is an enveloped virus.
- b)The virus contains an RNA dependent DNA polymerase.
- c)A DNA copy of the HIV genome integrates into the host cell DNA.
- d)The virus contains RNA polymerase.
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
HIV replicates its genome using unique mechanisms. Which of the following statements regarding the same are correct?
a)
HIV is an enveloped virus.
b)
The virus contains an RNA dependent DNA polymerase.
c)
A DNA copy of the HIV genome integrates into the host cell DNA.
d)
The virus contains RNA polymerase.
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
HIV is an enveloped virus and contains a RNA dependent DNA polymerase for infection. DNA copy of HIV genome is integrated into host cell DNA.
Gentamycin is an antibiotic, which is produced by- a)Bacillus sp.
- b)Cephalosporin sp.
- c)Micromonospora sp.
- d)Streptomyces sp.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Gentamycin is an antibiotic, which is produced by
a)
Bacillus sp.
b)
Cephalosporin sp.
c)
Micromonospora sp.
d)
Streptomyces sp.
|
|
Aamir Institute answered |
Gentamycin is an antibiotic produced by the bacteria belonging to Micromonospora sp. It inhibits translation by inhibiting 16s rRNA.
In a microbial culture, the maximum synthesis of antibiotics occurs in- a)Stationary phase
- b)Exponential phase
- c)Death phase
- d)Lag phase
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
In a microbial culture, the maximum synthesis of antibiotics occurs in
a)
Stationary phase
b)
Exponential phase
c)
Death phase
d)
Lag phase

|
Lekshmi Deshpande answered |
Maximum synthesis of antibiotics in a microbial culture occurs in stationary phase because in stationary phase, nutrition and space become limitation. So to prevent excess growth in limited resources and in this stress condition, microbes starts producing antibiotics (as a survival mechanism).
If a bacterial culture has a doubling time of 50 minutes then what will be the specific growth rate?- a)0.0125 min-1
- b)0.0138 min-1
- c)0.0235 min-1
- d)0.0135 min-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If a bacterial culture has a doubling time of 50 minutes then what will be the specific growth rate?
a)
0.0125 min-1
b)
0.0138 min-1
c)
0.0235 min-1
d)
0.0135 min-1

|
Anushka Chavan answered |
As specific growth is equal to ln 2/ Doubling time
Specific growth (µ) = 0.693/50
= 0.0138min–1
Specific growth (µ) = 0.693/50
= 0.0138min–1
Which of the following is/are the characteristic(s) of exotoxin?- a)They are secreted out of the cell
- b)They can be converted to toxoids and used as vaccines
- c)They are heat labile, and get inactivated rapidly at 60 to 80ºC
- d)Their chemical nature is lipopolysaccharide
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is/are the characteristic(s) of exotoxin?
a)
They are secreted out of the cell
b)
They can be converted to toxoids and used as vaccines
c)
They are heat labile, and get inactivated rapidly at 60 to 80ºC
d)
Their chemical nature is lipopolysaccharide

|
Anagha Bajaj answered |
Exotoxins are produced by some species of gram positive and gram negative bacteria.
- They are secreted out of the cell
- They are heat labile, and get inactivated rapidly at 60 to 80ºC
- They are polypeptides
- They can be converted to toxoids and used as vaccines.
- They are secreted out of the cell
- They are heat labile, and get inactivated rapidly at 60 to 80ºC
- They are polypeptides
- They can be converted to toxoids and used as vaccines.
Choose the correct statement (s) regarding acid dyes- a)They have negatively charged groups and bind to positively charged cell structures.
- b)They have positively charged groups and bind to negatively charged cell structures.
- c)Eosin and rose bengal are the common examples.
- d)Methylene blue & crystal violet are the common examples.
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct statement (s) regarding acid dyes
a)
They have negatively charged groups and bind to positively charged cell structures.
b)
They have positively charged groups and bind to negatively charged cell structures.
c)
Eosin and rose bengal are the common examples.
d)
Methylene blue & crystal violet are the common examples.

|
Rutuja Sengupta answered |
Acidic dyes have negative charge and bind to positively charged cell structures. Its examples includes eosin, rore bengal & acid fuschin.
Bird flu is caused by- a)H1N1
- b)H5N1
- c)H1H9
- d)H1N16
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bird flu is caused by
a)
H1N1
b)
H5N1
c)
H1H9
d)
H1N16

|
Sahana Roy answered |
Bird flu is caused by the influenza virus subtype H5N1.
Select the disease(s) caused by bacteria.- a)Tetanus
- b)Anthrax
- c)Whooping cough
- d)Meningococcal meningitis
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Select the disease(s) caused by bacteria.
a)
Tetanus
b)
Anthrax
c)
Whooping cough
d)
Meningococcal meningitis

|
Anisha Banerjee answered |
Tetanus is caused by Clostridium tetani
Anthrax is caused by Bacillus anthracis
Whooping cough is caused by Bordetella pertusis
Meningococcal meningitis caused by Bordetella pertusis
Anthrax is caused by Bacillus anthracis
Whooping cough is caused by Bordetella pertusis
Meningococcal meningitis caused by Bordetella pertusis
Which of the following events does not occur during the stationary phase of bacterial growth ?- a)Rise in cell number stops
- b)Cell size increases in some gram –ve bacteria such as E.coli
- c)Decrease in peptidoglycan cross linking
- d)Growth rate of bacterial cells nearly equal their death rate
Correct answer is option 'B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following events does not occur during the stationary phase of bacterial growth ?
a)
Rise in cell number stops
b)
Cell size increases in some gram –ve bacteria such as E.coli
c)
Decrease in peptidoglycan cross linking
d)
Growth rate of bacterial cells nearly equal their death rate

|
Niharika Kulkarni answered |
In stationary phase the cell size does not increase, it remains same and peptidoglycan cross linking also remains the same in stationary phase as the growth rate of cells nearly equal their death rate.
Correct sequence of events that occur during lytic cycle of bacteriophage infection.
P. Synthesis of viral nucleic acid and protein
Q. Release of new viruses by lysis of host cell
R. Attachment of virus on the surface of bacteria
S. Assembly and packaging of new virus
T. Penetration of viral DNA into the host- a)RSTPQ
- b)RTPSQ
- c)STRPQ
- d)TRPSQ
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Correct sequence of events that occur during lytic cycle of bacteriophage infection.
P. Synthesis of viral nucleic acid and protein
Q. Release of new viruses by lysis of host cell
R. Attachment of virus on the surface of bacteria
S. Assembly and packaging of new virus
T. Penetration of viral DNA into the host
P. Synthesis of viral nucleic acid and protein
Q. Release of new viruses by lysis of host cell
R. Attachment of virus on the surface of bacteria
S. Assembly and packaging of new virus
T. Penetration of viral DNA into the host
a)
RSTPQ
b)
RTPSQ
c)
STRPQ
d)
TRPSQ

|
Anisha Pillai answered |
Sequence of events that occur during lytic cycle of bacteriophage infection is,
(i) Virus attaches on to the surface of the host bacterium.
(ii) Penetration of viral DNA into the host
(iii) Synthesis of viral nucleic acid and protein
(iv) Assembly and packaging of new virus
(v) Release of new virus by lysis of the host cell
(i) Virus attaches on to the surface of the host bacterium.
(ii) Penetration of viral DNA into the host
(iii) Synthesis of viral nucleic acid and protein
(iv) Assembly and packaging of new virus
(v) Release of new virus by lysis of the host cell
Mode of action of streptomycin is by- a)preventing formation of 70S ribosomes
- b)inhibiting cell wall synthesis in bacteria
- c)inhibiting peptidyl transferase activity
- d)inhibiting DNA replication in bacteria
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Mode of action of streptomycin is by
a)
preventing formation of 70S ribosomes
b)
inhibiting cell wall synthesis in bacteria
c)
inhibiting peptidyl transferase activity
d)
inhibiting DNA replication in bacteria

|
Ameya Reddy answered |
Streptomycin inhibits translation in prokaryotes by preventing the formation of 70S ribosomes. It acts on the 30S subunit of prokaryotic ribosomes.
Dipicolinic acid is a component of the bacterial- a)Cell wall
- b)Cell membrane
- c)Capsule
- d)Endospore
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Dipicolinic acid is a component of the bacterial
a)
Cell wall
b)
Cell membrane
c)
Capsule
d)
Endospore

|
Jaya Sen answered |
The core of the endospore plays an important role in resistance from various unfavorable conditions. Dipicolinic acid combined with calcium ions is present in the core & plays a part in resistance.
Acid fast staining targets which of the following compound? - a)Teichoic acid in cell wall
- b)Mycolic acid in cell wall
- c)Diaminopimelic acid in cell wall
- d)Dipicolinic acid in cell wall
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Acid fast staining targets which of the following compound?
a)
Teichoic acid in cell wall
b)
Mycolic acid in cell wall
c)
Diaminopimelic acid in cell wall
d)
Dipicolinic acid in cell wall

|
Anisha Pillai answered |
Acid fast staining targets mycolic acid in the cell wall of Mycobacterium species.
Mode of action of penicillin is to inhibit - a)Protein synthesis on 70S ribosomes
- b)Protein synthesis on 8OS ribosomes
- c)Peptidoglycan breakdown
- d)Transpeptidation reaction
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Mode of action of penicillin is to inhibit
a)
Protein synthesis on 70S ribosomes
b)
Protein synthesis on 8OS ribosomes
c)
Peptidoglycan breakdown
d)
Transpeptidation reaction

|
Sravya Mehta answered |
Penicillin inhibits cell wall synthesis in bacteria by inhibiting the process of transpeptidation reaction, which is essential for cell wall synthesis.
The presence of D-amino acids in the cross links of peptidoglycan layer is most likely because- a)D-amino acids fit the structural constrains of the cell wall better than L-amino acids.
- b)Most L-amino acids have already been used for protein synthesis.
- c)D-amino acids are easier to cross link in the absence of ribosomes.
- d)Most peptidases can only cleave L-amino acids.
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The presence of D-amino acids in the cross links of peptidoglycan layer is most likely because
a)
D-amino acids fit the structural constrains of the cell wall better than L-amino acids.
b)
Most L-amino acids have already been used for protein synthesis.
c)
D-amino acids are easier to cross link in the absence of ribosomes.
d)
Most peptidases can only cleave L-amino acids.

|
Anagha Bajaj answered |
D-amino acids are most likely present in cross links of peptidioglycan layer as proteases easily cleave L-amino acids.
0.2 ml of a microbial culture was diluted by adding 9.8ml of buffer to 10 ml. 0.1ml of this was further diluted by adding 9.9 ml of buffer to 10 ml. Plating 0.5 ml from 2nd tube yields 80 colonies. Cell density in original culture was ____________ x 104 cells. (Round off to one decimal place)
Correct answer is between '1.4,1.7'. Can you explain this answer?
0.2 ml of a microbial culture was diluted by adding 9.8ml of buffer to 10 ml. 0.1ml of this was further diluted by adding 9.9 ml of buffer to 10 ml. Plating 0.5 ml from 2nd tube yields 80 colonies. Cell density in original culture was ____________ x 104 cells. (Round off to one decimal place)

|
Rohan Desai answered |
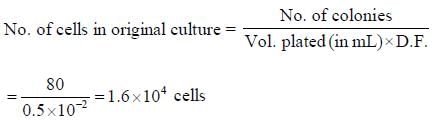
Gram positive cells- a)have a thick homogeneous cell wall.
- b)have large amounts of teichoic acids.
- c)do not contain an outer membrane.
- d)retain crystal violet stain.
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Gram positive cells
a)
have a thick homogeneous cell wall.
b)
have large amounts of teichoic acids.
c)
do not contain an outer membrane.
d)
retain crystal violet stain.

|
Stuti Patel answered |
All the characteristic present in options are correct regarding gram positive cells.
Malachite green is used to stain- a)Capsule
- b)Endospore
- c)Flagella
- d)Acid-fast bacteria
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Malachite green is used to stain
a)
Capsule
b)
Endospore
c)
Flagella
d)
Acid-fast bacteria

|
Vandana Gupta answered |
Bacterial endospores are stained using schaeffer-fulton procedure with malachite green.
Choose the correct statement regarding facultative anaerobes amongst the following- a)They do not require O2 for growth but grows better in its presence.
- b)They grow equally well in presence or absence of O2.
- c)They completely depend on atmospheric O2 for growth.
- d)They do not tolerate O2 and die in its presence.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct statement regarding facultative anaerobes amongst the following
a)
They do not require O2 for growth but grows better in its presence.
b)
They grow equally well in presence or absence of O2.
c)
They completely depend on atmospheric O2 for growth.
d)
They do not tolerate O2 and die in its presence.

|
Athul Chaudhary answered |
Facultative anaerobes are those that does not require O2 for their growth but grows better in the presence of O2.
A subunit of virus protein coat is called as- a)Capsid
- b)Nucleocapsid
- c)Icosahedran
- d)Capsomer
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A subunit of virus protein coat is called as
a)
Capsid
b)
Nucleocapsid
c)
Icosahedran
d)
Capsomer

|
Ishani Dasgupta answered |
The capsomer is a subunit of the capsid , an outer covering of protein that protects the genetic material of a virus. Capsomers self assemble to form the capsid.
Which of the following does not hold true for retroviruses.- a)They replicate through a DNA intermediate
- b)Their genome is ds DNA
- c)They show a property of reverse transcription
- d)Their hosts are mostly animal cells
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following does not hold true for retroviruses.
a)
They replicate through a DNA intermediate
b)
Their genome is ds DNA
c)
They show a property of reverse transcription
d)
Their hosts are mostly animal cells

|
Niharika Choudhary answered |
Genome of retroviruses is single stranded RNA and not ds DNA.
The anti bacterial drug chloramphenicol acts on- a)bacterial cell wall cross-linking
- b)30S ribosomal subunit
- c)50S ribosomal subunit
- d)DNA gyrase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The anti bacterial drug chloramphenicol acts on
a)
bacterial cell wall cross-linking
b)
30S ribosomal subunit
c)
50S ribosomal subunit
d)
DNA gyrase

|
Saanvi Roy answered |
Chloramphenicol binds to 23S rRNA of large ribosomal subunit (50S) to inhibit peptide chain elongation during protein synthesis.
Which of the following is not true for photolithoautotrophic organism.- a)They use CO2 as carbon source
- b)They use sunlight as energy source
- c)They use organic compound as carbon source
- d)They use inorganic compound as H+/e– source
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not true for photolithoautotrophic organism.
a)
They use CO2 as carbon source
b)
They use sunlight as energy source
c)
They use organic compound as carbon source
d)
They use inorganic compound as H+/e– source

|
Om Desai answered |
Photolithoautotrophs are the organisms which use
- CO2 as carbon source (Autotrophs)
- Inorganic ions / compounds as H+/e– source (Litho)
- Sunlight as energy source (Photo)
- CO2 as carbon source (Autotrophs)
- Inorganic ions / compounds as H+/e– source (Litho)
- Sunlight as energy source (Photo)
Creutzfeldt Jacob disease in humans is caused by- a)Viruses
- b)Viriod
- c)Prion
- d)Bacteriu
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Creutzfeldt Jacob disease in humans is caused by
a)
Viruses
b)
Viriod
c)
Prion
d)
Bacteriu
|
|
Chirag Verma answered |
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) is caused by an abnormal infectious protein in the brain called a prion. Proteins are molecules made up of amino acids that help the cells in our body function.
Which of the following disease (s) is/are caused by prions?- a)Kuru disease
- b)Elephantiasis
- c)Legionnaire’s disease
- d)Scrapie disease
Correct answer is option 'A,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following disease (s) is/are caused by prions?
a)
Kuru disease
b)
Elephantiasis
c)
Legionnaire’s disease
d)
Scrapie disease

|
Saanvi Roy answered |
Kuru disease is caused by prions in humans. Scrapie disease is caused by prions in sheep.
Which amongst the following is an example of monotrichous bacteria?- a)Vibrio cholera
- b)S. aureus
- c)E.coli
- d)Salmonella typhi
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which amongst the following is an example of monotrichous bacteria?
a)
Vibrio cholera
b)
S. aureus
c)
E.coli
d)
Salmonella typhi

|
Shivani Mehta answered |
Among given options, S. aureus is non motile and hence does not have flagella, E.coli and S. typhi both have peritrichous arrangement of flagella. Only V. cholera has monotrichous arrangement of flagella.
A bacterium of cocci group has a diameter of 3µm . Calculate the ratio of its surface area to volume (in ) _________(Answer should be an integer)
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
A bacterium of cocci group has a diameter of 3µm . Calculate the ratio of its surface area to volume (in ) _________(Answer should be an integer)
|
|
Vikram Kapoor answered |
Cocci bacterium has spherical shape.
Surface area of sphere = 4ar2
Volume of sphere = 4/3ar2
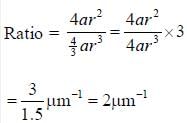
Surface area of sphere = 4ar2
Volume of sphere = 4/3ar2
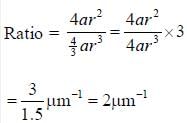
1 ml of microbial culture was diluted to 10ml and 1ml of diluted culture was further diluted by adding 99ml of buffer. 0.5 ml of final culture was plated on to an agar plate. Then, 200 colonies were observed. What was the number of bacteria per ml in the original culture?- a)1 × 105
- b)2 × 104
- c)2 × 105
- d)4 × 105
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
1 ml of microbial culture was diluted to 10ml and 1ml of diluted culture was further diluted by adding 99ml of buffer. 0.5 ml of final culture was plated on to an agar plate. Then, 200 colonies were observed. What was the number of bacteria per ml in the original culture?
a)
1 × 105
b)
2 × 104
c)
2 × 105
d)
4 × 105

|
Stuti Patel answered |
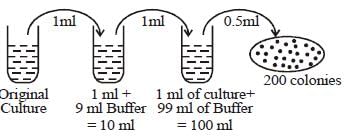
Dilution factor
- 1 ml original diluted to 10ml means 10 times dilution
- 1 ml of diluted culture further diluted to 100 ml means 100 times dilution
Total dilution factor = 1000 times = 10-3
Here. 0.5 ml of final culture contains 200 colonies

5 mL of a culture was added to 45 mL of distilled water. This suspension was further diluted to two serial, 1/100 dilutions. 0.1 mL of this final mixture was plated onto an agar plate. Suppose, an average of 137 colonies appeared on the plate after incubation. The CFU/mL of the original sample is _______ ×108.
Correct answer is between '1.35,1.39'. Can you explain this answer?
5 mL of a culture was added to 45 mL of distilled water. This suspension was further diluted to two serial, 1/100 dilutions. 0.1 mL of this final mixture was plated onto an agar plate. Suppose, an average of 137 colonies appeared on the plate after incubation. The CFU/mL of the original sample is _______ ×108.

|
Srishti Kulkarni answered |
Total dilutions = 5mL sample in 45 mL diluent = 1/10 = 10-1
It is next diluted by1/100 factor. Hence. 10-3.
Further dilution of 1/100 leads to 10-5.
Hence, Dilution factor = 10-5
Volume plated = 0.1 mL
No. of colonies = 137
CFU = ?
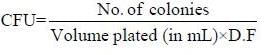
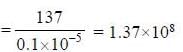
It is next diluted by1/100 factor. Hence. 10-3.
Further dilution of 1/100 leads to 10-5.
Hence, Dilution factor = 10-5
Volume plated = 0.1 mL
No. of colonies = 137
CFU = ?
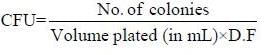
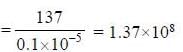
Which of the following statements is/are correct for cyanobacteria ?- a)They can not grow in a mineral medium exposed to light and air
- b)Usually filamentous forms are involved in N2 fixation
- c)They can perform oxygenic photosynthesis
- d)N2 fixation occurs in heterocyst
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following statements is/are correct for cyanobacteria ?
a)
They can not grow in a mineral medium exposed to light and air
b)
Usually filamentous forms are involved in N2 fixation
c)
They can perform oxygenic photosynthesis
d)
N2 fixation occurs in heterocyst

|
Rutuja Choudhary answered |
Cyanobacteria, a group of photosynthetic bacteria can grow easily in a medium exposed to light and air. They perform oxygenic photosynthesis. Some of them are nitrogen fixing in anaerobic conditions but can grow in aerobic conditions.
In which phase of bacterial growth, cryptic growth occurs?- a)Log phase
- b)Lag Phase
- c)Death phase
- d)Stationary phase
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In which phase of bacterial growth, cryptic growth occurs?
a)
Log phase
b)
Lag Phase
c)
Death phase
d)
Stationary phase

|
Athul Menon answered |
Cryptic growth means hidden growth of some of individual cells in a starving bacteria in death phase. The majority of cells do not grow at all in death phase but a few cells are able to multiply because these cells use product of lysis of dying cells.
The properties of an episome includes.- a)They can exist as an independent entity.
- b)They can exist after integration into the host chromosome
- c)They contain tra operon.
- d)They have no role in horizontal gene transfer
Correct answer is option 'A,B,C'. Can you explain this answer?
The properties of an episome includes.
a)
They can exist as an independent entity.
b)
They can exist after integration into the host chromosome
c)
They contain tra operon.
d)
They have no role in horizontal gene transfer

|
Sneha Menon answered |
An episome is that type of plasmid that can exist both, as an independent entity as well as after integrating into the host’s chromosome. They contain tra operon, where genes are responsible for the formation of the sex pili & the transfer of gene. Plasmids are necessary for conjugation (which is a type of horizontal gene transfer)
A bacteria divides after every 45 minutes. If a culture containing 107 cells per ml is grown for 180 minutes, what will be the cell concentration per ml after 180 minutes?- a)1.6 × 108
- b)3.2 × 108
- c)4.8 × 106
- d)128 × 107
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A bacteria divides after every 45 minutes. If a culture containing 107 cells per ml is grown for 180 minutes, what will be the cell concentration per ml after 180 minutes?
a)
1.6 × 108
b)
3.2 × 108
c)
4.8 × 106
d)
128 × 107

|
Aditi Basak answered |
Dividing time is 45 minutes. Total time is 180 minutes
Number of generations after 180 minutes = 180 45 = 4
Now applying the formula
N = N0 x 2n where N = Final number of cells., N0 = Initial number of cells
N = number of generations

Number of generations after 180 minutes = 180 45 = 4
Now applying the formula
N = N0 x 2n where N = Final number of cells., N0 = Initial number of cells
N = number of generations

Match the given substance with the correct method of its sterilization

- a)P-ii, Q-iv, R-i, S-iii
- b)P-ii, Q-i, R-iv, S-iii
- c)P-iv, Q-ii, R-iii, S-i
- d)P-iv, Q-iii, R-i, S-ii
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Match the given substance with the correct method of its sterilization


a)
P-ii, Q-iv, R-i, S-iii
b)
P-ii, Q-i, R-iv, S-iii
c)
P-iv, Q-ii, R-iii, S-i
d)
P-iv, Q-iii, R-i, S-ii

|
Sinjini Singh answered |
Culture media is always autoclaved before using. Serum, being highly heat sensitive is always filtered to remove any microbes. Heat sensitive materials like beer is sterilized by pasteurization. Hormones are cold-sterilized using gamma-radiation.
Whopping cough is caused by- a)Helicobacter pylori
- b)Haemophilus aegyptius
- c)Bordetella pertusis
- d)Campylobacter jejuni.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Whopping cough is caused by
a)
Helicobacter pylori
b)
Haemophilus aegyptius
c)
Bordetella pertusis
d)
Campylobacter jejuni.

|
Akash Kulkarni answered |
Causes. Pertussis, a respiratory illness commonly known as whooping cough, is a very contagious disease caused by a type of bacteria called Bordetella pertussis. These bacteria attach to the cilia (tiny, hair-like extensions) that line part of the upper respiratory system.
Plasmids are functionally involved in which of the following?- a)Transduction
- b)Synthesis of pili
- c)Transfer of chromosomal genes
- d)Transfer of drug resistance.
Correct answer is option 'B,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Plasmids are functionally involved in which of the following?
a)
Transduction
b)
Synthesis of pili
c)
Transfer of chromosomal genes
d)
Transfer of drug resistance.

|
Stuti Patel answered |
The tra genes present in the plasmid are responsible for the formation of sex pili & the transfer of chromosomal genes from F+/Hfr/F’ cells to F- cells. The transfer of a copy of resistance plasmid results in the transfer of drug resistance genes as well. Transduction is mediated by virus and their is no role of plasmid in transduction.
Find out the mismatch from the following.- a)

- b)

- c)

- d)
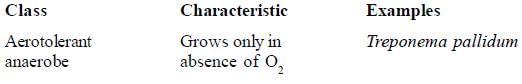
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Find out the mismatch from the following.
a)

b)

c)

d)
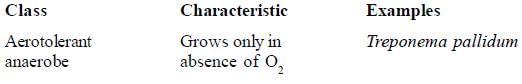
|
|
Umesh Singh answered |
Aerotolerant anaerobes grow equally well in the presence or absence of oxygen, eg. Streptococcus pyrogenes.
Chapter doubts & questions for Microbiology - Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026 2025 is part of Biotechnology Engineering (BT) exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the Biotechnology Engineering (BT) exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for Biotechnology Engineering (BT) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Microbiology - Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026 in English & Hindi are available as part of Biotechnology Engineering (BT) exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Biotechnology Engineering (BT) Exam by signing up for free.
Mock Test Series of IIT JAM Biotechnology 2026
7 docs|34 tests
|

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily