All Exams >
NEET >
NCERT Based Tests for NEET >
All Questions
All questions of Chemical Coordination and Integration for NEET Exam
Which one of the following part is an endocrine gland?- a)Pars radiata
- b)Crypts of Lieberkühn
- c)Juxtaglomerulus
- d)Brunner’s glands
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which one of the following part is an endocrine gland?
a)
Pars radiata
b)
Crypts of Lieberkühn
c)
Juxtaglomerulus
d)
Brunner’s glands
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Brunner's gland are present in small intestine and secrete intestinal juice through ducts.
Crypts of Lieberkühn, also known as Paneth cells, are tubular glands present in small intestine and secrete intestinal juice.
Pars radiata (medullary rays) are the extensions of medulla into cortex of kidney.
Juxtaglomerulus is present in kidneys and consists of juxtaglomerular cells or JG cells that secrete enzyme renin and hormone erythropoietin. Hence, juxtaglomerulus is endocrine (ductless glands) as it secretes a hormone.
So, the correct answer is 'Juxtaglomerulus'.
Crypts of Lieberkühn, also known as Paneth cells, are tubular glands present in small intestine and secrete intestinal juice.
Pars radiata (medullary rays) are the extensions of medulla into cortex of kidney.
Juxtaglomerulus is present in kidneys and consists of juxtaglomerular cells or JG cells that secrete enzyme renin and hormone erythropoietin. Hence, juxtaglomerulus is endocrine (ductless glands) as it secretes a hormone.
So, the correct answer is 'Juxtaglomerulus'.
The main function of prolactin hormone is to :-- a)Influence the activity of thyroid gland
- b)Control development of graffian follicles
- c)Initiate and maintain secretion of milk by mammary gland
- d)Cause ejection of milk
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The main function of prolactin hormone is to :-
a)
Influence the activity of thyroid gland
b)
Control development of graffian follicles
c)
Initiate and maintain secretion of milk by mammary gland
d)
Cause ejection of milk
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
Prolactin, also called as luteotropic hormone (LTH) or luteotropin, is a protein hormone produced by the pituitary gland of mammals, that acts with other hormones to initiate secretion of milk by the mammary glands.
Which of the following is NOT an endocrine gland?a)Salivary glandb)Pituitary glandc)Parathyroid glandd)Pancreas glandCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
|
|
Rohit Jain answered |
Endocrine glands are ductless glands of the endocrine system that secrete their products, hormones directly into the blood. The major glands of the endocrine system include the pineal gland, pituitary gland, pancreas, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, hypothalamus and adrenal glands.
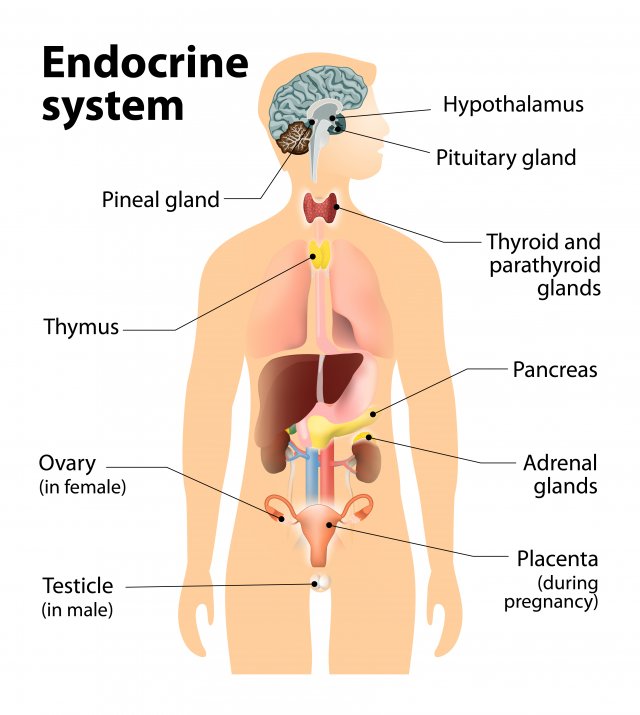
Hormone of hypothalamus are called :-
- a)Growth hormones
- b)Regulatory hormones
- c)Angiotensins
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hormone of hypothalamus are called :-
a)
Growth hormones
b)
Regulatory hormones
c)
Angiotensins
d)
None of these
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The hormones of the hypothalamus are called regulatory hormones. The hypothalamus is considered the master regulator of the endocrine system.
The hormone causing release of milk after the birth of young one is :- a)Oxytocin
- b)relaxin
- c)progesterone
- d)Prolactin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The hormone causing release of milk after the birth of young one is :
a)
Oxytocin
b)
relaxin
c)
progesterone
d)
Prolactin
|
|
Prem Darade answered |
The correct answer is oxytocin because oxytocin stimulates contraction of the myoepithelial cells surrounding the alveoli which already holds milk . the increased pressure causes milk to flow through the duct system and be released through the nipple .
The corpus luteum secretes a hormone called- a)Testosterone
- b)Prolactin
- c)Aldosterone
- d)Progesterone
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The corpus luteum secretes a hormone called
a)
Testosterone
b)
Prolactin
c)
Aldosterone
d)
Progesterone
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Corpus luteum secretes Progesterone (pregnancy hormone) ..option D
Which hormone among these is not secreted by an endocrine gland?- a)T4
- b)MSH
- c)ANF
- d)ADH
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which hormone among these is not secreted by an endocrine gland?
a)
T4
b)
MSH
c)
ANF
d)
ADH
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) is a 28 amino acid polypeptide hormone secreted mainly by the heart atria in response to atrial stretch. ANF acts on the kidney to increase sodium excretion and GFR, to antagonize renal vasoconstriction, and to inhibit renin secretion.
Withdrawal of which of the following hormones is the immediate cause of menstruation?- a)Progesterone
- b)FSH and LH
- c)FSH
- d)Oestrogens
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Withdrawal of which of the following hormones is the immediate cause of menstruation?
a)
Progesterone
b)
FSH and LH
c)
FSH
d)
Oestrogens

|
Tejas Chavan answered |
Menstruation is caused by the reduction of two hor... moremones, oestrogen, and progesterone, especially progesterone at the end of the monthly ovarian cycle. Hence, withdrawal of progesterone hormone will cause immediate menstruation.Thus, the correct answer is option A.
Which of the following is not paired correctly?- a)Parathyroid – Tetany
- b)Insulin – Raise blood glucose
- c)Grave’s disease – Exophthalmos
- d)Cretinism – Mentally retarded
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is not paired correctly?
a)
Parathyroid – Tetany
b)
Insulin – Raise blood glucose
c)
Grave’s disease – Exophthalmos
d)
Cretinism – Mentally retarded
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
Myxoedema also known as hypothyroidism is caused because of disorder of thyroid gland, It is characterized by swelling of the hands, face, feet.
Insulin is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreas and maintains the blood glucose level and not raises it.
Hypoparathyroidism has decreased the function of the parathyroid glands with underproduction of parathyroid hormone. This can lead to low levels of calcium in the blood, often causing cramping and twitching of muscles or tetany (involuntary muscle contraction).
Cretinism is a condition of severely stunted physical and mental growth due to untreated congenital deficiency of thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism). Hence, option B is the correct answer.
Hormones secreted by the hypothalamus show their influence on- a)Thyroid gland
- b)Pituitary gland
- c)Pancreas
- d)Adrenal gland
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Hormones secreted by the hypothalamus show their influence on
a)
Thyroid gland
b)
Pituitary gland
c)
Pancreas
d)
Adrenal gland
|
|
Abdul Saleem4367 answered |
Read ncert class 11 humen physiology ,hormone chapter..
Gonadotrophic hormone is produced by :-- a)Interstitial cells of testis
- b)Adrenal cortex
- c)Adenohypophysis
- d)Posterior part of thyroid
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Gonadotrophic hormone is produced by :-
a)
Interstitial cells of testis
b)
Adrenal cortex
c)
Adenohypophysis
d)
Posterior part of thyroid
|
|
Kadambala Hemalatha answered |
Option c is correct becose i will eliminate one by one option interstial cells (leading cells) produce androgens, adrenal cortex produce corticodis (glucocorticoids, minaralo corticodis), posterior part of thyroid gland is contains parathyroid glad it realese parathyroid hormone (hyper calcimic hormone),adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary, pars distalise) relese gondotrophic harmones (both FSH, LH).
Which gland stores hormone in intercellular space before its secretion into blood :-- a)Pancreas
- b)Thyroid
- c)Testis
- d)Ovary
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which gland stores hormone in intercellular space before its secretion into blood :-
a)
Pancreas
b)
Thyroid
c)
Testis
d)
Ovary
|
|
Ananya Das answered |
The Thyroid gland is the only endocrine gland that stores its secretory product in large quantities, normally about 10 days supplies in the extracellular space before discharging into the blood. It secretes iodinated hormone i.e., thyroxine and triiodothyronine that are stored in the colloid which fills the follicle cells and released to blood when needed.
Which of the following controls spermatogenesis :-- a)FSH
- b)LTH
- c)LH
- d)Vasopressin
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following controls spermatogenesis :-
a)
FSH
b)
LTH
c)
LH
d)
Vasopressin
|
|
Nithya Sri answered |
Frnd,
actually the correct answer might be LH
bcuz lh acts on leydig cells which enhance the production of androgens and controls spermatogenesis
actually the correct answer might be LH
bcuz lh acts on leydig cells which enhance the production of androgens and controls spermatogenesis
Which hormone has anti insulin effect :-- a)Cortisol
- b)Oxytocin
- c)Aldosterone
- d)Glucagon
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which hormone has anti insulin effect :-
a)
Cortisol
b)
Oxytocin
c)
Aldosterone
d)
Glucagon
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
Hormones that work against the action of insulin, raising blood glucose levels in response to hypoglycemia (low blood sugar). The main counterregulatory hormones are glucagon, epinephrine (also known as adrenaline), cortisol, and growth hormone.
The follicle stimulating hormone is secreted from :-- a)Posterior lobe of pituitary gland
- b)Reproductive gland
- c)Thyroid gland
- d)Anterior lobe of pituitary gland
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The follicle stimulating hormone is secreted from :-
a)
Posterior lobe of pituitary gland
b)
Reproductive gland
c)
Thyroid gland
d)
Anterior lobe of pituitary gland
|
|
Neha Mansoori answered |
Anterior lobe of pituitary gland. Option d is correct
Neurohypophysis secretes :-- a)Vasopressin
- b)Oxytocin
- c)Oxytocin & prolactin
- d)Vasopressin & oxytocin
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Neurohypophysis secretes :-
a)
Vasopressin
b)
Oxytocin
c)
Oxytocin & prolactin
d)
Vasopressin & oxytocin
|
|
Sai Nikhil answered |
Neurohypophysis secretes vasopressin&oxytocin vasopressin is for antidiuretic & oxytocin constrict smooth muscles to give pressure to milk to pass through mammary gland
Erythropoietin is a- a)Peptide hormone
- b)Steroid hormone
- c)Amine hormone
- d)Both 1 and 3 above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Erythropoietin is a
a)
Peptide hormone
b)
Steroid hormone
c)
Amine hormone
d)
Both 1 and 3 above

|
Arya Khanna answered |
Erythropoietin (EPO) is a hormone produced by the kidney that promotes the formation of red blood cells by the bone marrow. The kidney cells that make erythropoietin are sensitive to low oxygen levels in the blood that travels through the kidney.
Hormone secreted by pituitary gland is chemically- a)All protein
- b)All steroid
- c)Complex compounds of proteins and carbohydrates
- d)Some steroid and some protein
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Hormone secreted by pituitary gland is chemically
a)
All protein
b)
All steroid
c)
Complex compounds of proteins and carbohydrates
d)
Some steroid and some protein
|
|
Rajat Kapoor answered |
The pituitary gland is a small gland that sits in the sella turcica (‘Turkish saddle’), a bony hollow in the base of the skull, underneath the brain and behind the bridge of the nose. The pituitary gland has two main parts, the anterior pituitary gland and the posterior pituitary gland. The gland is attached to a part of the brain (the hypothalamus) that controls its activity. The anterior pituitary gland is connected to the brain by short blood vessels. The posterior pituitary gland is actually part of the brain and it secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream under the command of the brain.
One of the following is genetic :-- a)Simple Goitre
- b)Exopthalmic
- c)Sporadic goitre
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
One of the following is genetic :-
a)
Simple Goitre
b)
Exopthalmic
c)
Sporadic goitre
d)
None
|
|
Kadambala Hemalatha answered |
Option d is correct becose we will eliminate one by one 1st option simple goiter is caused by low secretion of thyroid hormone (hypo thyroidism) or low iodine levels in dite. 2nd option exothermic goiteris caused by high section of thyroid hormone (hyper thyroidism) ,3rd options sporadic goiter due to bigining of enlarge ment of thyroid gland. soo option d is correct.
Injection of which of the following increases metabolic rate :-- a)STH
- b)Insulin
- c)Thyroxine
- d)Testosterone
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Injection of which of the following increases metabolic rate :-
a)
STH
b)
Insulin
c)
Thyroxine
d)
Testosterone
|
|
Sathvika Tadri answered |
Thyroxine hormone increases BMR of body ...so option C
"Sella turcica" is a :-- a)Depression in brain enclosing pituitary
- b)Cavity of skull enclusing ears
- c)Covering of testis
- d)Kind of endocrine gland
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
"Sella turcica" is a :-
a)
Depression in brain enclosing pituitary
b)
Cavity of skull enclusing ears
c)
Covering of testis
d)
Kind of endocrine gland
|
|
Krishna Iyer answered |
Sella trucia or 'Turkish saddle' is a depression in the floor of the mammalian skull in the sphenoid (Basi spenoid) bone in which the pituitary gland is lodged. It is also found in skull of chimpanzees, gorilla etc.
Gorilla like man with large head and hands and protruding Jaws is produced due to :-- a)Over-secretion of thyroxine
- b)Over-secretion of growth hormone
- c)Excess of vitamin C in diet
- d)Excess secretion of TSH
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Gorilla like man with large head and hands and protruding Jaws is produced due to :-
a)
Over-secretion of thyroxine
b)
Over-secretion of growth hormone
c)
Excess of vitamin C in diet
d)
Excess secretion of TSH
|
|
Kadambala Hemalatha answered |
Option B is correct becose over secretion of growth harmone (somatotripin) is causes acromagale due to this deasese gorilla like appearance occurs.due to low secretion of growth harmone causes gigantism also called as pituitary dwarf.
The largest endocrine gland is- a)Testis
- b)Pituitary
- c)Pancreas
- d)Thyroid
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
The largest endocrine gland is
a)
Testis
b)
Pituitary
c)
Pancreas
d)
Thyroid

|
Kunal Rane answered |
Thyroid is the largest endocrine gland present in human body. This gland release thyroxin hormone that help in metabolism of carbohydrates, fats and proteins.
Hypophysis cerebri is the other name of :-- a)Adenohypo physis
- b)Islets of langerhans
- c)Neurohypophysis
- d)Pituitary gland
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Hypophysis cerebri is the other name of :-
a)
Adenohypo physis
b)
Islets of langerhans
c)
Neurohypophysis
d)
Pituitary gland

|
Supriya Senapati answered |
Pituitary gland. Located at the base of the brain, the pituitary gland is protected by a bony structure called the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone.
The term hypophysis (from the Greek for “lying under”)—another name for the pituitary—refers to the gland's position on the underside of the brain.
The term hypophysis (from the Greek for “lying under”)—another name for the pituitary—refers to the gland's position on the underside of the brain.
Diabetes insipidus disease is caused due to the deficiency of hormone produced by :-- a)Pituitary
- b)Adrenal
- c)Pancreas
- d)Thyroid
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Diabetes insipidus disease is caused due to the deficiency of hormone produced by :-
a)
Pituitary
b)
Adrenal
c)
Pancreas
d)
Thyroid
|
|
Om Desai answered |
Diabetes insipidus is a pathological endocrine condition characterized by excessive thirst and excessive production of very dilute urine. The disorder is caused by a lack of antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) or a blocking of its action. This hormone, produced by the hypothalamus, regulates the kidney's conservation of water and production of urine through its ability to stimulate reabsorption of water by the kidneys. Hence, Option A.
Thyroid gland do not secrete- a)T4
- b)Melatonin
- c)Calcitonin
- d)T3
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Thyroid gland do not secrete
a)
T4
b)
Melatonin
c)
Calcitonin
d)
T3
|
|
Vartika shukla answered |
The thyroid, or thyroid gland, is an endocrine gland in the neck consisting of two connected lobes. The lower two thirds of the lobes are connected by a thin band of tissue called the thyroid isthmus. The thyroid is located at the front of the neck, below the Adam's apple. Microscopically, the functional unit of the thyroid gland is the spherical thyroid follicle, lined with follicular cells (thyrocytes), and occasional parafollicular cells that surround a lumen containing colloid. The thyroid gland secretes three hormones: the two thyroid hormones – triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4) – and a peptide hormone, calcitonin. The thyroid hormones influence the metabolic rate and protein synthesis, and in children, growth and development. Calcitonin plays a role in calcium homeostasis.[1] Secretion of the two thyroid hormones is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which is secreted from the anterior pituitary gland. TSH is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which is produced by the hypothalamus.[2]
I.C.S.H. in male acts on :-- a)Cells of leydig
- b)Sertoli cells
- c)Spermatids
- d)Spermatogonia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
I.C.S.H. in male acts on :-
a)
Cells of leydig
b)
Sertoli cells
c)
Spermatids
d)
Spermatogonia
|
|
Mahi Desai answered |
**I.C.S.H. in Male Acts on Cells of Leydig**
ICSH (interstitial cell-stimulating hormone), also known as LH (luteinizing hormone), is a hormone produced and released by the anterior pituitary gland. In males, ICSH/LH primarily acts on the cells of Leydig in the testes.
**1. Functions of ICSH/LH in Males:**
ICSH/LH plays a crucial role in the regulation of male reproductive functions. Its main functions include:
1. **Stimulation of Testosterone Production:** The primary function of ICSH/LH in males is to stimulate the Leydig cells to produce and release testosterone. Leydig cells are located in the interstitial spaces of the testes and are responsible for the synthesis and secretion of testosterone.
2. **Maintenance of Testosterone Levels:** ICSH/LH maintains the optimal levels of testosterone in the blood. Testosterone is an essential hormone involved in various physiological processes, including the development and maintenance of male reproductive organs, secondary sexual characteristics, and spermatogenesis.
3. **Stimulation of Sperm Production:** Testosterone, under the influence of ICSH/LH, promotes the process of spermatogenesis, which is the production of sperm. It acts on the Sertoli cells, which are located within the seminiferous tubules of the testes and support the development and maturation of sperm cells.
**2. Target Cells of ICSH/LH in Males:**
ICSH/LH primarily acts on the cells of Leydig in the testes. These target cells include:
**a) Cells of Leydig:** ICSH/LH binds to specific receptors on the surface of Leydig cells, triggering a series of biochemical reactions within the cells. This leads to the production and release of testosterone into the bloodstream. Testosterone then acts on various target tissues and cells throughout the body, exerting its effects.
**b) Sertoli Cells:** Although ICSH/LH does not directly act on Sertoli cells, it indirectly influences their function. Testosterone, which is stimulated by ICSH/LH, acts on Sertoli cells to support the development and maturation of sperm cells during spermatogenesis.
**c) Spermatids:** Spermatids are the immature sperm cells formed during the process of spermatogenesis. ICSH/LH indirectly influences the development of spermatids by stimulating testosterone production, which acts on Sertoli cells to support their maturation into fully functional sperm cells.
**d) Spermatogonia:** Spermatogonia are the germ cells in the testes that undergo mitosis to produce more spermatogonia or differentiate into spermatocytes, which further develop into spermatids. ICSH/LH indirectly influences spermatogonia by promoting spermatogenesis and the development of mature sperm cells.
In summary, ICSH/LH acts primarily on the cells of Leydig in the testes, stimulating the production and release of testosterone. Testosterone, in turn, influences Sertoli cells, spermatids, and spermatogonia, supporting the process of spermatogenesis and the development of mature sperm cells.
ICSH (interstitial cell-stimulating hormone), also known as LH (luteinizing hormone), is a hormone produced and released by the anterior pituitary gland. In males, ICSH/LH primarily acts on the cells of Leydig in the testes.
**1. Functions of ICSH/LH in Males:**
ICSH/LH plays a crucial role in the regulation of male reproductive functions. Its main functions include:
1. **Stimulation of Testosterone Production:** The primary function of ICSH/LH in males is to stimulate the Leydig cells to produce and release testosterone. Leydig cells are located in the interstitial spaces of the testes and are responsible for the synthesis and secretion of testosterone.
2. **Maintenance of Testosterone Levels:** ICSH/LH maintains the optimal levels of testosterone in the blood. Testosterone is an essential hormone involved in various physiological processes, including the development and maintenance of male reproductive organs, secondary sexual characteristics, and spermatogenesis.
3. **Stimulation of Sperm Production:** Testosterone, under the influence of ICSH/LH, promotes the process of spermatogenesis, which is the production of sperm. It acts on the Sertoli cells, which are located within the seminiferous tubules of the testes and support the development and maturation of sperm cells.
**2. Target Cells of ICSH/LH in Males:**
ICSH/LH primarily acts on the cells of Leydig in the testes. These target cells include:
**a) Cells of Leydig:** ICSH/LH binds to specific receptors on the surface of Leydig cells, triggering a series of biochemical reactions within the cells. This leads to the production and release of testosterone into the bloodstream. Testosterone then acts on various target tissues and cells throughout the body, exerting its effects.
**b) Sertoli Cells:** Although ICSH/LH does not directly act on Sertoli cells, it indirectly influences their function. Testosterone, which is stimulated by ICSH/LH, acts on Sertoli cells to support the development and maturation of sperm cells during spermatogenesis.
**c) Spermatids:** Spermatids are the immature sperm cells formed during the process of spermatogenesis. ICSH/LH indirectly influences the development of spermatids by stimulating testosterone production, which acts on Sertoli cells to support their maturation into fully functional sperm cells.
**d) Spermatogonia:** Spermatogonia are the germ cells in the testes that undergo mitosis to produce more spermatogonia or differentiate into spermatocytes, which further develop into spermatids. ICSH/LH indirectly influences spermatogonia by promoting spermatogenesis and the development of mature sperm cells.
In summary, ICSH/LH acts primarily on the cells of Leydig in the testes, stimulating the production and release of testosterone. Testosterone, in turn, influences Sertoli cells, spermatids, and spermatogonia, supporting the process of spermatogenesis and the development of mature sperm cells.
Hormone that decrease calcium lavel in blood :-- a)Thyroxine
- b)Parathormone
- c)Thyrocalcitonin
- d)Cortisol
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Hormone that decrease calcium lavel in blood :-
a)
Thyroxine
b)
Parathormone
c)
Thyrocalcitonin
d)
Cortisol
|
|
Riya Banerjee answered |
The hormone calcitonin, which is produced by the parafollicular (or C) cells of the thyroid, has the opposite effect on blood calcium levels as PTH. Calcitonin decreases blood calcium levels by inhibiting osteoclasts, stimulating osteoblasts, and stimulating calcium excretion by the kidneys. Hence, Option C.
Thymosin stimulates :-[RPMT-2000]- a)Milk secretion
- b)Erythrocytes
- c)T-lymphocytes
- d)Melanocytes
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Thymosin stimulates :-
[RPMT-2000]
a)
Milk secretion
b)
Erythrocytes
c)
T-lymphocytes
d)
Melanocytes
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta G answered |
Thymosin is the hormone of the thymus, and it stimulates the development of disease-fighting T lymphocytes.
Throughout your childhood years, white blood cells called lymphocytes pass through the thymus, where they are transformed into T cells ( lymphocytes).
Throughout your childhood years, white blood cells called lymphocytes pass through the thymus, where they are transformed into T cells ( lymphocytes).
Parathormone regulates :-
- a)Blood calcium level
- b)phosphate level
- c)Body temperature
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Parathormone regulates :-
a)
Blood calcium level
b)
phosphate level
c)
Body temperature
d)
None
|
|
Rohit Shah answered |
The basal metabolic rate is regulated significantly by thyroid hormones, which also contribute to red blood cell formation. These hormones play a crucial role in overseeing the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Additionally, thyroid hormones impact the maintenance of water and electrolyte balance. The thyroid gland also produces thyrocalcitonin (TCT), a protein hormone that plays a role in regulating blood calcium levels.
Immediate cause of induction of ovulation in human female is large in plasma surge of :-- a)Progesterone
- b)LH
- c)FSH
- d)Estradiol
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Immediate cause of induction of ovulation in human female is large in plasma surge of :-
a)
Progesterone
b)
LH
c)
FSH
d)
Estradiol
|
|
Rocky Handsome answered |
----€ LH (luteinising hormone) is released by anterior lobe of pituitary gland. It causes ovulation, secretion of estrogen from mature ovarian follicle and progesterone from corpus luteum.
•FSH stimulates sperm formation in the male and growth of ovarian follicles in the female.
•Progesterone suspends ovulation during pregnancy, fixes the foetus to the uterine wall, forms placenta and controls the development of the foetus in the uterus.
•Estradiol is the major estrogen in humans.
•FSH stimulates sperm formation in the male and growth of ovarian follicles in the female.
•Progesterone suspends ovulation during pregnancy, fixes the foetus to the uterine wall, forms placenta and controls the development of the foetus in the uterus.
•Estradiol is the major estrogen in humans.
Injection Insulin to an animal leads to increased :-- a)Glucose level of blood
- b)Glucose level of wine
- c)Glucose level of cells
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Injection Insulin to an animal leads to increased :-
a)
Glucose level of blood
b)
Glucose level of wine
c)
Glucose level of cells
d)
None of these
|
|
Vishal Kumar answered |
Insulin and glucagon work together to balance your blood sugar levels, keeping them in the narrow range that your body requires. So insulin leads blood sugar cell.
If amount of ADH decrease in blood, micturition :-- a)Remains unchanged
- b)Increases
- c)Decreases
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
If amount of ADH decrease in blood, micturition :-
a)
Remains unchanged
b)
Increases
c)
Decreases
d)
None
|
|
Manisha Yadav answered |
Because ADS prevent loss of water .
ADS=anti diutric substance.
ADS=anti diutric substance.
FSH & LH is a :-- a)Catecholamine
- b)Glycoprotein
- c)Polypeptide
- d)None
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
FSH & LH is a :-
a)
Catecholamine
b)
Glycoprotein
c)
Polypeptide
d)
None

|
Ayush Joshi answered |
The gonadotropins, a family of closely related glycoprotein hormones, include follicle stimulating-hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) which are produced by the same pituitary cells, the gonadotrophs and chorionic gonadotropin (CG) which is of placental origin.
Choose the correct answer among the following options: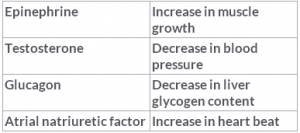
- a)A-iv, B-i, C-iii, D-ii
- b)A-ii, B-i, C-iii, D-iv
- c)A-i, B-iv, C-ii, D-iii
- d)A-i, B-ii, C-iii, D-iv
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Choose the correct answer among the following options:
a)
A-iv, B-i, C-iii, D-ii
b)
A-ii, B-i, C-iii, D-iv
c)
A-i, B-iv, C-ii, D-iii
d)
A-i, B-ii, C-iii, D-iv

|
Knowledge Hub answered |
Epinephrine (one of the catecholamines) increases the heart beat during any stress or emergency conditions.
Testosterone is responsible for muscle growth.
Glucagon helps in decreasing liver glycogen content.
Atrial Natriuretic Factor takes part in decreasing the Blood Pressure by RAAS.
Which of the following hormones stimulates the secretion of pancreatic enzyme from the pancreas?- a)Secretin
- b)Gastric inhibitory peptide
- c)Cholecystokinin
- d)Gastrin
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following hormones stimulates the secretion of pancreatic enzyme from the pancreas?
a)
Secretin
b)
Gastric inhibitory peptide
c)
Cholecystokinin
d)
Gastrin
|
|
Vijay Bansal answered |
cholecystokinin, is secreted in large amounts by the stomach in response to gastric distention and irritation. In addition to stimulating acid secretion by the parietal cell, gastrin stimulates pancreatic acinar cells to secrete digestive enzymes.
Role of thymus in homosepiens is chiefly concerned with :-- a)Reproduction
- b)Immunology
- c)Calcium balance
- d)Blood coagulation
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Role of thymus in homosepiens is chiefly concerned with :-
a)
Reproduction
b)
Immunology
c)
Calcium balance
d)
Blood coagulation
|
|
Hitakshi Tamta G answered |
The thymus gland is an integral part of immune system. It helps in the maturation of lymphocytes. As these cells are involved in providing immunity to the body, the role of the thymus in human beings is chiefly concerned with immunology.
So, the correct answer is option B.
So, the correct answer is option B.
Storage gland is :-- a)Pancreas
- b)Testis
- c)Thyroid
- d)Adrenal
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Storage gland is :-
a)
Pancreas
b)
Testis
c)
Thyroid
d)
Adrenal
|
|
Suresh Iyer answered |
The thyroid gland lies in the neck, in front of the upper part of the trachea. Two types of hormones are produced, which are the iodine containing hormones; tri-iodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). The gland consists of varying sized follicles, which are bounded by a single layer of cuboidal epithelial cells (follicular cells} and a basement membrane, surrounding a central lumen filled with a homogenous protein rich colloid (thyroglobulin).
The colloid is a storage of thyroid hormones prior to secretion. The thyroid gland is the only endocrine gland to store its hormone in large quantities.
Which of the following is called emergency gland of the body?
- a)Testis
- b)Adrenal Medulla
- c)Thymus
- d)Pituitary
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following is called emergency gland of the body?
a)
Testis
b)
Adrenal Medulla
c)
Thymus
d)
Pituitary
|
|
Vivek Patel answered |
Adrenal gland is called the emergency gland of the body. Adrenaline is secreted by adrenal medulla on stimulation by sympathetic nervous system for meeting an emergency of stress condition, like injury, pain fear, Accident, grief, fall in blood pressure etc. Hence adrenal gland is called emergency hormone.
Gigantism and acromegaly are due to :-- a)Hyperpituitrism
- b)Hypopituitrism
- c)Hypothyroidism
- d)Hyperthyroidism
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Gigantism and acromegaly are due to :-
a)
Hyperpituitrism
b)
Hypopituitrism
c)
Hypothyroidism
d)
Hyperthyroidism
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Gigantism and acromegaly occur when the pituitary gland makes too much growth hormone (hyperpituitarism) due to a tumor on the gland. The difference between acromegaly and gigantism is that acromegaly occurs in adults, typically between the ages of 30 and 50. Hence, option A is correct.
Which is called "Master gland" of the body :-- a)Thyroid
- b)Pituitary
- c)Thymus
- d)Adrenal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Which is called "Master gland" of the body :-
a)
Thyroid
b)
Pituitary
c)
Thymus
d)
Adrenal
|
|
User5881746 answered |
Pituitary gland controls the secretion of the most of the hormones in the humane body so it is called master gland
Can you explain the answer of this question below:Vasopressin is responsible for :-
- A:
Controlling Oogenesis
- B:
Regulating blood pressure and act on the nephron tubules.
- C:
Regulating formation of pigment.
- D:
Controlling spermatogenesis.
The answer is b.
Vasopressin is responsible for :-
Controlling Oogenesis
Regulating blood pressure and act on the nephron tubules.
Regulating formation of pigment.
Controlling spermatogenesis.

|
Saumya Ahuja answered |
Ans.
Vasopressin, also called antidiuretic hormone, hormone that plays a key role in maintaining osmolality (the concentration of dissolved particles, such as salts and glucose, in the serum) and therefore in maintaining the volume of water in the extracellular fluid (the fluid space that surrounds cells).
Which of the following hormones will stimulate gluconeogenesis?- a)mineralocorticoids and glucagon
- b)mineralocorticoids and insulin
- c)glucocorticoids and insulin
- d)glucocorticoids and glucagon
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Which of the following hormones will stimulate gluconeogenesis?
a)
mineralocorticoids and glucagon
b)
mineralocorticoids and insulin
c)
glucocorticoids and insulin
d)
glucocorticoids and glucagon

|
Kunal Rane answered |
Glucocorticoids stimulate gluconeogenesis. Similarly, glucagon also stimulates the process of gluconeogenesis which also contributes to hyperglycemia.
The same hormone can be known by various names given in which set :-- a)Secretin, enterokinin, gastrin
- b)Gametokinetic factor, testosterone, LTH
- c)ADH, pitressin, and vasopressin
- d)Oxytocin, tri-iodo-thyronine, thyroxine
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
The same hormone can be known by various names given in which set :-
a)
Secretin, enterokinin, gastrin
b)
Gametokinetic factor, testosterone, LTH
c)
ADH, pitressin, and vasopressin
d)
Oxytocin, tri-iodo-thyronine, thyroxine
|
|
Gaurav Kumar answered |
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is secreted by the posterior pituitary gland and targets nephrons to increase water reabsorption and thereby decreasing water content in urine. The man-made form of ADH hormones is named as vasopressin which is administered to the patient with diabetes insipidus. Thu, the correct answer is C.
Chapter doubts & questions for Chemical Coordination and Integration - NCERT Based Tests for NEET 2025 is part of NEET exam preparation. The chapters have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. The Chapter doubts & questions, notes, tests & MCQs are made for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, notes, meanings, examples, exercises, MCQs and online tests here.
Chapter doubts & questions of Chemical Coordination and Integration - NCERT Based Tests for NEET in English & Hindi are available as part of NEET exam.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.

Contact Support
Our team is online on weekdays between 10 AM - 7 PM
Typical reply within 3 hours
|
Free Exam Preparation
at your Fingertips!
Access Free Study Material - Test Series, Structured Courses, Free Videos & Study Notes and Prepare for Your Exam With Ease

 Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
Join the 10M+ students on EduRev
|

|
Create your account for free
OR
Forgot Password
OR
Signup to see your scores
go up
within 7 days!
within 7 days!
Takes less than 10 seconds to signup













