All Exams >
NEET >
Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Thermodynamics for NEET Exam
Consider the following properties.  Select intensive and extensive properties.
Select intensive and extensive properties.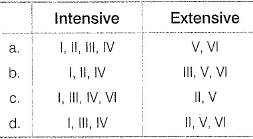
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following properties.
Select intensive and extensive properties.
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Preeti Khanna answered |
Intensive means that the property is mass independent. We can see that Boiling point, pH, EMF of cell and surface tension are intensive pont .
While Extensive property depends on mass and in given options Volume and entropy are mass dependents.
While Extensive property depends on mass and in given options Volume and entropy are mass dependents.
One mole each of CaC2, AI4C3 and Mg2C3 reacts with H2O in separate open flasks at 25° C. Numerical value of the work done by the system is in order- a)CaC2 < AI4C3 = Mg2C3
- b)CaC2 < AI4C3 < Mg2C3
- c)CaC2 = Mg2C3 < AI4C3
- d)CaC2 = Mg2C3 = AI4C3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
One mole each of CaC2, AI4C3 and Mg2C3 reacts with H2O in separate open flasks at 25° C. Numerical value of the work done by the system is in order
a)
CaC2 < AI4C3 = Mg2C3
b)
CaC2 < AI4C3 < Mg2C3
c)
CaC2 = Mg2C3 < AI4C3
d)
CaC2 = Mg2C3 = AI4C3

|
Ciel Knowledge answered |
i) CaC2 + 2H2O → C2H2(g) + Ca(OH)2
ii) Mg2C3 + 4H2O → CH3-C≡CH(g) + 2Mg(OH)2
iii) Al4C3 + 12H2O → 3CH4(g) + 4Al(OH)3
Work done = -∆ngRT
Or W ∝ ∆ng
Wecan see that in case iii) we have maximum no of moles in the product side(∆ng = 3). So work done will be maximum in case iii). After that in i) and ii), we have the same number of moles on the product side(∆ng = 1), so work done will be the same.
Therefore, option c is correct.
ii) Mg2C3 + 4H2O → CH3-C≡CH(g) + 2Mg(OH)2
iii) Al4C3 + 12H2O → 3CH4(g) + 4Al(OH)3
Work done = -∆ngRT
Or W ∝ ∆ng
Wecan see that in case iii) we have maximum no of moles in the product side(∆ng = 3). So work done will be maximum in case iii). After that in i) and ii), we have the same number of moles on the product side(∆ng = 1), so work done will be the same.
Therefore, option c is correct.
A reaction occurs spontaneously if [2005]a) TΔS < ΔH and both ΔH and ΔS are + veb) TΔS > ΔH an d ΔH is + ve and ΔS is -vec) TΔS > ΔH and both ΔH and ΔS are + ved) TΔS = ΔH and both ΔH and ΔS are + veCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?

|
Abhishek Choudhary answered |
For a spontaneous reaction ΔG(–ve), which is possible if ΔS = +ve, ΔH = +ve and TΔS > ΔH [As ΔG = ΔH – TΔS]
Specific heat of water is 4.184 JK-1g-1, Rise in temperature when 1 kJ of heat is absorbed by 2 moles of H2O is- a)119.5o
- b)0.37o
- c)0.12o
- d)6.64o
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Specific heat of water is 4.184 JK-1g-1, Rise in temperature when 1 kJ of heat is absorbed by 2 moles of H2O is
a)
119.5o
b)
0.37o
c)
0.12o
d)
6.64o
|
|
Rajesh Gupta answered |
We have,
Q = ms∆T
1000 = 2*18*4.184*∆T
∆T = 6.63 K
Q = ms∆T
1000 = 2*18*4.184*∆T
∆T = 6.63 K
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 - 18) This section contains 3 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).Q. Temperature of one mole of an ideal gas is increased by 1° at constant pressure. What is mechanical work done (in cals)?
Correct answer is '2'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 16 - 18) This section contains 3 questions. when worked out will result in an integer from 0 to 9 (both inclusive).
Q. Temperature of one mole of an ideal gas is increased by 1° at constant pressure. What is mechanical work done (in cals)?
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
From ideal gas equation
PV=nRT
hence PV=W
W = nR∆T
W = 1×2×1 = 2cal
PV=nRT
hence PV=W
W = nR∆T
W = 1×2×1 = 2cal
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Five moles of an ideal gas at 27° C are allowed to expand isothermally from an initial pressure of 10.0 atm to a final pressure of 4.0 atm against a constant external pressure of 1.0 atm. Thus, work done will be
- A:
- 1870.6 J
- B:
- 1870.6J
- C:
-18.47 J
- D:
+18.47 J
The answer is a.
Five moles of an ideal gas at 27° C are allowed to expand isothermally from an initial pressure of 10.0 atm to a final pressure of 4.0 atm against a constant external pressure of 1.0 atm. Thus, work done will be
- 1870.6 J
- 1870.6J
-18.47 J
+18.47 J
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
Work done during isothermal irreversible process is given by the formula w = -pext (nrt/p2-nrt/p1)
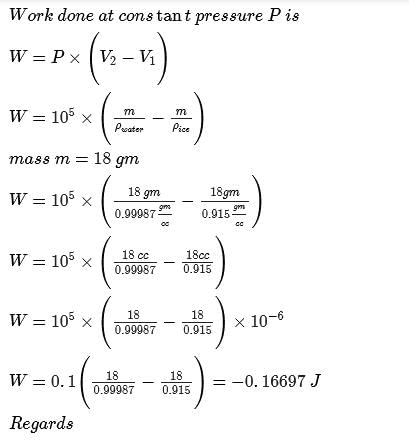
Bond energy of (N— H)bond is x kJ mol-1 under standard state. Thus, change in internal energy in the following process is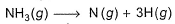
- a)x kJ mol-1
- b)3x kJ mol-1
- c)- x kJ mol-1
- d)- 3x kJ mol-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Bond energy of (N— H)bond is x kJ mol-1 under standard state. Thus, change in internal energy in the following process is
a)
x kJ mol-1
b)
3x kJ mol-1
c)
- x kJ mol-1
d)
- 3x kJ mol-1

|
EduRev Humanities answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
H−N−H (three N-H) bonds
∣
H
Thus, ΔE=3xKJmol-1
H−N−H (three N-H) bonds
∣
H
Thus, ΔE=3xKJmol-1
What happens to the ions, when an ionic compound dissolves in a solvent?- a)They leave their ordered position in the crystal lattice and gets hydrated.
- b)They leave their ordered position in the crystal lattice and doesn’t hydrate.
- c)They doesn’t leave their ordered position in the crystal lattice and gets hydrated.
- d)None of the above.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
What happens to the ions, when an ionic compound dissolves in a solvent?
a)
They leave their ordered position in the crystal lattice and gets hydrated.
b)
They leave their ordered position in the crystal lattice and doesn’t hydrate.
c)
They doesn’t leave their ordered position in the crystal lattice and gets hydrated.
d)
None of the above.
|
|
Pooja Shah answered |
When an ionic compound is dissolved in the solvent, the compound dissociate into ions and due to external medium i. e. solvent it leave its original position in crystal lattice n gets hydrated..
Eg. NaCl(aq) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
Eg. NaCl(aq) → Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq)
The equilibrium constant for a reaction is 10. Calculate the value of ΔG° at 300K , R = R =8.314 JK−1mol−1
- a)-5.527 kJ/mol–
- b)4.744 kJ/mol
- c)-4.744 kJ/mol–
- d)- 5.744 kJ/mol
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The equilibrium constant for a reaction is 10. Calculate the value of ΔG° at 300K , R = R =8.314 JK−1mol−1
a)
-5.527 kJ/mol–
b)
4.744 kJ/mol
c)
-4.744 kJ/mol–
d)
- 5.744 kJ/mol

|
Infinity Academy answered |
The value of equilibrium constant(k) = 10
∆G° = -2.303RTlogk
On calculating values, we will get ∆G° = -5.744kJmol-1
∆G° = -2.303RTlogk
On calculating values, we will get ∆G° = -5.744kJmol-1
A gas absorbs 200 J of heat and expands by 500 cm3 against a constant pressure of 2 x 105 Nm-2. Change in internal energy is - a)- 300 J
- b)- 100 J
- c)+100 J
- d)+300 J
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
A gas absorbs 200 J of heat and expands by 500 cm3 against a constant pressure of 2 x 105 Nm-2. Change in internal energy is
a)
- 300 J
b)
- 100 J
c)
+100 J
d)
+300 J
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The expression for the change in internal energy is given by,
ΔU=q+w
q = heat absorbed = 200 J
w = work done = −P x V
=−2×10⁵ × 500×10−6
= −100 N - m
ΔU=200−100J= 100 J
Hence, the correct option is C.
ΔU=q+w
q = heat absorbed = 200 J
w = work done = −P x V
=−2×10⁵ × 500×10−6
= −100 N - m
ΔU=200−100J= 100 J
Hence, the correct option is C.
In an endothermic reaction, the value of ΔH is always- a)Constant
- b)> 0
- c)< 0
- d)= 0
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
In an endothermic reaction, the value of ΔH is always
a)
Constant
b)
> 0
c)
< 0
d)
= 0
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
According to me, for an endothermic reaction ,the value of ∆H is always >0 .
A cyclic proces ABCD is shown in PV diagram for an ideal gas.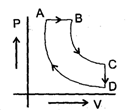 Which of the following diagram represents the same process
Which of the following diagram represents the same process- a)
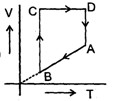
- b)
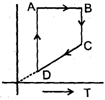
- c)
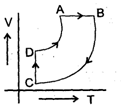
- d)
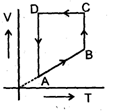
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A cyclic proces ABCD is shown in PV diagram for an ideal gas.
Which of the following diagram represents the same process
a)
b)
c)
d)
|
|
Raghav Bansal answered |
In such type of graph conversions, the best way to work is to make a parameter constant and then derive the results between others.
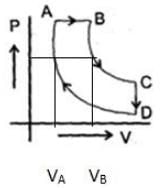
Let us make pressure constant. Then we have, VB>VA
Or
(nrTA/P)<(nrTB/P) or TA<TB
In terms of V-T curve, the thing happens as follow:-
A to B (Volume increase from VA to VB. No change in pressure). B to C (temperature is constant), C to D (Volume remains constant) and D to A (Volume decreases but temperature remains constant. However the constant value is less than from B to C). On these all conditions, only graph d stands.
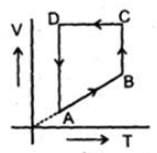

Let us make pressure constant. Then we have, VB>VA
Or
(nrTA/P)<(nrTB/P) or TA<TB
In terms of V-T curve, the thing happens as follow:-
A to B (Volume increase from VA to VB. No change in pressure). B to C (temperature is constant), C to D (Volume remains constant) and D to A (Volume decreases but temperature remains constant. However the constant value is less than from B to C). On these all conditions, only graph d stands.

For the following process, H2 (g) → 2 H(g), it absorbs 436 kJ mol-1. Thus,
- a)internal energy of the system is 436 kJ mol-1
- b)change in internal energy is 436 kJ mol-1
- c)internal energy of the system is 218 kJ mol-1
- d)change in internal energy of the system is 218 kJ mol-1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
For the following process, H2 (g) → 2 H(g), it absorbs 436 kJ mol-1. Thus,
a)
internal energy of the system is 436 kJ mol-1
b)
change in internal energy is 436 kJ mol-1
c)
internal energy of the system is 218 kJ mol-1
d)
change in internal energy of the system is 218 kJ mol-1
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
In this process, one molecule of hydrogen gas dissociated into two gaseous atoms i.e. the number of gaseous particles increase leading to a more disordered state.
.Breaking of bond requires energy
.Breaking of bond requires energy
It is not mentioned that the process is isobaric. If we assume that process is isobaric because volume can not remain constant as number of gaseous particles are increased, then change in internal energy = 436 kJ mol-1. The data of absorption gives us the value of q.
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 15 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.Q. Assign the sign of work done (based on SI convention) in the following chemical changes taking place against external atmospheric pressure :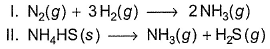
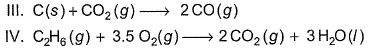

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 1-15) This section contains 15 multiple choice questions. Each question has four choices (a), (b), (c) and (d), out of which ONLY ONE option is correct.
Q. Assign the sign of work done (based on SI convention) in the following chemical changes taking place against external atmospheric pressure :
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Lavanya Menon answered |
Work done = - (change in moles) RT For work done positive change in moles negative and vice versa We only cosider the moles that are in gass phase.
Standard entropies of X2, Y2 and XY3 are given below the reaction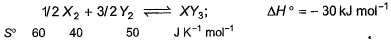 Q. At what temperature, reaction would be in equilibrium?
Q. At what temperature, reaction would be in equilibrium? - a)500 K
- b)750 K
- c)1000 K
- d)1250 K
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Standard entropies of X2, Y2 and XY3 are given below the reaction
Q. At what temperature, reaction would be in equilibrium?
a)
500 K
b)
750 K
c)
1000 K
d)
1250 K
|
|
Suresh Reddy answered |
1/2X2 + 3/2Y2 ⟶XY3,
ΔH= −30 kJ
ΔSreaction = ∑ΔSproduct−∑ΔSreactant
X2 + 3Y2 → 2XY3
ΔH=−60 kJ
ΔSreaction = 2×50−3×40−1×60 =100−120−60=−80 JK−1mol−1
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS=0
ΔH=TΔS
1000×(−60)=−80×T
T=750 K
ΔH= −30 kJ
ΔSreaction = ∑ΔSproduct−∑ΔSreactant
X2 + 3Y2 → 2XY3
ΔH=−60 kJ
ΔSreaction = 2×50−3×40−1×60 =100−120−60=−80 JK−1mol−1
ΔG=ΔH−TΔS=0
ΔH=TΔS
1000×(−60)=−80×T
T=750 K
Consider the following properties.
 State functions are : [IITJEE2009]
State functions are : [IITJEE2009]
- a)I, II, III, IV, V
- b)I, II, III, VI
- c)I, II, IV, VI
- d)I, II, III, IV
Correct answer is option `A`. Can you explain this answer?
Consider the following properties.
State functions are : [IITJEE2009]
a)
I, II, III, IV, V
b)
I, II, III, VI
c)
I, II, IV, VI
d)
I, II, III, IV
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
First 4 are fundamental examples of state functions as they are path independent. Since reversible expansion depends on the path followed by process, so it is a path function. However, irreversible expansion work is independent of the path and so, it is a state function.
8 g of O2 gas at STP is expanded so that volume is doubled. Thus, work done is- a)22.4 L atm
- b)11.2 L atm
- c)5.6 L atm
- d)- 5.6 L atm
Correct answer is 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
8 g of O2 gas at STP is expanded so that volume is doubled. Thus, work done is
a)
22.4 L atm
b)
11.2 L atm
c)
5.6 L atm
d)
- 5.6 L atm

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
Let atomic weight of x = Mx
atomic weight of y = My
atomic weight of y = My
we know,
mole = weight /atomic weight
a/c to question,
mole = weight /atomic weight
a/c to question,
mole of xy2 = 0.1
so,
0.1 = 10g/( Mx +2My)
so,
0.1 = 10g/( Mx +2My)
Mx + 2My = 100g -------(1)
for x3y2 ; mole of x3y2 = 0.05
0.05 = 9/( 3Mx + 2My )
3Mx + 2My = 9/0.05 = 9 × 20 = 180 g ---(2)
solve eqns (1) and (2)
solve eqns (1) and (2)
2Mx = 80
Mx = 40g/mol
Mx = 40g/mol
and My = 30g/mole
From the following data, the heat of formation of Ca(OH)2(s) at 18°C is ………..kcal: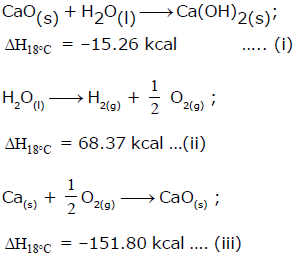
- a)-98.69
- b)-235.43
- c)194.91
- d) 98.69
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
From the following data, the heat of formation of Ca(OH)2(s) at 18°C is ………..kcal:
a)
-98.69
b)
-235.43
c)
194.91
d)
98.69

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
The correct answer is Option B.
Ca(s) + O2(g) + H2(g) → Ca(OH)2 , ΔHf = ?
Desired equation = eq (iii) + eq(i) - eq (ii)
ΔHf = (−151.80)+(−15.26)−(−68.37)
ΔHf = (-151.80)+(-15.26)-(-68.37)
ΔHf = −235.43KCalmol−1
ΔHf = (-151.80)+(-15.26)-(-68.37)
ΔHf = −235.43KCalmol−1
The heat capacity ratio, r was determined for cyanogen as 1.177. Thus, Cp for this gas is- a)55.3 JK-1 mol-1
- b)33.26 JK-1 mol-1
- c)8.314 JK-1 mol-1
- d)24.94 JK-1 mol-1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
The heat capacity ratio, r was determined for cyanogen as 1.177. Thus, Cp for this gas is
a)
55.3 JK-1 mol-1
b)
33.26 JK-1 mol-1
c)
8.314 JK-1 mol-1
d)
24.94 JK-1 mol-1
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
γ = 1.177
CV = R/γ-1
= 8.314/0.177 = 46.97
Also γ = CP/CV
1.177 = CP/46.97
Or CP = 55.28
CV = R/γ-1
= 8.314/0.177 = 46.97
Also γ = CP/CV
1.177 = CP/46.97
Or CP = 55.28
Direction (Q. Nos. 19-20) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).The following diagram represents the (p-V) changes of a gas.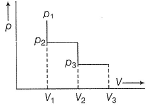 Select isochoric changes
Select isochoric changes- a)when pressure changes from p1 to p2
- b)when pressure changes from p2 to p3
- c)when pressure changes from p1 to p3
- d)when pressure changes from p3 to p1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Direction (Q. Nos. 19-20) This section contains a paragraph, wach describing theory, experiments, data etc. three Questions related to paragraph have been given.Each question have only one correct answer among the four given options (a),(b),(c),(d).
The following diagram represents the (p-V) changes of a gas.
Select isochoric changes
a)
when pressure changes from p1 to p2
b)
when pressure changes from p2 to p3
c)
when pressure changes from p1 to p3
d)
when pressure changes from p3 to p1
|
|
Geetika Shah answered |
Isochoric change is one in which volume doesn't change(remains constant) From P1 to P2 , volume is constant(V1) (also work done = 0)
One mole of an ideal gas is put through a series of changes as shown in the figure in which 1,2,3 mark the three stages of the system. Pressure at the stages 1, 2, and 3 respectively will be (in bar)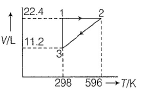

- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One mole of an ideal gas is put through a series of changes as shown in the figure in which 1,2,3 mark the three stages of the system. Pressure at the stages 1, 2, and 3 respectively will be (in bar)
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Applying ideal gas eqn. at 1
p×22.4 = 1×0.0821×298 (since vol. Is in L. R should haave constaant with lit in it.)
p = 1.09 atm. To convert it into bar, we multiply it by 1.01 or we have 1.03 bar
Similarly at 2 and 3, we get value of pressure at 2 and 3.
The most closest answer is option d
p×22.4 = 1×0.0821×298 (since vol. Is in L. R should haave constaant with lit in it.)
p = 1.09 atm. To convert it into bar, we multiply it by 1.01 or we have 1.03 bar
Similarly at 2 and 3, we get value of pressure at 2 and 3.
The most closest answer is option d
Among the following enthalpies, which is always less than zero?- a)ΔcH°
- b)ΔsubH°
- c)ΔmixH°
- d)ΔfH°
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Among the following enthalpies, which is always less than zero?
a)
ΔcH°
b)
ΔsubH°
c)
ΔmixH°
d)
ΔfH°
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
The symbol represents enthalpy of combustion which is always exothermic. For exothermic rxn delta H is always -ve.
An ideal gas expands in volume from 1 x 10-3 m3 to 1 x 10-2 m2 at 300 K against a constant pressure of 1 x 105 Nm-2. The work done is[AIEEE 2004]- a)- 900 J
- b)- 900 KJ
- c)270 KJ
- d)+900 KJ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
An ideal gas expands in volume from 1 x 10-3 m3 to 1 x 10-2 m2 at 300 K against a constant pressure of 1 x 105 Nm-2. The work done is
[AIEEE 2004]
a)
- 900 J
b)
- 900 KJ
c)
270 KJ
d)
+900 KJ
|
|
Naina Bansal answered |
Work done due to change in volume against constant pressure is
W = - p(V2-V1)
= - 1 x 10^5 Nm^-2 (1 x 10^-2- 1 x 10^-3)m^3
For an endothermic reaction when ΔH represents the enthalpy of the reaction in kJ mol-1, the minimum value for the energy of activation will be[IIT JEE 1992]- a)less than ΔH
- b)Zero
- c)More than ΔH
- d)Equal to ΔH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
For an endothermic reaction when ΔH represents the enthalpy of the reaction in kJ mol-1, the minimum value for the energy of activation will be
[IIT JEE 1992]
a)
less than ΔH
b)
Zero
c)
More than ΔH
d)
Equal to ΔH
|
|
Hansa Sharma answered |
,More than ΔH
In endothermic reactions, the energy of reactants is less than that of the products. Potential energy diagram for endothermic reactions is,
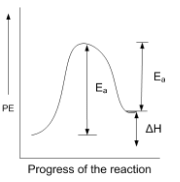
Where Ea = activation energy of forwarding reaction
Ea' = activation energy of backwards reaction
ΔH = enthalpy of the reaction
From the above diagram,
Ea = Ea' + ΔH
Thus, Ea > ΔH
The reaction CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g) has ΔH = -25 kCal.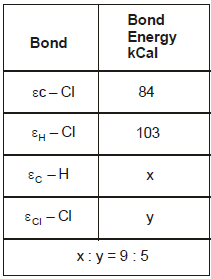 From the given data, what is the bond energy of Cl - Cl bond
From the given data, what is the bond energy of Cl - Cl bond- a)70 kCal
- b)80 kCal
- c) 67.75 kCal
- d) 57.75 kCal
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The reaction CH4(g) + Cl2(g) → CH3Cl(g) + HCl(g) has ΔH = -25 kCal.
From the given data, what is the bond energy of Cl - Cl bond
a)
70 kCal
b)
80 kCal
c)
67.75 kCal
d)
57.75 kCal

|
Kamna Science Academy answered |
During bond breakage energy is absorbed and during bond formation it is released. From the reaction we can say that 1 C-H bond is broken 1 Cl-Cl bond is broken 1 c-cl bond is formed and 1 h-cl bond is formed. so using the sign conventions the equation becomes
x+y-84-103= -25 (∆H = -25)
5x=9y ..putting x=9/5y we get y = 57.75 kCal
x+y-84-103= -25 (∆H = -25)
5x=9y ..putting x=9/5y we get y = 57.75 kCal
NH3(g) + 3Cl2(g)  NCl3(g) + 3HCl(g) ; -ΔH1N2(g) + 3H2(g)
NCl3(g) + 3HCl(g) ; -ΔH1N2(g) + 3H2(g)  2NH3(g) ; ΔH2H2(g) + Cl2(g)
2NH3(g) ; ΔH2H2(g) + Cl2(g) 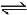 2HCl(g) ; ΔH3The heat of formation of NCl3 (g) in the terms of ΔH1, ΔH2 and ΔH3 is
2HCl(g) ; ΔH3The heat of formation of NCl3 (g) in the terms of ΔH1, ΔH2 and ΔH3 is- a)
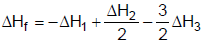
- b)
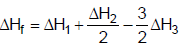
- c)
- d) None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
NH3(g) + 3Cl2(g) 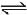 NCl3(g) + 3HCl(g) ; -ΔH1
NCl3(g) + 3HCl(g) ; -ΔH1
N2(g) + 3H2(g) 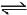 2NH3(g) ; ΔH2
2NH3(g) ; ΔH2
H2(g) + Cl2(g) 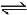 2HCl(g) ; ΔH3
2HCl(g) ; ΔH3
The heat of formation of NCl3 (g) in the terms of ΔH1, ΔH2 and ΔH3 is
a)
b)
c)
d)
None
|
|
Naina Sharma answered |
The formation of NCl3 be like
½ N2 + 3/2Cl2 ⇋ NCl3
We can see that for this setup, we need to have eqn (ii) divided by 2, reversing eqn (iii) and multiplying it by 3/2 and then adding all these to equation (i).
So option a is correct.
½ N2 + 3/2Cl2 ⇋ NCl3
We can see that for this setup, we need to have eqn (ii) divided by 2, reversing eqn (iii) and multiplying it by 3/2 and then adding all these to equation (i).
So option a is correct.
Heat of combustion ΔHº for C (s), H2(g) and CH4(g) are –94, –68 and –213 kcal/mol, then ΔHº for C(s) + 2H2(g) → CH4(g) is [2002]- a)–17 kcal
- b)– 111 kcal
- c)–170 kcal
- d)–85 kcal
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Heat of combustion ΔHº for C (s), H2(g) and CH4(g) are –94, –68 and –213 kcal/mol, then ΔHº for C(s) + 2H2(g) → CH4(g) is [2002]
a)
–17 kcal
b)
– 111 kcal
c)
–170 kcal
d)
–85 kcal

|
Savita Soni answered |
∆Hcomb.= Reactant - product
so -94-68×2(because there are 2moles of H2)-(-213)
∆Hcomb.= -17 kcal
so -94-68×2(because there are 2moles of H2)-(-213)
∆Hcomb.= -17 kcal
During complete combustion of one mole of butane, 2658 kJ of heat is released. The thermochemical reaction for above change is ΔfU0 of formation of CH4 (g) at certain temperature is –393 kJ mol−1. The value of ΔfH0is- a)equal to ΔfU0
- b)< ΔfU0
- c)zero
- d)> ΔfU0
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
During complete combustion of one mole of butane, 2658 kJ of heat is released. The thermochemical reaction for above change is ΔfU0 of formation of CH4 (g) at certain temperature is –393 kJ mol−1. The value of ΔfH0is
a)
equal to ΔfU0
b)
< ΔfU0
c)
zero
d)
> ΔfU0

|
Ipsita Sen answered |
Can you explain the answer of this question below:8 g of O2 gas at STP is expanded so that volume is doubled. Thus, work done is
- A:
22.4 L atm
- B:
11.2 L atm
- C:
5.6 L atm
- D:
- 5.6 L atm
The answer is d.
8 g of O2 gas at STP is expanded so that volume is doubled. Thus, work done is
22.4 L atm
11.2 L atm
5.6 L atm
- 5.6 L atm

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Let atomic weight of x = Mx
atomic weight of y = My
atomic weight of y = My
we know,
mole = weight /atomic weight
a/c to question,
mole = weight /atomic weight
a/c to question,
mole of xy2 = 0.1
so,
0.1 = 10g/( Mx +2My)
so,
0.1 = 10g/( Mx +2My)
Mx + 2My = 100g -------(1)
for x3y2 ; mole of x3y2 = 0.05
0.05 = 9/( 3Mx + 2My )
3Mx + 2My = 9/0.05 = 9 × 20 = 180 g ---(2)
solve eqns (1) and (2)
solve eqns (1) and (2)
2Mx = 80
Mx = 40g/mol
Mx = 40g/mol
and My = 30g/mole
A chemical reaction will be spontaneous if it is accompanied by a decrease of [1994]- a)entropy of the system
- b)enthalpy of the system
- c)internal energy of the system
- d)free energy of the system
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
A chemical reaction will be spontaneous if it is accompanied by a decrease of [1994]
a)
entropy of the system
b)
enthalpy of the system
c)
internal energy of the system
d)
free energy of the system

|
Raghav Khanna answered |
ΔG is negative for a spontaneous process.
How many kcal of heat is evolved by the complete neutralisation of one mole sulphuric acid with NaOH -- a)13.7 kcal
- b)27.4 kcal
- c)6.85 kcal
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
How many kcal of heat is evolved by the complete neutralisation of one mole sulphuric acid with NaOH -
a)
13.7 kcal
b)
27.4 kcal
c)
6.85 kcal
d)
None of the above
|
|
Om Desai answered |
For the reaction of 1 mole of H+ and OH-,we have 13.6 kcal energy released. In H2SO4, we have 2 moles of H+. So for its complete neutralisation, we need 2 moles of NaOH.
So in the end, 2 moles of H+ reacts with2 moles of OH- and 13.6 2 = 27.4 kcal energy is released.
So in the end, 2 moles of H+ reacts with2 moles of OH- and 13.6 2 = 27.4 kcal energy is released.
In the combustion of 4g. of CH4, 2.5 K cal of heat is liberated. The heat of combustion of CH4 is -- a) 20 K. cals
- b) 10 K. cals
- c) 2.5 K. cals
- d)5 K. cals
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
In the combustion of 4g. of CH4, 2.5 K cal of heat is liberated. The heat of combustion of CH4 is -
a)
20 K. cals
b)
10 K. cals
c)
2.5 K. cals
d)
5 K. cals
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Mol. wt. of methane =16gm
Heat liberated during the combustion of 4gm methane = 2.5kcal
Heat liberated during the combustion of 16gm methane = 2.5/4×16=10kcal
Hence the heat of combustion of methane is 10 kcal.
Heat liberated during the combustion of 4gm methane = 2.5kcal
Heat liberated during the combustion of 16gm methane = 2.5/4×16=10kcal
Hence the heat of combustion of methane is 10 kcal.
Bond dissociation enthalpy of H2, Cl2 and HCl are 434 , 242 and 431 kJ mol–1 respectively.Enthalpy of formation of HCl is : [2008]- a)93 kJ mol–1
- b)– 245 kJmol–1
- c)– 93 kJmol–1
- d)245 kJmol–1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Bond dissociation enthalpy of H2, Cl2 and HCl are 434 , 242 and 431 kJ mol–1 respectively.Enthalpy of formation of HCl is : [2008]
a)
93 kJ mol–1
b)
– 245 kJmol–1
c)
– 93 kJmol–1
d)
245 kJmol–1

|
Rohan Unni answered |
The reaction for formation of HCl can be written as H2 + Cl2 → 2HCI
H – H + Cl – Cl → 2 (H – Cl)
Substituting the given values, we get enthalpy of formation of 2HCl = – ( 862 – 676) = –186 kJ.
∴ Enthalpy of formation of
H – H + Cl – Cl → 2 (H – Cl)
Substituting the given values, we get enthalpy of formation of 2HCl = – ( 862 – 676) = –186 kJ.
∴ Enthalpy of formation of
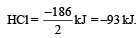
A cylinder confines 2.00 L gas under a pressure of 1.00 atm. The external pressure is also 1.00 atm. The gas is heated slowly, with the piston sliding freely outward to maintain the pressure of the gas close to 1.00 atm. Suppose the heating continues until a final volume of 3.50 L is reached. Calculate the work done on the gas.
- a)-152 J
- b)-112 J
- c)-172 J
- d)-132 J
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A cylinder confines 2.00 L gas under a pressure of 1.00 atm. The external pressure is also 1.00 atm. The gas is heated slowly, with the piston sliding freely outward to maintain the pressure of the gas close to 1.00 atm. Suppose the heating continues until a final volume of 3.50 L is reached. Calculate the work done on the gas.
a)
-152 J
b)
-112 J
c)
-172 J
d)
-132 J

|
Arindam Unni answered |



The difference between Cp and Cv is equal to- a)8.314 ergs K-1 mol-1
- b)2 kcal mol-1
- c)8.314 JK-1mol-1
- d)1.99 cal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The difference between Cp and Cv is equal to
a)
8.314 ergs K-1 mol-1
b)
2 kcal mol-1
c)
8.314 JK-1mol-1
d)
1.99 cal
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Cp-Cv = R
R is gas constant whose value is 8.314 J/K/mol
R is gas constant whose value is 8.314 J/K/mol
Entropy is a state function and measures- a)the internal energy of the system
- b)the degree of randomness or disorder in the system
- c)the degree of regularity or order in the system
- d)the enthalpy of the system
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Entropy is a state function and measures
a)
the internal energy of the system
b)
the degree of randomness or disorder in the system
c)
the degree of regularity or order in the system
d)
the enthalpy of the system

|
Nabanita Basu answered |
Entropy is a state function and it is measure of randomness of a system.
Sulphur (2.56 g) is burned in a constant volume calorimeter with excess O2(g). The temperature increases from 21.25°C to 26.72°C . The bomb has a heat capacity of 923 JK-1. Calorimeter contains 815 g of water. Thus, change in internal energy per mole of SO2 formed for the reaction is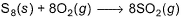 (specific heat of water is 4.184 JK-1g-1.)
(specific heat of water is 4.184 JK-1g-1.)- a)- 296.27 kJ
- b)+ 296.27 kJ
- c)- 2370.13 kJ
- d)+ 2370.13 kJ
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Sulphur (2.56 g) is burned in a constant volume calorimeter with excess O2(g). The temperature increases from 21.25°C to 26.72°C . The bomb has a heat capacity of 923 JK-1. Calorimeter contains 815 g of water. Thus, change in internal energy per mole of SO2 formed for the reaction is
(specific heat of water is 4.184 JK-1g-1.)
a)
- 296.27 kJ
b)
+ 296.27 kJ
c)
- 2370.13 kJ
d)
+ 2370.13 kJ

|
Mohit Rajpoot answered |
Moles of S8 = 2.56/256 = 0.01
So, moles of SO2 formed = 0.08
Rise in temperature = (273+26.72)K - (273+21.25)K
= 5.47 K
Total Energy in internal energy (as system is at constant volume) = -(923 jK-1 × 5.47 +815g×4.18)
= -23701.29 J = -23.70129 kJ
Thus change in internal energy per mole of formed = -23.7012kJ/0.08 = -296.3 kJ
So, moles of SO2 formed = 0.08
Rise in temperature = (273+26.72)K - (273+21.25)K
= 5.47 K
Total Energy in internal energy (as system is at constant volume) = -(923 jK-1 × 5.47 +815g×4.18)
= -23701.29 J = -23.70129 kJ
Thus change in internal energy per mole of formed = -23.7012kJ/0.08 = -296.3 kJ
The absolute enthalpy of neutralisation of the reaction: MgO (s) + 2HCl (aq) —→ MgCl2(aq) + H2O (l) will be:[2005]- a)-57.33 kJ mol-1
- b)Greater than -57.33 kJ mol-1
- c)Less than -57.33 kJ mol-1
- d)57.33 kJ mol-1
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The absolute enthalpy of neutralisation of the reaction: MgO (s) + 2HCl (aq) —→ MgCl2(aq) + H2O (l) will be:[2005]
a)
-57.33 kJ mol-1
b)
Greater than -57.33 kJ mol-1
c)
Less than -57.33 kJ mol-1
d)
57.33 kJ mol-1

|
Swara Desai answered |
As MgO is a oxide of weak base hence some energy is lost to break MgO (s). Hence enthalpy is less than –57.33 kJ mol–1.
Assuming the composition of air to be X (N2) = 0.80, X (O2) = 0.18 and X (CO2) = 0.02, molar heat capacity of air at constant pressure is- a)3.50R
- b)4.00R
- c)2.50R
- d)3.51R
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Assuming the composition of air to be X (N2) = 0.80, X (O2) = 0.18 and X (CO2) = 0.02, molar heat capacity of air at constant pressure is
a)
3.50R
b)
4.00R
c)
2.50R
d)
3.51R
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
(Cp)mixture = (µ1Cp1+µ2Cp2+µ3Cp3+.........)/µ1+µ2+µ3+......... where µ is the no of moles.
Or (Cp)mixture = ƞ1Cp1+ƞ2Cp2+ƞ3Cp3+............. Where ƞ is the corr. mole fraction.
On putting the values, we have
Cpmixture= ( 7/2*0.8 +7/2*0.18 +4*0.02)R
=3.15R
Or (Cp)mixture = ƞ1Cp1+ƞ2Cp2+ƞ3Cp3+............. Where ƞ is the corr. mole fraction.
On putting the values, we have
Cpmixture= ( 7/2*0.8 +7/2*0.18 +4*0.02)R
=3.15R
Enthalpy is defined as- a)H = U + pV
- b)H = U+V/P
- c)H = U + TV
- d)H = U+ n p/v
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Enthalpy is defined as
a)
H = U + pV
b)
H = U+V/P
c)
H = U + TV
d)
H = U+ n p/v

|
Amrita Sharma answered |
H =U+pV. H is enthalpy of reaction.
A solution of 500 ml of 0.2 M KOH and 500 ml of 0.2 M HCl is mixed and stirred; the rise in temperature is T1. The experiment is repeated using 250 ml of each solution, the temperature raised is T2. Which of the following is true -- a)T1 = T2
- b)T1 = 2T2
- c)T1 = 4T2
- d)T2 = 9T1
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
A solution of 500 ml of 0.2 M KOH and 500 ml of 0.2 M HCl is mixed and stirred; the rise in temperature is T1. The experiment is repeated using 250 ml of each solution, the temperature raised is T2. Which of the following is true -
a)
T1 = T2
b)
T1 = 2T2
c)
T1 = 4T2
d)
T2 = 9T1
|
|
Shreya Gupta answered |
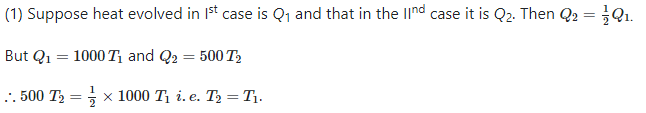
Which of the following pairs of a chemical reaction is certain to result in a spontaneous reaction? [2005]- a)Exothermic and increasing disorder
- b)Exothermic and decreasing disorder
- c)Endothermic and increasing disorder
- d)Endothermic and decreasing disorder
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following pairs of a chemical reaction is certain to result in a spontaneous reaction? [2005]
a)
Exothermic and increasing disorder
b)
Exothermic and decreasing disorder
c)
Endothermic and increasing disorder
d)
Endothermic and decreasing disorder

|
Arpita Tiwari answered |
Measure of disor der of a system is noth ing but Entropy. For a spontaneous reaction, ΔG < 0. As per Gibbs Helmnoltz equation, ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
Thus ΔG is –ve only When ΔH = –ve (exothermic) and ΔS = +ve (increasing disorder)
Thus ΔG is –ve only When ΔH = –ve (exothermic) and ΔS = +ve (increasing disorder)
Which reaction, with the following values of ΔH and ΔS at 400 K is spontaneous and endothermic?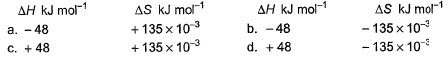
- a)a
- b)b
- c)c
- d)d
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which reaction, with the following values of ΔH and ΔS at 400 K is spontaneous and endothermic?
a)
a
b)
b
c)
c
d)
d
|
|
Om Desai answered |
∆G = ∆H - T∆S
For opt (c), ∆G = 48000 - 400(135)
= 48000 - 54000
= -6000
∆G is -ve
Therefore reaction is spontaneous.
For opt (c), ∆G = 48000 - 400(135)
= 48000 - 54000
= -6000
∆G is -ve
Therefore reaction is spontaneous.
The pressure-volume work for an ideal gas can be calculated using the expression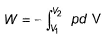 This type of work can also be calculated using the area under the curve within the specified limits. When an ideal gas is compressed, (I) reversibly or (II) irreversibly, then
This type of work can also be calculated using the area under the curve within the specified limits. When an ideal gas is compressed, (I) reversibly or (II) irreversibly, then- a)W(I) = W(II)
- b)W(I) < W(II)
- c)W(I) > W(II)
- d)W(I) = W (II) + pexΔV
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
The pressure-volume work for an ideal gas can be calculated using the expression
This type of work can also be calculated using the area under the curve within the specified limits. When an ideal gas is compressed, (I) reversibly or (II) irreversibly, then
a)
W(I) = W(II)
b)
W(I) < W(II)
c)
W(I) > W(II)
d)
W(I) = W (II) + pexΔV
|
|
Neha Joshi answered |
Work done is the area under the P−V curve. It can be seen in the curve above that the area under the P−V curve for irreversible compression of the gas is more than the area under the curve for reversible compression.
Thus, work done for irreversible compression is more than that for reversible compression.
Thus, work done for irreversible compression is more than that for reversible compression.
Statement-1 : Due to adiabatic free expansion temperature of real gas may increaseStatement-2 : In adiabatic free expansion, temperature is always constant irrespective of real or ideal gas- a)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is. True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- b)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- c)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False.
- d)Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement-1 : Due to adiabatic free expansion temperature of real gas may increase
Statement-2 : In adiabatic free expansion, temperature is always constant irrespective of real or ideal gas
a)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is. True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
b)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
c)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False.
d)
Statement-1 is False, Statement-2 is True.
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
For ideal gas, change in internal energy=ΔU∝ΔT
During free adiabatic expansion,ΔQ=ΔW=0⇒ΔU=0⇒ΔT=0
However for real gases, ΔU=f(V,T)
In this case, for free adiabatic expansion ΔU=0⇒f(V,T)=0
Thus T may change in this case.
So, statement I is true while statement II is false.
During free adiabatic expansion,ΔQ=ΔW=0⇒ΔU=0⇒ΔT=0
However for real gases, ΔU=f(V,T)
In this case, for free adiabatic expansion ΔU=0⇒f(V,T)=0
Thus T may change in this case.
So, statement I is true while statement II is false.
Statement-1 : 'Diamonds are forever is generally quoted for diamond as rate of conversion of diamond to graphite at room condition is nearly zero.Statement-2 : At room condition, conversion of diamond into graphite is spontaneons.- a)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- b)Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
- c)Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False.
- d)Statement-2 is False, Statement-2 is True.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Statement-1 : 'Diamonds are forever is generally quoted for diamond as rate of conversion of diamond to graphite at room condition is nearly zero.
Statement-2 : At room condition, conversion of diamond into graphite is spontaneons.
a)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1.
b)
Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is True; Statement-2 is NOT a correct explanation for Statement-1.
c)
Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is False.
d)
Statement-2 is False, Statement-2 is True.
|
|
Preeti Iyer answered |
Thermodynamically it is favourable for diamond to turn into graphite, but it do not normally happen because there is high energy of activation for the process. So, option b is correct.
During isothermal expansion of an ideal gas, its- a)internal energy increases [1991, 94]
- b)enthalpy decreases
- c)enthalpy remains unaffected
- d)enthalpy reduces to zero.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
During isothermal expansion of an ideal gas, its
a)
internal energy increases [1991, 94]
b)
enthalpy decreases
c)
enthalpy remains unaffected
d)
enthalpy reduces to zero.

|
Shanaya Rane answered |
During isothermal expansion of ideal gas,
ΔT = 0. Now H = E + PV
∵ ΔH = ΔE + Δ(PV)
∴ ΔH = ΔE + Δ(nRTT));
Thus if ΔT = 0., ΔH = ΔE i.e., remain unaffected
ΔT = 0. Now H = E + PV
∵ ΔH = ΔE + Δ(PV)
∴ ΔH = ΔE + Δ(nRTT));
Thus if ΔT = 0., ΔH = ΔE i.e., remain unaffected
Chapter doubts & questions for Thermodynamics - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Thermodynamics - Topic-wise MCQ Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup on EduRev and stay on top of your study goals
10M+ students crushing their study goals daily